 Your shopping cart is currently empty
Your shopping cart is currently empty

1-Oleoyl Lysophosphatidic Acid (1-Oleoyl LPA) is a biologically active phospholipid that can exert multiple biological effects in various disease states of the kidney by activating a complex network of at least six homologous G protein-coupled receptors and their heterotrimeric G proteins. 1-Oleoyl Lysophosphatidic Acid promotes polarization of BV-2 and primary murine microglia toward an M1-like phenotype and can be used to study cancer and atherosclerosis.
| Pack Size | Price | USA Warehouse | Global Warehouse | Quantity |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 mg (22.91 mM * 100 μL in Ethanol) | $94 | 35 days | 35 days | |
| 5 mg (22.91 mM * 500 μL in Ethanol) | $369 | 35 days | 35 days | |
| 10 mg (22.91 mM * 1 mL in Ethanol) | $593 | 35 days | 35 days | |
| 25 mg (22.91 mM * 2.5 mL in Ethanol) | $1,270 | 35 days | 35 days |
| Description | 1-Oleoyl Lysophosphatidic Acid (1-Oleoyl LPA) is a biologically active phospholipid that can exert multiple biological effects in various disease states of the kidney by activating a complex network of at least six homologous G protein-coupled receptors and their heterotrimeric G proteins. 1-Oleoyl Lysophosphatidic Acid promotes polarization of BV-2 and primary murine microglia toward an M1-like phenotype and can be used to study cancer and atherosclerosis. |
| In vivo | METHODS: 1-Oleoyl Lysophosphatidic Acid(0.4-2 μg, i.v. for 9 weeks) treated rats and behaviorally assessed. RESULTS: 1-Oleoyl Lysophosphatidic Acid induced anxiety-like responses in the elevated plus maze (EPM). [5] |
| Synonyms | Oleoyl-sn-3-Glycerophosphate, 1-Oleoyl LPA |
| Molecular Weight | 436.52 |
| Formula | C21H41O7P |
| Cas No. | 65528-98-5 |
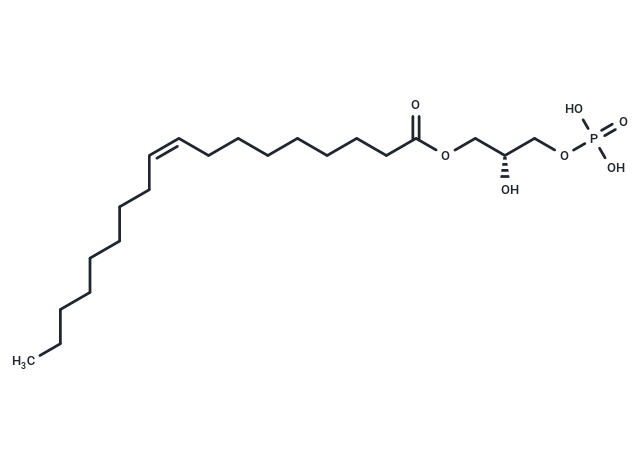
| Smiles | O(C(CCCCCCC/C=C\CCCCCCCC)=O)C[C@H](COP(=O)(O)O)O |
| Relative Density. | 1.103 g/cm3 (Predicted) |
| Storage | store at low temperature | Powder: -20°C for 3 years | In solvent: -80°C for 1 year | Shipping with blue ice/Shipping at ambient temperature. |
| Solubility Information | Ethanol: 10 mg/mL (22.91 mM), Sonication is recommended. PBS (pH 7.2): 1 mg/mL (2.29 mM), Sonication is recommended. DMF: 1 mg/mL (2.29 mM), Sonication is recommended. DMSO: 1 mg/mL (2.29 mM), Sonication is recommended. PBS (pH 7.2): 1 mg/mL (2.29 mM), Sonication is recommended. |
Solution Preparation Table | |
Dissolve 2 mg of the compound in 100 μL DMSO![]() to obtain a stock solution at a concentration of 20 mg/mL . If the required concentration exceeds the compound's known solubility, please contact us for technical support before proceeding.
to obtain a stock solution at a concentration of 20 mg/mL . If the required concentration exceeds the compound's known solubility, please contact us for technical support before proceeding.
1) Add 100 μL of the DMSO![]() stock solution to 400 μL PEG300
stock solution to 400 μL PEG300![]() and mix thoroughly until the solution becomes clear.
and mix thoroughly until the solution becomes clear.
2) Add 50 μL Tween 80 and mix well until fully clarified.
3) Add 450 μL Saline,PBS or ddH2O![]() and mix thoroughly until a homogeneous solution is obtained.
and mix thoroughly until a homogeneous solution is obtained.
| Size | Quantity | Unit Price | Amount | Operation |
|---|

Copyright © 2015-2026 TargetMol Chemicals Inc. All Rights Reserved.