 Your shopping cart is currently empty
Your shopping cart is currently empty

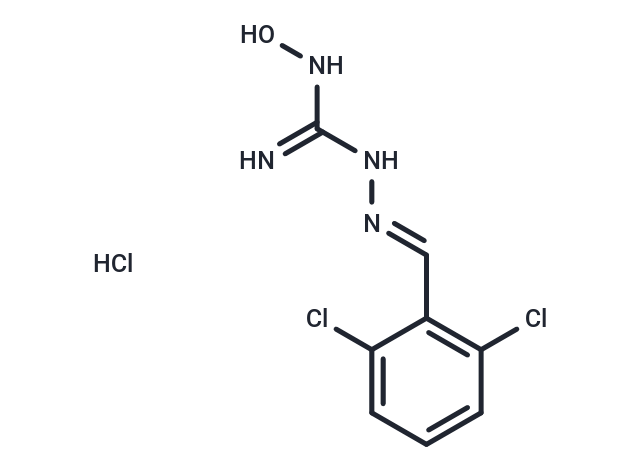
Guanoxabenz (Hydroxyguanabenz) hydrochloride is an α2 adrenergic receptor agonist with a Ki of 4000 nM and a fully activated form of 40 nM for the α2A adrenoceptor[1][2][3].
| Pack Size | Price | USA Warehouse | Global Warehouse | Quantity |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 25 mg | $1,400 | 6-8 weeks | 6-8 weeks | |
| 50 mg | $1,820 | 6-8 weeks | 6-8 weeks | |
| 1 mL x 10 mM (in DMSO) | $363 | 6-8 weeks | 6-8 weeks |
| Description | Guanoxabenz (Hydroxyguanabenz) hydrochloride is an α2 adrenergic receptor agonist with a Ki of 4000 nM and a fully activated form of 40 nM for the α2A adrenoceptor[1][2][3]. |
| In vitro | The inhibition of high-affinity Guanoxabenz binding is caused by both a series of N-hydroxyguanidine analogs (to Guanoxabenz) and various metabolic inhibitors, which include allopurinol, 1-chloro-2,4-dinitrobenzene, 5,59-dithiobis-(2-nitrobenzoic acid), cibacron blue, phenyl-p-benzoquinone, didox, and trimidox. Additionally, the LW03 N-hydroxyguanidine analogue of Guanoxabenz exhibits a time- and concentration-dependent inhibition of this binding when membranes are preincubated with it. Furthermore, the conversion of Guanoxabenz to guanabenz by the spleen cytosolic fraction significantly increases affinity, as guanabenz binds nearly 100 times more effectively to rat alpha2A-adrenoceptors than Guanoxabenz. |
| In vivo | Guanoxabenz and guanabenz are centrally acting antihypertensive agents. They show increased binding affinity in rat brain membranes when NADH or NADPH cofactors are added, suggesting the presence of an enzyme in the rat cerebral cortex that activates Guanoxabenz, creating a metabolite with high affinity for alpha 2-adrenoceptors. Moreover, Guanoxabenz administration (0.1-3 mg/kg, i.p.) results in a dose-dependent decrease in rat locomotor activity, with 1 mg/kg being optimal for inducing significant sustained behavioral hypoactivity. In a specified animal model involving rats, a 0.5 mg/kg dose (using RX 781094 or saline as a vehicle) was injected intravenously (tail vein) to counteract the peak effects of agonists at predefined times. Notably, RX 781094 (0.1-1.0 mg/kg, i.v.) counters the EEG and behavioral effects of clonidine and Guanoxabenz rapidly and effectively within less than 5 seconds, signifying its role as a potent antagonist. |
| Molecular Weight | 283.54 |
| Formula | C8H9Cl3N4O |
| Cas No. | 23256-40-8 |
| Smiles | Cl.ONC(=N)N\N=C\c1c(Cl)cccc1Cl |
| Storage | Powder: -20°C for 3 years | In solvent: -80°C for 1 year | Shipping with blue ice/Shipping at ambient temperature. |
Dissolve 2 mg of the compound in 100 μL DMSO![]() to obtain a stock solution at a concentration of 20 mg/mL . If the required concentration exceeds the compound's known solubility, please contact us for technical support before proceeding.
to obtain a stock solution at a concentration of 20 mg/mL . If the required concentration exceeds the compound's known solubility, please contact us for technical support before proceeding.
1) Add 100 μL of the DMSO![]() stock solution to 400 μL PEG300
stock solution to 400 μL PEG300![]() and mix thoroughly until the solution becomes clear.
and mix thoroughly until the solution becomes clear.
2) Add 50 μL Tween 80 and mix well until fully clarified.
3) Add 450 μL Saline,PBS or ddH2O![]() and mix thoroughly until a homogeneous solution is obtained.
and mix thoroughly until a homogeneous solution is obtained.
| Size | Quantity | Unit Price | Amount | Operation |
|---|

Copyright © 2015-2026 TargetMol Chemicals Inc. All Rights Reserved.