 Your shopping cart is currently empty
Your shopping cart is currently empty

4-aminobenzoic acid is an organic acid with UV-absorbing and antifibrotic properties. When exposed to light, 4-aminobenzoic acid absorbs UV light and releases excess energy through a photochemical reaction, which may cause DNA damage.4-aminobenzoic acid also increases oxygen uptake at the tissue level and may enhance monoamine oxidase (MAO) activity to promote serotonin degradation, which in excess may lead to fibrotic Changes.
| Pack Size | Price | USA Warehouse | Global Warehouse | Quantity |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2 g | $30 | In Stock | In Stock | |
| 5 g | $40 | - | In Stock | |
| 10 g | $56 | - | In Stock | |
| 1 mL x 10 mM (in DMSO) | $29 | In Stock | In Stock |
| Description | 4-aminobenzoic acid is an organic acid with UV-absorbing and antifibrotic properties. When exposed to light, 4-aminobenzoic acid absorbs UV light and releases excess energy through a photochemical reaction, which may cause DNA damage.4-aminobenzoic acid also increases oxygen uptake at the tissue level and may enhance monoamine oxidase (MAO) activity to promote serotonin degradation, which in excess may lead to fibrotic Changes. |
| In vivo | Plants produce PABA in their chloroplasts and store it as a glucose ester (PABA-Glc) in their tissues. Humans lack the enzymes to convert PABA to folate, so require folate from dietary sources such as green leafy vegetables. In humans, most people have colon bacteria that generate PABA[1]. |
| Synonyms | Vitamin H1, Vitamin Bx, para-Aminobenzoic acid, PABA |
| Molecular Weight | 137.14 |
| Formula | C7H7NO2 |
| Cas No. | 150-13-0 |
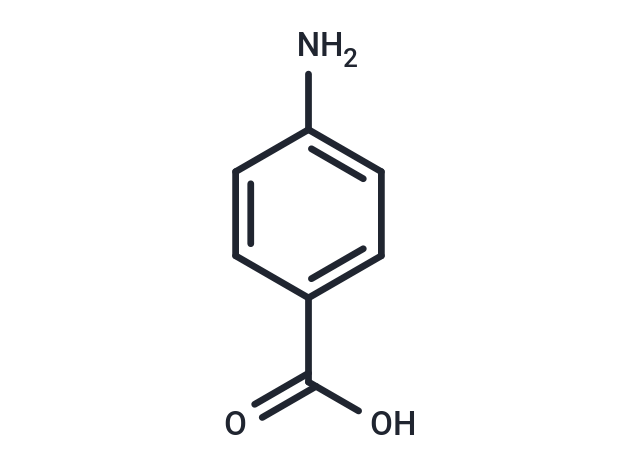
| Smiles | NC1=CC=C(C=C1)C(O)=O |
| Relative Density. | 1.37 g/cm3. Temperature:20 °C. |
| Storage | Powder: -20°C for 3 years | In solvent: -80°C for 1 year | Shipping with blue ice/Shipping at ambient temperature. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Solubility Information | DMSO: 250 mg/mL (1822.95 mM), Sonication is recommended. H2O: < 1 mg/mL (insoluble or slightly soluble) Ethanol: 26 mg/mL (189.59 mM), Sonication is recommended. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| In Vivo Formulation | 10% DMSO+40% PEG300+5% Tween 80+45% Saline: 2 mg/mL (14.58 mM), Sonication is recommended. Please add the solvents sequentially, clarifying the solution as much as possible before adding the next one. Dissolve by heating and/or sonication if necessary. Working solution is recommended to be prepared and used immediately. The formulation provided above is for reference purposes only. In vivo formulations may vary and should be modified based on specific experimental conditions. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Solution Preparation Table | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Ethanol/DMSO
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Dissolve 2 mg of the compound in 100 μL DMSO![]() to obtain a stock solution at a concentration of 20 mg/mL . If the required concentration exceeds the compound's known solubility, please contact us for technical support before proceeding.
to obtain a stock solution at a concentration of 20 mg/mL . If the required concentration exceeds the compound's known solubility, please contact us for technical support before proceeding.
1) Add 100 μL of the DMSO![]() stock solution to 400 μL PEG300
stock solution to 400 μL PEG300![]() and mix thoroughly until the solution becomes clear.
and mix thoroughly until the solution becomes clear.
2) Add 50 μL Tween 80 and mix well until fully clarified.
3) Add 450 μL Saline,PBS or ddH2O![]() and mix thoroughly until a homogeneous solution is obtained.
and mix thoroughly until a homogeneous solution is obtained.
| Size | Quantity | Unit Price | Amount | Operation |
|---|

Copyright © 2015-2026 TargetMol Chemicals Inc. All Rights Reserved.