 Your shopping cart is currently empty
Your shopping cart is currently empty

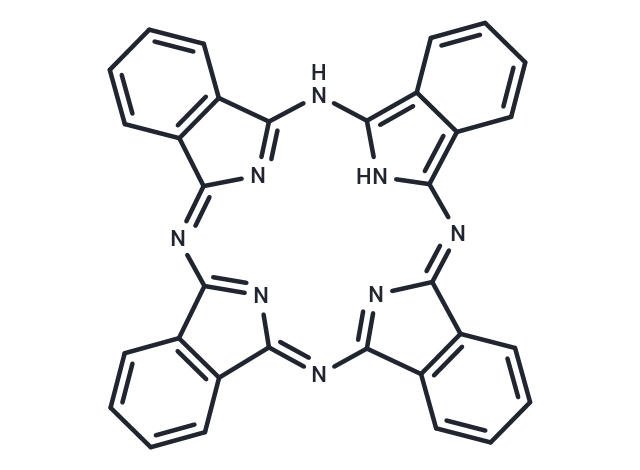
Phthalocyanine (29H,31H-Phthalocyanine) is an important multifunctional dye. It is a planar macrocyclic conjugated system composed of four isoindole units. It can form complexes with a variety of metals and can be used to synthesize new organic materials.
| Pack Size | Price | USA Warehouse | Global Warehouse | Quantity |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 500 mg | $31 | - | In Stock |
| Description | Phthalocyanine (29H,31H-Phthalocyanine) is an important multifunctional dye. It is a planar macrocyclic conjugated system composed of four isoindole units. It can form complexes with a variety of metals and can be used to synthesize new organic materials. |
| In vitro | To develop the required theranostic system, novel low-oxygen graphene nanosheets were chemically modified with polypropylenimine dendrimers loaded with Phthalocyanine as a photosensitizer. Such a molecular design prevents fluorescence quenching of the Phthalocyanine by graphene nanosheets, providing the possibility of fluorescence imaging. [2] |
| Kinase Assay | V. Research on Reactive Oxygen Species (ROS) Generation: 1. Use: Phthalocyanine can generate reactive oxygen species (ROS) under specific light conditions. These ROS can cause oxidative damage to cells or be used to study the role of ROS in cellular processes. 2. Usage: Phthalocyanine is used as a photosensitizer to generate ROS after activation. It is often used in combination with fluorescent probes (such as DCFH-DA) to detect the generation of ROS. 3. Dosage: The amount of phthalocyanine used is generally low, about 1 μM to 20 μM. Precautions: 1) Phthalocyanine compounds generally need to be stored in a lightless environment to avoid their premature activation under light. 2) During the experiment, excessive or uneven light exposure should be avoided to avoid unnecessary damage to cells. 3) When performing photodynamic therapy, pay attention to controlling the dose to avoid adverse reactions. The above information is based on published literature. Experimental procedures should be appropriately modified to meet specific research demands. |
| Cell Research | Instructions 1. Photodynamic therapy (PDT): Use: Phthalocyanine derivatives (such as copper phthalocyanine) are used as photosensitizers in photodynamic therapy, especially for cancer treatment. These photosensitizers produce singlet oxygen (¹O₂) under irradiation with light of a specific wavelength, which can kill tumor cells or bacteria. 1. Usage method: Phthalocyanine photosensitizers are generally dissolved in physiological saline and introduced into the body or tissue by intravenous injection or local application. After injection, the photosensitizer needs to take a certain amount of time to be absorbed by cells or tissues (usually between a few hours and a day), and then a laser of a specific wavelength is used to activate the photosensitizer. 2. Dosage: The specific dosage depends on experimental or clinical needs. Usually, the dosage of photosensitizer is a few milligrams per kilogram of body weight (for example, 0.1-5 mg/kg body weight). The specific dosage will be adjusted according to the type of drug, experimental or treatment requirements. Precautions: Avoid exposure to strong light before and after treatment to avoid unnecessary photosensitivity reactions. The wavelength and intensity of laser irradiation also need to be precisely controlled. 2. Fluorescent labeling and molecular probes: 1. Use: Phthalocyanine compounds can be used as fluorescent probes for cell or tissue imaging. Due to their strong fluorescence properties, they are often used to label cells, detect certain molecules, or monitor intracellular reactions. 2. Usage: Phthalocyanine can bind to certain biomacromolecules (such as antibodies, proteins, or nucleic acids) to form fluorescent markers. The location and concentration of phthalocyanine markers can be detected by equipment such as fluorescence microscopes or flow cytometers. 3. Dosage: In fluorescent labeling experiments, the concentration of phthalocyanine is usually between 10 μM and 100 μM. The specific concentration depends on the experimental objectives and the optical properties of phthalocyanine derivatives. 3. Intracellular photochemical research: 1. Use: In some basic biological experiments, phthalocyanine is used as a photosensitizer for cells to study biological reactions such as cell responses to light and oxidative stress. 2. Usage: Phthalocyanine is usually dissolved in an appropriate solvent, such as DMSO (Dimethyl sulfoxide) or water, and then added to the cell culture medium. After cells are exposed to phthalocyanine, the photosensitizer is activated by appropriate light exposure to study the biological response of the cells, such as the generation of ROS (reactive oxygen species), cell death, etc. 3. Dosage: The concentration of phthalocyanine added is usually between 1 μM and 50 μM, and the specific concentration depends on the cell type and target response of the experiment. IV. Oxidative stress research: 1. Use: Phthalocyanine can be used as an inducer of oxidative stress in biological research. They can produce singlet oxygen (¹O₂) through light exposure, causing oxidative damage in cells. 2. Usage: Phthalocyanine or its derivatives are added to the cell culture medium and irradiated with light of a specific wavelength to produce oxidative damage. This method is often used to study the effects of oxidative damage on cells, the protective effects of antioxidants, etc. 3. Dosage: Phthalocyanine concentration is usually between 1 μM and 10 μM. The above information is based on published literature. Experimental procedures should be appropriately modified to meet specific research demands. |
| Synonyms | 29H,31H-Phthalocyanine |
| Molecular Weight | 514.54 |
| Formula | C32H18N8 |
| Cas No. | 574-93-6 |
| Smiles | N1=C2N=C(N=C3N=C(NC=4NC(N=C5N=C1C=6C=CC=CC56)=C7C=CC=CC74)C=8C=CC=CC38)C=9C=CC=CC29 |
| Relative Density. | 1.31g/cm3 |
| Storage | keep away from direct sunlight | Powder: -20°C for 3 years | In solvent: -80°C for 1 year | Shipping with blue ice/Shipping at ambient temperature. |
| Solubility Information | Ethanol: < 1 mg/mL (insoluble) H2O: < 1 mg/mL (insoluble) DMSO: < 1 mg/mL (insoluble) |
Dissolve 2 mg of the compound in 100 μL DMSO![]() to obtain a stock solution at a concentration of 20 mg/mL . If the required concentration exceeds the compound's known solubility, please contact us for technical support before proceeding.
to obtain a stock solution at a concentration of 20 mg/mL . If the required concentration exceeds the compound's known solubility, please contact us for technical support before proceeding.
1) Add 100 μL of the DMSO![]() stock solution to 400 μL PEG300
stock solution to 400 μL PEG300![]() and mix thoroughly until the solution becomes clear.
and mix thoroughly until the solution becomes clear.
2) Add 50 μL Tween 80 and mix well until fully clarified.
3) Add 450 μL Saline,PBS or ddH2O![]() and mix thoroughly until a homogeneous solution is obtained.
and mix thoroughly until a homogeneous solution is obtained.
| Size | Quantity | Unit Price | Amount | Operation |
|---|

Copyright © 2015-2026 TargetMol Chemicals Inc. All Rights Reserved.