 Your shopping cart is currently empty
Your shopping cart is currently empty

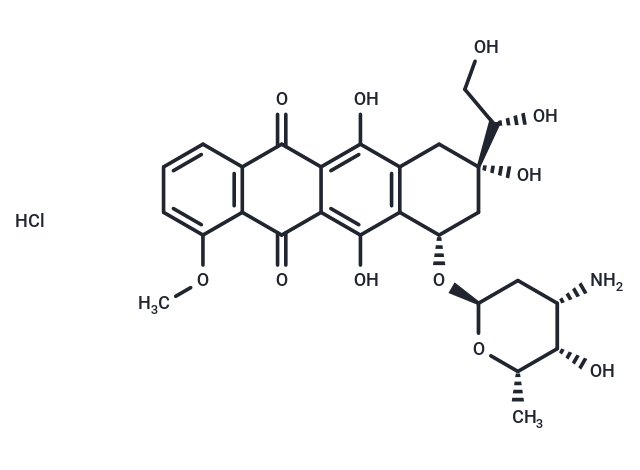
Doxorubicinol hydrochloride, also known as 13-Dihydroadriamycin hydrochloride, is a secondary alcohol metabolite derived from Doxorubicin.
| Pack Size | Price | USA Warehouse | Global Warehouse | Quantity |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 25 mg | Inquiry | Inquiry | Inquiry |
| Description | Doxorubicinol hydrochloride, also known as 13-Dihydroadriamycin hydrochloride, is a secondary alcohol metabolite derived from Doxorubicin. |
| In vitro | Doxorubicinol hydrochloride is generated through a two-electron, NADPH-dependent reduction of the Doxorubicin (C13) side-chain carbonyl group, resulting in a secondary alcohol[1]. Compared to Doxorubicin (DOX), Doxorubicinol hydrochloride exhibits substantially reduced DNA binding activity. Unlike Doxorubicin, which primarily accumulates in the nucleus, Doxorubicinol hydrochloride is predominantly localized within the cytoplasm or lysosomes[1]. |
| In vivo | In vivo studies on tumor-bearing mice have demonstrated that Nilotinib, functioning as an ABCB1 inhibitor, enhances the accumulation of Doxorubicin and Doxorubicinol hydrochloride in cancer tissues. This suggests that the diminished anticancer efficacy of Doxorubicinol hydrochloride may be due to its elevated affinity for ABC transporters, resulting in a reduced intracellular concentration[1]. Furthermore, when compared to wild-type mice, mdr1a(-/-) mice exhibit a 1.6-fold increase in the terminal half-life and a 1.2-fold increase in the area under the plasma concentration-time curve for Doxorubicin. Additionally, the retention of Doxorubicin and its metabolite Doxorubicinol hydrochloride is significantly extended in the hearts of mdr1a(-/-) mice[2]. |
| Synonyms | 13-Dihydroadriamycin hydrochloride |
| Molecular Weight | 582.0 |
| Formula | C27H32ClNO11 |
| Cas No. | 63950-05-0 |
| Smiles | Cl.COc1cccc2C(=O)c3c(O)c4C[C@](O)(C[C@H](O[C@H]5C[C@H](N)[C@H](O)[C@H](C)O5)c4c(O)c3C(=O)c12)[C@@H](O)CO |
| Relative Density. | 1.61g/cm3 |
| Storage | Powder: -20°C for 3 years | In solvent: -80°C for 1 year | Shipping with blue ice/Shipping at ambient temperature. |
Dissolve 2 mg of the compound in 100 μL DMSO![]() to obtain a stock solution at a concentration of 20 mg/mL . If the required concentration exceeds the compound's known solubility, please contact us for technical support before proceeding.
to obtain a stock solution at a concentration of 20 mg/mL . If the required concentration exceeds the compound's known solubility, please contact us for technical support before proceeding.
1) Add 100 μL of the DMSO![]() stock solution to 400 μL PEG300
stock solution to 400 μL PEG300![]() and mix thoroughly until the solution becomes clear.
and mix thoroughly until the solution becomes clear.
2) Add 50 μL Tween 80 and mix well until fully clarified.
3) Add 450 μL Saline,PBS or ddH2O![]() and mix thoroughly until a homogeneous solution is obtained.
and mix thoroughly until a homogeneous solution is obtained.
| Size | Quantity | Unit Price | Amount | Operation |
|---|

Copyright © 2015-2026 TargetMol Chemicals Inc. All Rights Reserved.