 Your shopping cart is currently empty
Your shopping cart is currently empty

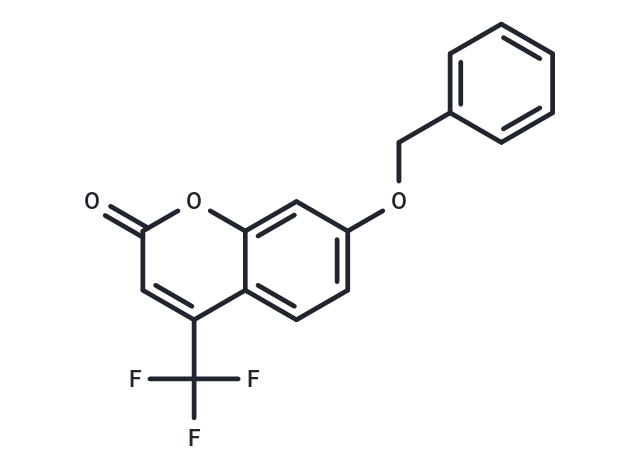
7-BFC (7-Benzyloxy-4-(trifluoromethyl)coumarin) is a coumarin-like fluorescent substrate that serves as a biomarker for cytochrome P 450 and can be used to study CYP isoforms and cytochrome P 450 metabolism.
| Pack Size | Price | USA Warehouse | Global Warehouse | Quantity |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 5 mg | $40 | In Stock | In Stock | |
| 10 mg | $64 | In Stock | In Stock | |
| 25 mg | $135 | In Stock | In Stock | |
| 50 mg | $213 | In Stock | In Stock | |
| 100 mg | $347 | In Stock | In Stock |

| Description | 7-BFC (7-Benzyloxy-4-(trifluoromethyl)coumarin) is a coumarin-like fluorescent substrate that serves as a biomarker for cytochrome P 450 and can be used to study CYP isoforms and cytochrome P 450 metabolism. |
| In vitro | I. CYP activity detection 1. Material preparation: 1) 7-BFC solution: usually prepared as a 1-10 µM solution, dissolved in an appropriate solvent (such as DMSO or PBS). 2) Enzyme source: CYP subtype (such as CYP3A4, CYP2D6, etc.) expression system, or use human liver microsomes. 3) Reaction buffer: usually use phosphate buffer (pH 7.4) containing NADPH to simulate the in vivo metabolic environment. 4) Fluorescence detection equipment: such as fluorescence spectrophotometer, excitation wavelength 405 nm, emission wavelength 460 nm (specific wavelength depends on the experimental setting). 2. Steps: 1) Prepare the reaction system: mix the 7-BFC solution with CYP subtypes or liver microsomes, and add NADPH as an electron donor. 2) Reaction incubation: Incubate the reaction system at 37°C for 15-30 minutes to allow 7-BFC to undergo metabolic reactions and produce fluorescence. 3) Fluorescence detection: Use a fluorescence spectrophotometer to detect the fluorescence intensity of the product, usually setting the excitation wavelength to 405 nm and the emission wavelength to 460 nm. 4) Data analysis: By measuring the changes in fluorescence intensity, the activity of cytochrome P450 and its metabolic efficiency on 7-BFC can be evaluated. II. CYP subtype-specific detection 1. Material preparation: 1) CYP subtype inhibitors: such as ketoconazole (an inhibitor of CYP3A4), or inhibitors of specific subtypes. 2) Metabolite analysis: Metabolites can be further analyzed by techniques such as high-performance liquid chromatography (HPLC). 3. Steps: 1) Set up experimental groups: Add different CYP inhibitors to identify the metabolic effects of specific CYP subtypes on 7-BFC. 2) Fluorescence detection and data analysis: Compare the fluorescence signal intensity of different inhibitors and untreated samples to further confirm the metabolic characteristics of specific CYP subtypes. Notes: 1) Reaction conditions: The choice of temperature, pH and buffer will affect the efficiency of the reaction and should be optimized according to the experimental requirements. 2) Solvent effect: When dissolving 7-BFC, a solvent that has no effect on the experimental system should be selected to avoid inhibition of CYP activity. 3) Fluorescence stability: The fluorescence signal of 7-BFC is relatively stable, but long-term exposure to strong light should be avoided. The above information is based on published literature. Experimental procedures should be appropriately modified to meet specific research demands. |
| Synonyms | Y040-0031, 7-Benzyloxy-4-(trifluoromethyl)coumarin |
| Molecular Weight | 320.26 |
| Formula | C17H11F3O3 |
| Cas No. | 220001-53-6 |
| Smiles | FC(F)(F)c1cc(=O)oc2cc(OCc3ccccc3)ccc12 |
| Relative Density. | 1.375 g/cm3 (Predicted) |
| Storage | Powder: -20°C for 3 years | In solvent: -80°C for 1 year | Shipping with blue ice/Shipping at ambient temperature. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Solubility Information | DMSO: 55 mg/mL (171.74 mM), Sonication is recommended. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Solution Preparation Table | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
DMSO
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Dissolve 2 mg of the compound in 100 μL DMSO![]() to obtain a stock solution at a concentration of 20 mg/mL . If the required concentration exceeds the compound's known solubility, please contact us for technical support before proceeding.
to obtain a stock solution at a concentration of 20 mg/mL . If the required concentration exceeds the compound's known solubility, please contact us for technical support before proceeding.
1) Add 100 μL of the DMSO![]() stock solution to 400 μL PEG300
stock solution to 400 μL PEG300![]() and mix thoroughly until the solution becomes clear.
and mix thoroughly until the solution becomes clear.
2) Add 50 μL Tween 80 and mix well until fully clarified.
3) Add 450 μL Saline,PBS or ddH2O![]() and mix thoroughly until a homogeneous solution is obtained.
and mix thoroughly until a homogeneous solution is obtained.
| Size | Quantity | Unit Price | Amount | Operation |
|---|

Copyright © 2015-2026 TargetMol Chemicals Inc. All Rights Reserved.