Shopping Cart
Remove All Your shopping cart is currently empty
Your shopping cart is currently empty
GS-9667, a selective and partial agonist of the A(1) adenosine receptor (AR), represents an effective therapy for Type 2 diabetes (T2DM) and dyslipidemia via lowering of free fatty acids (FFA).
| Pack Size | Price | USA Warehouse | Global Warehouse | Quantity |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 mg | $68 | In Stock | In Stock | |
| 5 mg | $173 | In Stock | In Stock | |
| 10 mg | $238 | In Stock | In Stock | |
| 25 mg | $392 | In Stock | In Stock | |
| 50 mg | $535 | In Stock | In Stock | |
| 100 mg | $738 | In Stock | In Stock | |
| 200 mg | $993 | - | In Stock |
| Description | GS-9667, a selective and partial agonist of the A(1) adenosine receptor (AR), represents an effective therapy for Type 2 diabetes (T2DM) and dyslipidemia via lowering of free fatty acids (FFA). |
| In vivo | In the single ascending dose study, healthy, non-obese, and obese subjects received GS-9667 (30-1,800 mg; oral; single dose). In the multiple, ascending dose study, healthy, obese subjects received GS-9667 (600-2,400 mg QD, 1,200 mg BID, or 600 mg QID) for 14 days. Doses of GS-9667 ≥300 mg caused dose-dependent reductions in FFA levels that were reproducible over 14 days without evidence of desensitization or rebound. All doses were well tolerated. GS-9667 was rapidly absorbed and distributed; Steady-state concentrations were achieved within 3-5 days. The A(1) AR partial agonist GS-9667 reduced plasma FFA, exhibited linear kinetics, and was well-tolerated in healthy non-obese and obese subjects.[1] |
| Synonyms | CVT-3619, CVT 3619 |
| Molecular Weight | 461.51 |
| Formula | C21H24FN5O4S |
| Cas No. | 618380-90-8 |
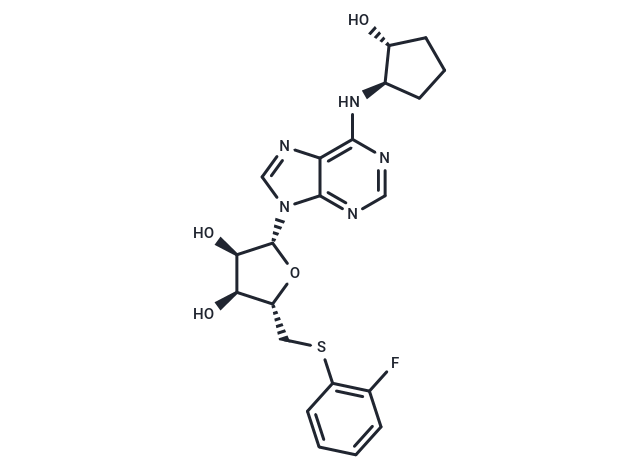
| Smiles | O[C@H]1[C@H](N2C=3C(N=C2)=C(N[C@H]4[C@H](O)CCC4)N=CN3)O[C@H](CSC5=C(F)C=CC=C5)[C@H]1O |
| Relative Density. | 1.68 g/cm3 (Predicted) |
| Color | Yellow |
| Appearance | Solid |
| Storage | Powder: -20°C for 3 years | In solvent: -80°C for 1 year | Shipping with blue ice/Shipping at ambient temperature. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Solubility Information | DMSO: 55 mg/mL (119.17 mM), Sonication is recommended. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Solution Preparation Table | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
DMSO
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Size | Quantity | Unit Price | Amount | Operation |
|---|

Copyright © 2015-2026 TargetMol Chemicals Inc. All Rights Reserved.