 Your shopping cart is currently empty
Your shopping cart is currently empty

Carboxy-PTIO is a highly effective nitric oxide (NO) scavenger known for its rapid reaction rate with NO, resulting in the formation of nitric dioxide (NO2). Its direct scavenging action against NO plays a crucial role in preventing hypotension and endotoxic shock, particularly in lipopolysaccharide-stimulated rat models.
| Pack Size | Price | USA Warehouse | Global Warehouse | Quantity |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 25 mg | $1,520 | Inquiry | Inquiry |
| Description | Carboxy-PTIO is a highly effective nitric oxide (NO) scavenger known for its rapid reaction rate with NO, resulting in the formation of nitric dioxide (NO2). Its direct scavenging action against NO plays a crucial role in preventing hypotension and endotoxic shock, particularly in lipopolysaccharide-stimulated rat models. |
| In vitro | Carboxy-PTIO, at a concentration of 200 μM and administered 1 hour before physalin A for a duration of 24 hours, effectively inhibits the increase in NO expression triggered by physalin A, without affecting baseline NO levels[1]. Furthermore, it mitigates the physalin A-induced activation of apoptotic pathways by preventing the cleavage of procaspase-3 and PARP, downregulating ICAD expression, and reducing nuclear DNA fragmentation[1]. Additionally, Carboxy-PTIO does not alter iNOS expression levels but negates the physalin A-induced reduction in both mTOR and phosphorylated mTOR, while also inhibiting the autophagic process by preventing the conversion of LC3 I to LC3 II in A375-S2 cells[1]. This was corroborated by a Cell Viability Assay on A375-S2 cells, where Carboxy-PTIO, pre-administered at 200 μM for 1 hour followed by physalin A exposure for 24 hours, decreased the cleavage of procaspase-3 and PARP induced by physalin A[1]. |
| In vivo | Carboxy-PTIO (intravenous injection; 0.056-1.70 mg/kg/min; infused for 1 hr beginning 90 min after the LPS injection) significantly ameliorates hypotension, renal dysfunction, and enhances survival rates in LPS-treated SD rats by directly scavenging nitric oxide (NO), without affecting these parameters in normal rats. |
| Molecular Weight | 277.3 |
| Formula | C14H17N2O4 |
| Cas No. | 145757-47-7 |
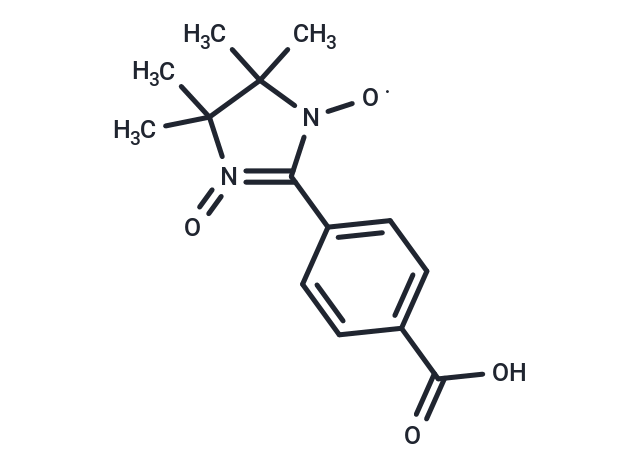
| Smiles | CC1(C)N([O])C(c2ccc(cc2)C(O)=O)=N(=O)C1(C)C |^1:4| |
| Storage | Powder: -20°C for 3 years | In solvent: -80°C for 1 year | Shipping with blue ice/Shipping at ambient temperature. |
Dissolve 2 mg of the compound in 100 μL DMSO![]() to obtain a stock solution at a concentration of 20 mg/mL . If the required concentration exceeds the compound's known solubility, please contact us for technical support before proceeding.
to obtain a stock solution at a concentration of 20 mg/mL . If the required concentration exceeds the compound's known solubility, please contact us for technical support before proceeding.
1) Add 100 μL of the DMSO![]() stock solution to 400 μL PEG300
stock solution to 400 μL PEG300![]() and mix thoroughly until the solution becomes clear.
and mix thoroughly until the solution becomes clear.
2) Add 50 μL Tween 80 and mix well until fully clarified.
3) Add 450 μL Saline,PBS or ddH2O![]() and mix thoroughly until a homogeneous solution is obtained.
and mix thoroughly until a homogeneous solution is obtained.
| Size | Quantity | Unit Price | Amount | Operation |
|---|

Copyright © 2015-2026 TargetMol Chemicals Inc. All Rights Reserved.