 Your shopping cart is currently empty
Your shopping cart is currently empty

MEG hemisulfate (Mercaptoethylguanidine hemisulfate) acts as a highly potent and selective suppressor of inducible NO synthase (iNOS), demonstrating EC50 values of 11.5 μM for iNOS, 110 μM for ecNOS, and 60 μM for bNOS in tissue homogenates. It is notably effective as a peroxynitrite scavenger and blocks peroxynitrite-triggered oxidative mechanisms. Furthermore, this compound offers protective benefits across various experimental inflammation prototypes, such as ischemia/reperfusion injury, hemorrhagic shock, periodontitis, inflammatory bowel disease, and both endotoxic and septic shock.
| Pack Size | Price | USA Warehouse | Global Warehouse | Quantity |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 mg | $30 | - | In Stock | |
| 5 mg | $47 | - | In Stock | |
| 10 mg | $68 | - | In Stock | |
| 25 mg | Preferential | - | In Stock | |
| 50 mg | Preferential | - | In Stock | |
| 1 mL x 10 mM (in DMSO) | $58 | - | In Stock |
| Description | MEG hemisulfate (Mercaptoethylguanidine hemisulfate) acts as a highly potent and selective suppressor of inducible NO synthase (iNOS), demonstrating EC50 values of 11.5 μM for iNOS, 110 μM for ecNOS, and 60 μM for bNOS in tissue homogenates. It is notably effective as a peroxynitrite scavenger and blocks peroxynitrite-triggered oxidative mechanisms. Furthermore, this compound offers protective benefits across various experimental inflammation prototypes, such as ischemia/reperfusion injury, hemorrhagic shock, periodontitis, inflammatory bowel disease, and both endotoxic and septic shock. |
| In vitro | MEG, administered in various concentrations (0.1-1000 µM for 18 hours), reduces nitrite accumulation in the supernatant of LPS (10 µg/mL) and INF (50 µg/mL) activated J774.2 macrophages, while also inhibiting iNOS activity in lung homogenates from LPS-treated rats. Additionally, MEG effectively inhibits peroxynitrite-induced oxidative processes, including the oxidation of cytochrome c2+ and hydroxylation of benzoate, across a range of concentrations (1 µM-3 mM over 3 minutes). It also protects against the suppression of mitochondrial respiration and DNA single strand breakage in J774 cells, and the impairment of vascular contractility in thoracic aortic rings, suggesting broad protective effects against peroxynitrite-induced damage. |
| In vivo | MEG (30-60 mg/kg; a single i.p.) decreases mean arterial blood pressure (MAP) of normal rats[1]. MEG (10 mg/kg; i.p. for 5 d) attenuates the degree of lipid peroxidation, protein oxidation, and peroxynitrites level and ameliorated the decrease of antioxidant enzymes activities in the esophagus of rats subjected to caustic burn injury[3]. MEG (10 mg/kg; a single i.p.) improves the renal dysfunction and tissue injury induced by ischemia/reperfusion (I/R) of rat kidney[4]. |
| Synonyms | Mercaptoethylguanidine hemisulfate |
| Molecular Weight | 336.44 |
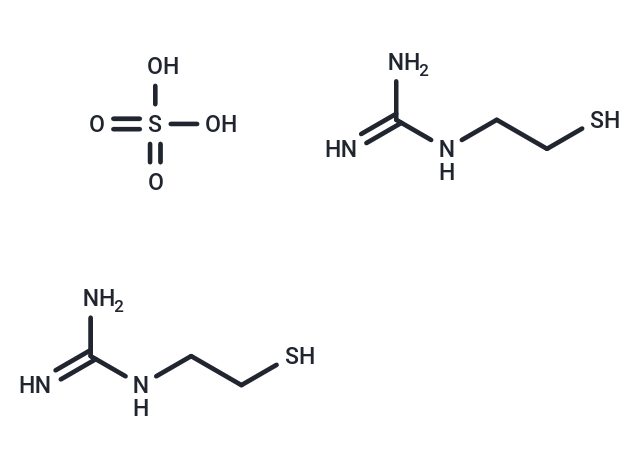
| Formula | C6H20N6O4S3 |
| Cas No. | 3979-00-8 |
| Smiles | O=S(O)(O)=O.N=C(NCCS)N.N=C(NCCS)N |
| Relative Density. | no data available |
| Storage | Pure form: -20°C for 3 years | In solvent: -80°C for 1 year | Shipping with blue ice/Shipping at ambient temperature. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Solubility Information | DMSO: 45 mg/mL (133.75 mM), Sonication is recommended. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Solution Preparation Table | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
DMSO
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Dissolve 2 mg of the compound in 100 μL DMSO![]() to obtain a stock solution at a concentration of 20 mg/mL . If the required concentration exceeds the compound's known solubility, please contact us for technical support before proceeding.
to obtain a stock solution at a concentration of 20 mg/mL . If the required concentration exceeds the compound's known solubility, please contact us for technical support before proceeding.
1) Add 100 μL of the DMSO![]() stock solution to 400 μL PEG300
stock solution to 400 μL PEG300![]() and mix thoroughly until the solution becomes clear.
and mix thoroughly until the solution becomes clear.
2) Add 50 μL Tween 80 and mix well until fully clarified.
3) Add 450 μL Saline,PBS or ddH2O![]() and mix thoroughly until a homogeneous solution is obtained.
and mix thoroughly until a homogeneous solution is obtained.
| Size | Quantity | Unit Price | Amount | Operation |
|---|

Copyright © 2015-2026 TargetMol Chemicals Inc. All Rights Reserved.