Shopping Cart
Remove All Your shopping cart is currently empty
Your shopping cart is currently empty
Azelaic acid (Anchoic acid) is a component of hair and skin conditioners and is produced by the ozonolysis of oleic acid. Azelaic acid has bacteriostatic activity against Propionibacterium acnes and Staphylococcus epidermidis by inhibiting protoprotein synthesis in microbial cells. Azelaic acid also has the ability to inhibit pigmentation due to its free radical scavenging action.
| Pack Size | Price | USA Warehouse | Global Warehouse | Quantity |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 g | $29 | In Stock | In Stock | |
| 1 mL x 10 mM (in DMSO) | $29 | In Stock | In Stock |
| Description | Azelaic acid (Anchoic acid) is a component of hair and skin conditioners and is produced by the ozonolysis of oleic acid. Azelaic acid has bacteriostatic activity against Propionibacterium acnes and Staphylococcus epidermidis by inhibiting protoprotein synthesis in microbial cells. Azelaic acid also has the ability to inhibit pigmentation due to its free radical scavenging action. |
| In vitro | AZ(Azelaic acid) combined with taurine (Tau) show more inhibitory effects in melanocytes than the treatment of AZ alone. AZ combined with Tau inhibits the melanin production and tyrosinase activity of B16F10 melanoma cells without significant cytotoxicity. Also inhibitory effects after treatment with these combined chemical are stronger than AZ alone on melanogenesis[2]. |
| In vivo | Azelaic acid exhibits an anti-atherogenic effect. Its athero-protective effect is not related to changes in plasma lipid content. Azelaic acid supplementation decreases the level of CD68 macrophage marker by 34% (p<0.05)[1]. |
| Cell Research | B16F10 melanoma cells are seeded at a density of 2.5×105 cells/60 mm culture dish. The cells are treated with Azelaic acid combined with Tau for 24 hr. The cells pellets are dissolved in 1 N NaOH at 60°C for 1 hr. The relative melanin content is determined by measuring the absorbance at 475 nm in ELISA reader. (Only for Reference) |
| Synonyms | Nonanedioic acid, Finacea, Azelex, Anchoic acid |
| Molecular Weight | 188.22 |
| Formula | C9H16O4 |
| Cas No. | 123-99-9 |
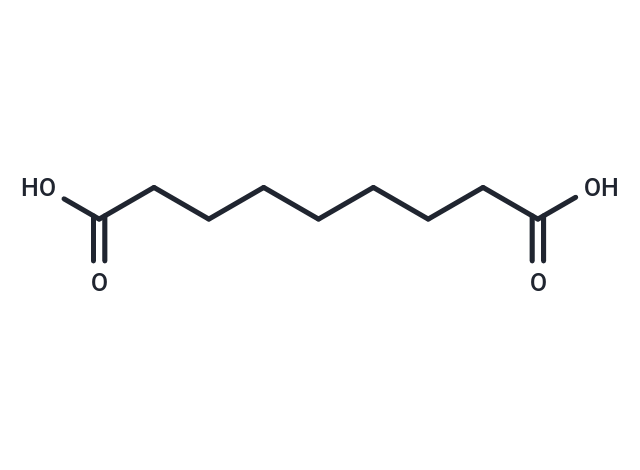
| Smiles | OC(=O)CCCCCCCC(O)=O |
| Relative Density. | 1 225 kg/m3. Temperature:25 °C. |
| Storage | Powder: -20°C for 3 years | In solvent: -80°C for 1 year | Shipping with blue ice/Shipping at ambient temperature. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Solubility Information | Ethanol: 35 mg/mL (185.95 mM), Sonication is recommended. DMSO: 245 mg/mL (1301.67 mM), Sonication is recommended. H2O: 34 mg/mL (180.64 mM), Sonication is recommended. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| In Vivo Formulation | 10% DMSO+40% PEG300+5% Tween 80+45% Saline: 2 mg/mL (10.63 mM), Sonication is recommended. Please add the solvents sequentially, clarifying the solution as much as possible before adding the next one. Dissolve by heating and/or sonication if necessary. Working solution is recommended to be prepared and used immediately. The formulation provided above is for reference purposes only. In vivo formulations may vary and should be modified based on specific experimental conditions. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Solution Preparation Table | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
H2O/Ethanol/DMSO
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Size | Quantity | Unit Price | Amount | Operation |
|---|

Copyright © 2015-2025 TargetMol Chemicals Inc. All Rights Reserved.