Shopping Cart
- Remove All
 Your shopping cart is currently empty
Your shopping cart is currently empty

Ripisartan (UP-269-6) is a potent and specific angiotensin II receptor antagonist that inhibits angiotensin II-mediated sympathetic tachycardia responses.
| Pack Size | Price | Availability | Quantity |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 mg | $115 | In Stock | |
| 5 mg | $282 | In Stock | |
| 10 mg | $413 | In Stock | |
| 25 mg | $648 | In Stock | |
| 50 mg | $922 | In Stock | |
| 100 mg | $1,260 | In Stock | |
| 200 mg | $1,690 | In Stock |
| Description | Ripisartan (UP-269-6) is a potent and specific angiotensin II receptor antagonist that inhibits angiotensin II-mediated sympathetic tachycardia responses. |
| Targets&IC50 | Smooth muscle cells (SMCs):23.8 nM, Adrenal membranes:35.8 nM |
| In vitro | UP 269-6 bound selectively to AT1 receptors as evidenced by the inhibition of specific [125I] Sar1, Ile8-AII binding in rat adrenal membranes (IC50 = 35.8 nM) and in cultured vascular smooth muscle cells (IC50 = 23.8 nM). UP 269-6 displayed a very high selectivity for the AT1 compared to the AT2 receptor subtype (IC50 >10,000 nM). UP 269-6 inhibited the AII-induced contraction of isolated rabbit aortic strips.[4] UP 269-6 at low concentrations (10(-10), 3 x 10(-10), 10(-9) M) of UP 269-6 and insurmountable antagonism at higher concentrations (3 x 10(-9), 10(-8), 3 x 10(-8) M). Based on the calculated pA2 values, UP 269-6 (9.86 +/- 0.25) was an angiotensin II receptor antagonist as potent as L-158,809 (9.82 +/- 0.37) and much more potent than losartan (7.96 +/- 0.38). UP 269-6 was devoid of affinity (IC50 > 10,000 nM) for many other receptors, ion channels and uptake sites, demonstrating its high specificity for AII receptors. Furthermore, this compound did not affect the contractile response to KCl or phenylephrine in rabbit aorta and exhibited no effect on angiotensin-converting enzyme activity. These data demonstrate that UP 269-6 is a highly potent, selective, and specific AT1 receptor antagonist.[4] |
| In vivo | Ripisartan(0.03-1 mg/kg; i.v.; rats) shifted dose-dependently to the right of the dose-pressor response curve for angiotensin II and decreased the maximum response. Ripisartanantagonized the angiotensin II sympathetic-mediated tachycardiac response.[1] Ripisartaninhibited dose-dependently the pressor response to angiotensin II with an ID50 of 4.5 micrograms/kg, i.v. in conscious normotensive dogs.[1] Ripisartan(0.1 to 30 mg/kg; Oral) resulted in a dose-dependent and long-lasting inhibition of the angiotensin II-induced pressor response in conscious normotensive rats and dogs.[1] Ripisartanis a potent and specific angiotensin II receptor antagonist and does not possess agonistic properties. |
| Alias | UP269-6, UP-269-6, UP-2696, UP 269-6, UP 2696 |
| Molecular Weight | 426.47 |
| Formula | C23H22N8O |
| Cas No. | 148504-51-2 |
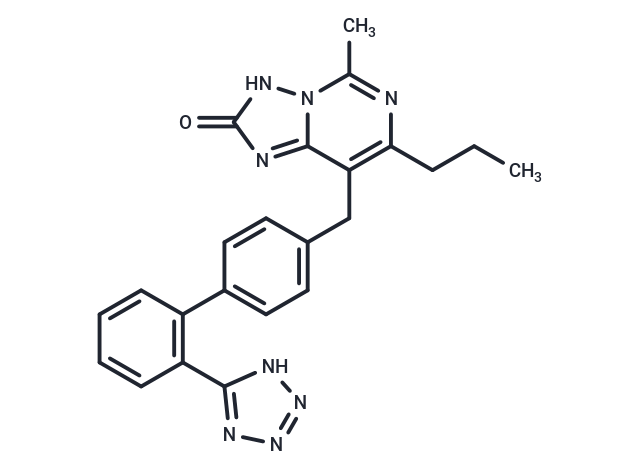
| Smiles | C(C=1C=2N(C(C)=NC1CCC)NC(=O)N2)C3=CC=C(C=C3)C4=C(C=CC=C4)C=5NN=NN5 |
| Relative Density. | 1.31g/cm3 |
| Storage | Powder: -20°C for 3 years | In solvent: -80°C for 1 year | Shipping with blue ice. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Solubility Information | DMSO: 55 mg/mL (128.97 mM), Sonication is recommended. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Solution Preparation Table | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
DMSO
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||

Copyright © 2015-2025 TargetMol Chemicals Inc. All Rights Reserved.