 Your shopping cart is currently empty
Your shopping cart is currently empty

JC-1 (CBIC2) is a fluorescent lipophilic carbonyl cyanine dye. JC-1 is used to measure mitochondrial membrane potential. When the mitochondrial membrane potential is relatively high, JC-1 converges in the matrix to form a polymer, which can produce red fluorescence (λex=585 nm, λem=590 nm). When the mitochondrial membrane potential is low, JC-1 cannot accumulate in the mitochondrial matrix and exists in the form of monomers to produce green fluorescence (λex=510 nm, λem=527 nm).
| Pack Size | Price | USA Warehouse | Global Warehouse | Quantity |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 mg | $59 | In Stock | In Stock | |
| 2 mg | $81 | In Stock | In Stock | |
| 5 mg | $153 | In Stock | In Stock | |
| 10 mg | $252 | In Stock | In Stock | |
| 25 mg | $423 | In Stock | In Stock | |
| 50 mg | $628 | In Stock | In Stock | |
| 100 mg | $893 | - | In Stock |
| Description | JC-1 (CBIC2) is a fluorescent lipophilic carbonyl cyanine dye. JC-1 is used to measure mitochondrial membrane potential. When the mitochondrial membrane potential is relatively high, JC-1 converges in the matrix to form a polymer, which can produce red fluorescence (λex=585 nm, λem=590 nm). When the mitochondrial membrane potential is low, JC-1 cannot accumulate in the mitochondrial matrix and exists in the form of monomers to produce green fluorescence (λex=510 nm, λem=527 nm). |
| Targets&IC50 | α-synuclein:2.6 μM (Kd) |
| In vitro | JC-1 fluorescence is usually excited by the 488nm laser wavelength common in flow cytometers[1]. JC-1 (2.5μM) exposed to murine L1210 lymphoblasts, can be detected the presence of both cytoplasmic JC-1 monomer and mitochondrial J-aggregates in these cells. Fluorescent labeling of mitochondria with either JC-1 (1 μg/mL, 15 min), reveals that are distributed irregularly, resulting in regions of high and low mitochondrial content within astrocytes[2]. JC-1 is avidly accumulated in sensitive K562 cells where it displays both a green cytoplasmic and red mitochondrial fluorescence. JC-1 is poorly accumulated in resistant K562 cells, which displays only a slight green fluorescence[4]. JC-1 has been shown to interact with α-synuclein at the acidic C-terminal region with a Kd of 2.6 μM. JC-1 itself does not accelerate the protein aggregation of α-synuclein in the absence of iron, insted, it decelerates the aggregation process by extending the lag phase approx[3]. |
| Cell Research | Instructions I. Solution preparation 1. Stock solution preparation: JC-1 is dissolved in DMSO to prepare a stock solution. The concentration of the stock solution is usually 5 mg/ml. Please refer to the manufacturer's instructions for the specific concentration. 2. Working concentration: The working concentration of JC-1 is usually 1-20 µg/ml, but the optimal concentration may need to be optimized depending on the cell type and experimental conditions. 3. Dilution: Dilute the stock solution with cell culture medium or appropriate buffer before use. II. Staining cells 1. Cell preparation: Culture the cells to be tested under appropriate conditions (e.g., 37°C, 5% CO₂). 2. Incubation with JC-1: Add the diluted JC-1 working solution to the cells. Depending on the cell type and experimental conditions, incubate for 15-30 minutes. 3. Washing: After incubation, wash the cells 1-2 times with preheated cell culture medium or PBS to remove excess dye. 3. Fluorescence detection 1. Fluorescence microscopy: Use a fluorescence microscope equipped with appropriate filters to detect green (monomer JC-1) and red (aggregate JC-1) fluorescence. The excitation wavelength of green fluorescence is usually 485-490 nm, and that of red fluorescence is 525-530 nm, with emission peaks at 535 nm (green) and 590 nm (red), respectively. 2. Flow cytometry: Flow cytometry can also be used for quantitative analysis. Use appropriate filters (e.g., 525/40 nm for green fluorescence and 585/42 nm for red fluorescence) for detection. 3. Data interpretation: An increase in red fluorescence indicates a higher mitochondrial membrane potential, while an increase in green fluorescence indicates a loss or decrease in membrane potential. The above information is based on published literature. Experimental procedures should be appropriately modified to meet specific research demands. |
| Synonyms | CBIC2 |
| Molecular Weight | 652.23 |
| Formula | C25H27Cl4IN4 |
| Cas No. | 3520-43-2 |
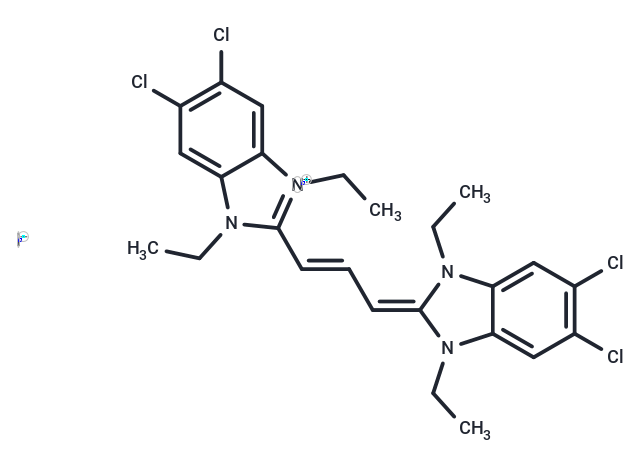
| Smiles | [I-].CCN1C(=C\C=C\c2n(CC)c3cc(Cl)c(Cl)cc3[n+]2CC)N(CC)c2cc(Cl)c(Cl)cc12 |
| Relative Density. | no data available |
| Storage | keep away from direct sunlight,store at low temperature,keep away from moisture | In solvent: -80°C for 1 year | Shipping with blue ice/Shipping at ambient temperature. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Solubility Information | DMSO: 14 mg/mL (21.46 mM), Sonication is recommended. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
Solution Preparation Table | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
DMSO
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Dissolve 2 mg of the compound in 100 μL DMSO![]() to obtain a stock solution at a concentration of 20 mg/mL . If the required concentration exceeds the compound's known solubility, please contact us for technical support before proceeding.
to obtain a stock solution at a concentration of 20 mg/mL . If the required concentration exceeds the compound's known solubility, please contact us for technical support before proceeding.
1) Add 100 μL of the DMSO![]() stock solution to 400 μL PEG300
stock solution to 400 μL PEG300![]() and mix thoroughly until the solution becomes clear.
and mix thoroughly until the solution becomes clear.
2) Add 50 μL Tween 80 and mix well until fully clarified.
3) Add 450 μL Saline,PBS or ddH2O![]() and mix thoroughly until a homogeneous solution is obtained.
and mix thoroughly until a homogeneous solution is obtained.
| Size | Quantity | Unit Price | Amount | Operation |
|---|

Copyright © 2015-2026 TargetMol Chemicals Inc. All Rights Reserved.