Shopping Cart
- Remove All
 Your shopping cart is currently empty
Your shopping cart is currently empty

AZ876 is a potent, highly selective LXR agonist with Ki/EC50 of 7/6 nM and 11/73 nM for hLXRα and hLXRβ respectively.
| Pack Size | Price | Availability | Quantity |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 mg | $45 | In Stock | |
| 5 mg | $82 | In Stock | |
| 10 mg | $126 | In Stock | |
| 25 mg | $165 | In Stock | |
| 50 mg | $207 | In Stock | |
| 100 mg | $369 | In Stock |
| Description | AZ876 is a potent, highly selective LXR agonist with Ki/EC50 of 7/6 nM and 11/73 nM for hLXRα and hLXRβ respectively. |
| Targets&IC50 | LXR:6 nM (EC50, cell free) |
| In vitro | AZ876 suppressed up-regulation of hypertrophy- and fibrosis-related genes and further inhibited prohypertrophic and profibrotic TGFβ-Smad2/3 signaling. In cardiomyocytes, phenylephrine-stimulated cellular hypertrophy was significantly decreased in AZ876-treated cells. In cardiac fibroblasts, AZ876 prevented TGFβ- and angiotensin II-induced fibroblast collagen synthesis, and inhibited up-regulation of the myofibroblastic marker, α-smooth muscle actin [2]. |
| In vivo | Low-dose AZ876 had no effect on plasma or liver lipids, whereas high-dose AZ876 increased plasma triglycerides and reduced cholesterol compared with controls. Low-dose AZ876 reduced lesion area; and high-dose AZ876 strongly decreased lesion area, lesion number, and severity. In either dose, AZ876 did not affect lesion composition [1]. Cardiac hypertrophy was induced in C57Bl6/J mice via transverse aortic constriction (TAC) for 6 weeks. During this period, mice received chow supplemented or not with AZ876 (20?μmol/kg/day). In murine hearts, LXRα protein expression was up-regulated ~7-fold in response to TAC. LXR activation with AZ876 attenuated this increase, and significantly reduced TAC-induced increases in heart weight, myocardial fibrosis, and cardiac dysfunction without affecting blood pressure [2]. |
| Kinase Assay | Binding vectors for His-tagged protein production were prepared by inserting the ligand-binding domain cDNA of human LXRα (amino acids 205–447) in pET28 and the ligand-binding domain cDNA of LXRβ (amino acids 216–461) in pET24D. Proteins were expressed in Escherichia coli and purified on Ni+ columns. Binding assays using LXRα and LXRβ protein were run by adding reagents to Wallac Isoplate 1450–514. Briefly, each 96 plate well contained assay buffer (20 mM Tris pH 7.5, 80 mM NaCl, 2 mM dithiothreitol, 0.125% Chaps and 10% glycerol), 0.1 mg SPA beads (polylysine-coated yttrium silicate beads), LXRα (0.5 μg) or LXRβ (0.25 μg), 30 nM 3H-ligand (specific activity of 473 Kbq/nmol) and test compound in a 10-point dose-response dilution. The assay mixture was shaken gently for 2 h on a plate shaker after which the beads were allowed to settle for 1 hour before counting. Transactivation vectors were prepared by inserting the ligand-binding domain cDNA sequences of human or mouse LXRα and LXRβ in frame with the yeast Gal4 transcription factor DNA binding domain and the nuclear localization signal from the T-antigen of polyomavirus in the eucaryotic expression vector pSG5. The ligand-binding domain cDNA of human LXRα and LXRβ was the same as mentioned previously. The mouse sequence corresponded to amino acids 203–445 for LXRα and amino acids 201–446 for LXRβ. The vectors were co-transfected with a pGL3 luciferase reporter plasmid containing a minimal SV40 promoter and five copies of the UAS Gal4 recognition site into U2/OS osteosarcoma cells. Ligands were added as 10-point dose-response curves and then luciferase activity was measured after 48 h [1]. |
| Animal Research | Cardiac hypertrophy was induced in male C57Bl6/J mice via transverse aortic constriction (TAC) for 6 weeks. During this period, sham and TAC-operated mice were randomized to receive either regular chow (control) or chow supplemented with AZ876 (20 μmol/kg/day). Cardiac function was assessed with echocardiography and invasive haemodynamics. In vitro studies were performed in isolated neonatal rat ventricular myocytes (NRVMs) and adult rat cardiac fibroblasts. Leucine and proline tracer assays were used to measure protein and collagen synthesis, respectively [2]. |
| Molecular Weight | 439.57 |
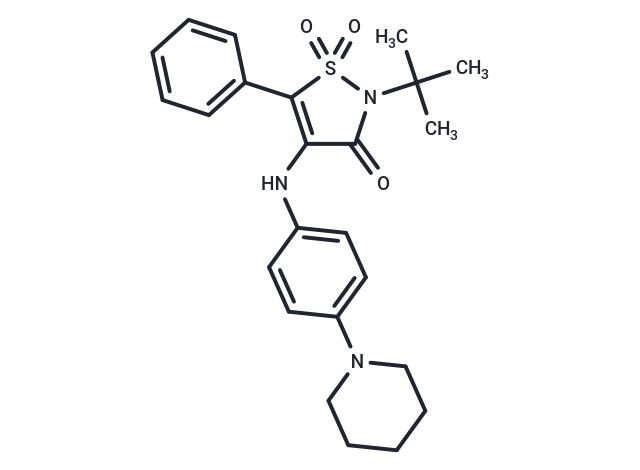
| Formula | C24H29N3O3S |
| Cas No. | 898800-26-5 |
| Smiles | CC(C)(C)N1C(=O)C(Nc2ccc(cc2)N2CCCCC2)=C(c2ccccc2)S1(=O)=O |
| Relative Density. | 1.293 g/cm3 (Predicted) |
| Storage | Powder: -20°C for 3 years | In solvent: -80°C for 1 year | Shipping with blue ice. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Solubility Information | DMSO: 55 mg/mL (125.12 mM), Sonication is recommended. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| In Vivo Formulation | 5% DMSO+40% PEG300+5% Tween 80+50% Saline: 2.5 mg/mL (5.69 mM), Solution. Please add the solvents sequentially, clarifying the solution as much as possible before adding the next one. Dissolve by heating and/or sonication if necessary. Working solution is recommended to be prepared and used immediately. The formulation provided above is for reference purposes only. In vivo formulations may vary and should be modified based on specific experimental conditions. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Solution Preparation Table | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
DMSO
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||

Copyright © 2015-2025 TargetMol Chemicals Inc. All Rights Reserved.