 Your shopping cart is currently empty
Your shopping cart is currently empty

XMU-MP-1 is a reversible and selective MST1/2 kinase inhibitor, and its IC50 values for MST1 and MST2 are 71.1 nM and 38.1 nM, respectively.
| Pack Size | Price | USA Warehouse | Global Warehouse | Quantity |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 mg | $48 | In Stock | In Stock | |
| 2 mg | $72 | In Stock | In Stock | |
| 5 mg | $98 | In Stock | In Stock | |
| 10 mg | $155 | In Stock | In Stock | |
| 25 mg | $322 | In Stock | In Stock | |
| 50 mg | $538 | In Stock | In Stock | |
| 100 mg | $698 | In Stock | In Stock | |
| 1 mL x 10 mM (in DMSO) | $96 | In Stock | In Stock |
| Description | XMU-MP-1 is a reversible and selective MST1/2 kinase inhibitor, and its IC50 values for MST1 and MST2 are 71.1 nM and 38.1 nM, respectively. |
| Targets&IC50 | MST1:71.1 nM, MST2:38.1 nM, MST2:18.2 nM, MST3:44.8 nM, MST4:27.3 nM |
| In vitro | METHODS: HepG2 cells, mouse macrophage-like cells, human osteosarcoma, and human colorectal adenocarcinoma cells were treated with XMU-MP-1 (0-3 μM) for 15 minutes, and the phosphorylation levels were detected by western blot. RESULTS: XMU-MP-1 reduces the phosphorylation of endogenous MOB1, LATS1/2 and YAP in HepG2 cells in a dose-dependent manner. XMU-MP-1 inhibits hydrogen peroxide-stimulated phosphorylation of MOB1 and autophosphorylation of MST1/2 in mouse macrophagocyte-like cells, human osteosarcoma, and human colorectal adenocarcinoma cells. [1] |
| In vivo | METHODS: To study the effect of XMU-MP-1 on cardiac function, C57Bl/6 mice underwent transverse aortic cotation (TAC) surgery to induce cardiac hypertrophy and dysfunction. XMU-MP-1 (1 mg/kg) or solvent (DMSO) treatment was administered 3 weeks after the operation, once every 2 days for 10 consecutive days. RESULTS: The cardiac systolic function of mice treated with XMU-MP-1 was significantly improved, manifested as an increase in ejection fraction. The cross-sectional area of myocardial cells in mice treated with XMU-MP-1 decreased, and the expression of the hypertrophy marker brain natriuretic peptide (BNP) decreased. The number of TunEL-positive cardiomyocytes in the hearts of mice treated with XMU-MP-1 decreased, and the degree of fibrosis was reduced, indicating that this drug inhibited cardiomyocyte apoptosis and fibrosis. [2] METHODS: To study the ability of XMU-MP-1 in liver injury repair, XMU-MP-1 (1-3 mg/kg) was intraperitoneally injected into mouse models of acute/chronic liver injury. RESULTS: XMU-MP-1 has good pharmacokinetic characteristics in vivo and can improve the repair and regeneration ability of the intestinal tract and liver of mice. METHODS: To study the anti-tumor activity of XMU-MP-1, XMU-MP-1 was injected daily into NSG mice supplemented with estrogen. RESULTS: XMU-MP-1 significantly inhibited tumor growth in MCF-7 xenografts, and the treated xenografts showed increased nuclear localization of YAP and expression of target genes. [3] METHODS: To study the effect of XMU-MP-1 on osteoarthritis, XMU-MP-1 (1 mg/kg) was intraperitoneally injected into a mouse model of osteoarthritis for two consecutive weeks. RESULTS: XMU-MP-1 can inhibit the erosion of the articular cartilage surface and the thickening of the synovial membrane, and alleviate the symptoms of osteoarthritis. |
| Kinase Assay | XMU-MP-1 is dissolved in DMSO (stock concentration, 10 mM). For the in vitro kinase inhibition assays, recombinant GST-tagged MOB1a and various forms of recombinant His-tagged full-length MST1 or MST2 kinase are expressed and purified from Escherichia coli. The assays are performed with the various doses of XMU-MP-1 in the kinase assay buffer for 30 min at 30°C[1]. |
| Molecular Weight | 416.48 |
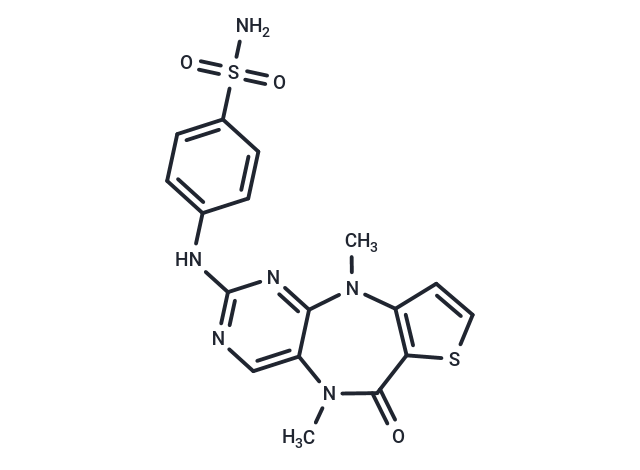
| Formula | C17H16N6O3S2 |
| Cas No. | 2061980-01-4 |
| Smiles | CN1c2ccsc2C(=O)N(C)c2cnc(Nc3ccc(cc3)S(N)(=O)=O)nc12 |
| Relative Density. | 1.523 g/cm3 (Predicted) |
| Storage | store at low temperature | Powder: -20°C for 3 years | In solvent: -80°C for 1 year | Shipping with blue ice/Shipping at ambient temperature. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Solubility Information | DMSO: 12.5 mg/mL (30.01 mM), Sonication is recommended. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
| In Vivo Formulation | 10% DMSO+40% PEG300+5% Tween-80+45% Saline: 0.5 mg/mL (1.2 mM), Sonication is recommended. Please add the solvents sequentially, clarifying the solution as much as possible before adding the next one. Dissolve by heating and/or sonication if necessary. Working solution is recommended to be prepared and used immediately. The formulation provided above is for reference purposes only. In vivo formulations may vary and should be modified based on specific experimental conditions. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
Solution Preparation Table | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
DMSO
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Dissolve 2 mg of the compound in 100 μL DMSO![]() to obtain a stock solution at a concentration of 20 mg/mL . If the required concentration exceeds the compound's known solubility, please contact us for technical support before proceeding.
to obtain a stock solution at a concentration of 20 mg/mL . If the required concentration exceeds the compound's known solubility, please contact us for technical support before proceeding.
1) Add 100 μL of the DMSO![]() stock solution to 400 μL PEG300
stock solution to 400 μL PEG300![]() and mix thoroughly until the solution becomes clear.
and mix thoroughly until the solution becomes clear.
2) Add 50 μL Tween 80 and mix well until fully clarified.
3) Add 450 μL Saline,PBS or ddH2O![]() and mix thoroughly until a homogeneous solution is obtained.
and mix thoroughly until a homogeneous solution is obtained.
| Size | Quantity | Unit Price | Amount | Operation |
|---|

Copyright © 2015-2026 TargetMol Chemicals Inc. All Rights Reserved.