Shopping Cart
Remove All Your shopping cart is currently empty
Your shopping cart is currently empty
FIN56, a specific inducer of ferroptosis, is identified by its IUPAC name [1,3,8-trihydroxy-6-methylanthracen-9(10H)-one].
| Pack Size | Price | USA Warehouse | Global Warehouse | Quantity |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2 mg | $35 | In Stock | In Stock | |
| 5 mg | $57 | In Stock | In Stock | |
| 10 mg | $91 | In Stock | In Stock | |
| 25 mg | $203 | In Stock | In Stock | |
| 50 mg | $359 | In Stock | In Stock | |
| 100 mg | $563 | In Stock | In Stock | |
| 200 mg | $788 | In Stock | In Stock | |
| 1 mL x 10 mM (in DMSO) | $66 | In Stock | In Stock |
| Description | FIN56, a specific inducer of ferroptosis, is identified by its IUPAC name [1,3,8-trihydroxy-6-methylanthracen-9(10H)-one]. |
| Targets&IC50 | HT29 cells:21.26 μM, LN-229 cells:4.2 µM, Caco-2 cells:15.23 μM, U118 cells:2.6 µM, Human foreskin fibroblasts cells:24 μM |
| In vitro | FIN56 triggers ferroptosis through a mechanism involving the regulation of GPX4 protein abundance. FIN56 causes the loss of GPX4 activity in cell lysates. FIN56-induced cell death is suppressed by GFP-GPX4 fusion protein overexpression. |
| Cell Research | 1000 cells/36 μL are seeded in each well in 384-well plates. Lethal compounds are dissolved and a 2-fold, 12-point dilution series are prepared in DMSO. Compound solutions are further diluted with media at 1:25 and 4 μL/well of the diluted solutions are added to cell cultures immediately after cells are seeded. When ferroptosis inhibitors (100 μM α-tocopherol, 152 μM deferoxamine, or 10 μM U-0126) are co-treated with lethal inducers, they are supplemented to cell culture at the same time as lethal compounds are added, and the cells are incubated for 24 hrs. When other cell death modulating compounds (100 nM sodium selenite, 1 μM cerivastatin, 100 μg/mL mevalonic acid) are co-treated, they are first supplemented to cell culture for 24 hrs before lethal compounds are added to cell culture and further incubated for 24 hrs at 37°C under 5% CO2. On the day of the viability measurement, 10 μL/well of 50% Alamar Blue diluted in media is added and further incubated at 37°C for 6 hrs. Fluorescence intensity (ex/em: 530/590) is measured with a Victor 3 plate reader and the normalized viability is calculated by VL = (IL-I0)/(IV-I0), where VL, I0, IV, and IL are the normalized viability, raw fluorescence intensities from the wells containing media, cells treated with a vehicle (negative control), and cells with the lethal compound (L), respectively. When the effect of a chemical modulator (M) on L is calculated, we instead used the equation: VL|M = (IM, L-I0)/(IM, V-I0), where VL|M, IM, L and IM, V are the normalized viability, and fluorescence intensity from cells treated with M and V, and from cells with M and L. respectively. The viability is typically measured in biological triplicates unless otherwise specified. A representative dose-response curve, the mean and standard error of normalized viability from one replicate are plotted. |
| Molecular Weight | 517.66 |
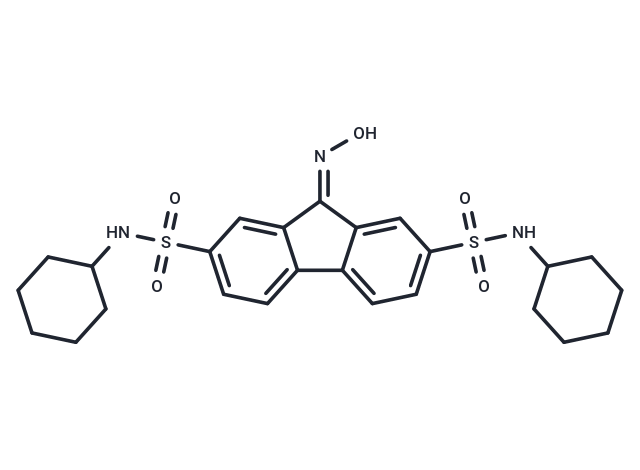
| Formula | C25H31N3O5S2 |
| Cas No. | 1083162-61-1 |
| Smiles | ON=C1c2cc(ccc2-c2ccc(cc12)S(=O)(=O)NC1CCCCC1)S(=O)(=O)NC1CCCCC1 |
| Relative Density. | 1.50 g/cm3 (Predicted) |
| Storage | The compound is unstable in solution. Please use soon | In solvent: -80°C for 1 year | Shipping with blue ice/Shipping at ambient temperature. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Solubility Information | DMSO: 247.5 mg/mL (478.11 mM), The compound is unstable in solution, please use soon. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| In Vivo Formulation | 10% DMSO+90% Corn Oil: 3.3 mg/mL (6.37 mM), Sonication is recommended. Please add the solvents sequentially, clarifying the solution as much as possible before adding the next one. Dissolve by heating and/or sonication if necessary. Working solution is recommended to be prepared and used immediately. The formulation provided above is for reference purposes only. In vivo formulations may vary and should be modified based on specific experimental conditions. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Solution Preparation Table | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
DMSO
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Size | Quantity | Unit Price | Amount | Operation |
|---|

Copyright © 2015-2026 TargetMol Chemicals Inc. All Rights Reserved.