Shopping Cart
Remove All Your shopping cart is currently empty
Your shopping cart is currently empty
FH1 (NSC-12407) (BRD-K4477), a small molecule, enhances the functions of hepatocytes and promotes differentiation hepatocytes derived by iPS.
| Pack Size | Price | USA Warehouse | Global Warehouse | Quantity |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 25 mg | $48 | In Stock | In Stock | |
| 50 mg | $89 | In Stock | In Stock | |
| 100 mg | $158 | In Stock | In Stock | |
| 200 mg | $205 | In Stock | In Stock | |
| 1 mL x 10 mM (in DMSO) | $30 | In Stock | In Stock |
| Description | FH1 (NSC-12407) (BRD-K4477), a small molecule, enhances the functions of hepatocytes and promotes differentiation hepatocytes derived by iPS. |
| In vivo | Within hepatocytes, FH1(BRD-K4477) facilitates the differentiation of fully-integrated iHeps into a mature state, enhancing cellular functionality. |
| Kinase Assay | Affinity determination: Binding affinities (Ki or IC50) of ABT-263 against different isoforms of Bcl-2 family are determined with competitive fluorescence polarization assays. The following peptide probe/protein pairs are used: f-bad (1 nM) and Bcl-xL (6 nM), f-Bax (1 nM) and Bcl-2 (10 nM), f-Bax (1 nM) and Bcl-w (40 nM), f-Noxa (2 nM) and Mcl-1 (40 nM), and f-Bax (1 nM) and Bcl-2-A1 (15 nM). Binding affinities for Bcl-xL are also determined using a time-resolved fluorescence resonance energy transfer assay. Bcl-xL (1 nM, His tagged) is mixed with 200 nM f-Bak, 1 nM Tb-labeled anti-His antibody, and ABT-263 at room temperature for 30 min. Fluorescence is measured on an Envision plate reader using a 340/35 nm excitation filter and 520/525 (f-Bak) and 495/510 nm (Tb-labeled anti-His antibody) emission filters. |
| Synonyms | NSC 12407, BRD-K4477 |
| Molecular Weight | 282.34 |
| Formula | C17H18N2O2 |
| Cas No. | 2719-05-3 |
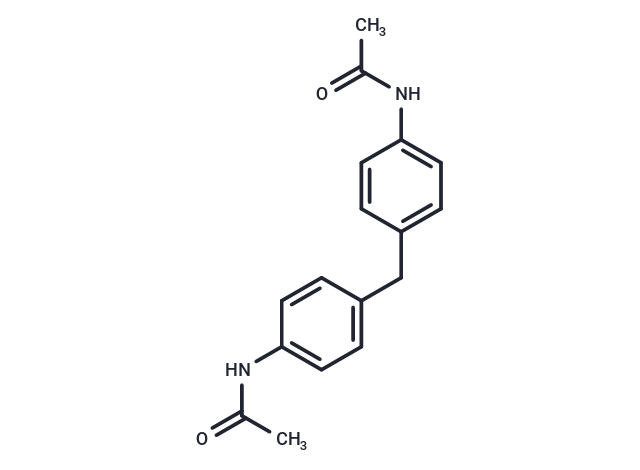
| Smiles | CC(=O)Nc1ccc(Cc2ccc(NC(C)=O)cc2)cc1 |
| Relative Density. | 1.201 g/cm3 (Predicted) |
| Storage | Powder: -20°C for 3 years | In solvent: -80°C for 1 year | Shipping with blue ice/Shipping at ambient temperature. | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Solubility Information | Ethanol: < 1 mg/mL (insoluble or slightly soluble) DMSO: 4.62 mg/mL (16.36 mM), Sonication is recommended. | ||||||||||||||||||||
| In Vivo Formulation | 10% DMSO+40% PEG300+5% Tween 80+45% Saline: 1 mg/mL (3.54 mM), Sonication is recommended. Please add the solvents sequentially, clarifying the solution as much as possible before adding the next one. Dissolve by heating and/or sonication if necessary. Working solution is recommended to be prepared and used immediately. The formulation provided above is for reference purposes only. In vivo formulations may vary and should be modified based on specific experimental conditions. | ||||||||||||||||||||
Solution Preparation Table | |||||||||||||||||||||
DMSO
| |||||||||||||||||||||
| Size | Quantity | Unit Price | Amount | Operation |
|---|

Copyright © 2015-2025 TargetMol Chemicals Inc. All Rights Reserved.