Shopping Cart
Remove All Your shopping cart is currently empty
Your shopping cart is currently empty
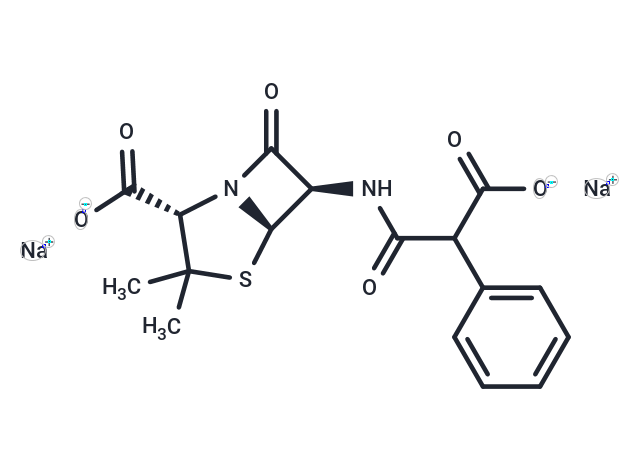
Carbenicillin disodium (BRL-2064) is a broad-spectrum, semi-synthetic penicillin antibiotic with bactericidal and beta-lactamase resistant activity.
| Pack Size | Price | USA Warehouse | Global Warehouse | Quantity |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 500 mg | $44 | In Stock | In Stock | |
| 1 g | $48 | In Stock | In Stock | |
| 5 g | $147 | - | In Stock |
| Description | Carbenicillin disodium (BRL-2064) is a broad-spectrum, semi-synthetic penicillin antibiotic with bactericidal and beta-lactamase resistant activity. |
| In vitro | In patients with cystic fibrosis, Carbenicillin (0.1μg/mL) exhibited no hypersensitivity drug reactions as measured by antibody levels. In chrysanthemums and TOBC, Carbenicillin (50 μg/mL) induced phytotoxicity in a concentration-dependent manner. |
| In vivo | Carbenicillin (125 mg/L) effectively suppresses the proliferation of soil bacteria, increases the volume of somatic embryos, and the number of somatic embryos per callus tissue. Within the callus tissue, Carbenicillin at concentrations of 250 mg/L to 500 mg/L can enhance the fresh weight of the tissue. At a higher concentration of 1 g/L, Carbenicillin reduces the germination frequency of leaf disc explants. Additionally, in vitro exposure of patients' isolated leukocytes to Carbenicillin (0.1 g/ml) does not result in histamine release. |
| Synonyms | Sodium carbenicillin, BRL-2064 |
| Molecular Weight | 422.36 |
| Formula | C17H16N2Na2O6S |
| Cas No. | 4800-94-6 |
| Smiles | [Na+].[C@H]1(C(=O)N2[C@@H]1SC([C@@H]2C(=O)[O-])(C)C)NC(=O)C(C(=O)[O-])c1ccccc1.[Na+] |
| Relative Density. | no data available |
| Color | White |
| Appearance | Solid |
| Storage | The compound is unstable in solution. Please use soon | In solvent: -80°C for 1 year | Shipping with blue ice/Shipping at ambient temperature. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Solubility Information | H2O: < 1 mg/mL (insoluble), The compound is unstable in solution, please use soon. Ethanol: < 1 mg/mL (insoluble or slightly soluble), The compound is unstable in solution, please use soon. DMSO: 62.5 mg/mL (147.98 mM), Sonication is recommended. The compound is unstable in solution, please use soon. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| In Vivo Formulation | 10% DMSO+40% PEG300+5% Tween 80+45% Saline: 2 mg/mL (4.74 mM), Sonication is recommended. Please add the solvents sequentially, clarifying the solution as much as possible before adding the next one. Dissolve by heating and/or sonication if necessary. Working solution is recommended to be prepared and used immediately. The formulation provided above is for reference purposes only. In vivo formulations may vary and should be modified based on specific experimental conditions. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Solution Preparation Table | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
DMSO
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Size | Quantity | Unit Price | Amount | Operation |
|---|

Copyright © 2015-2026 TargetMol Chemicals Inc. All Rights Reserved.