 Your shopping cart is currently empty
Your shopping cart is currently empty

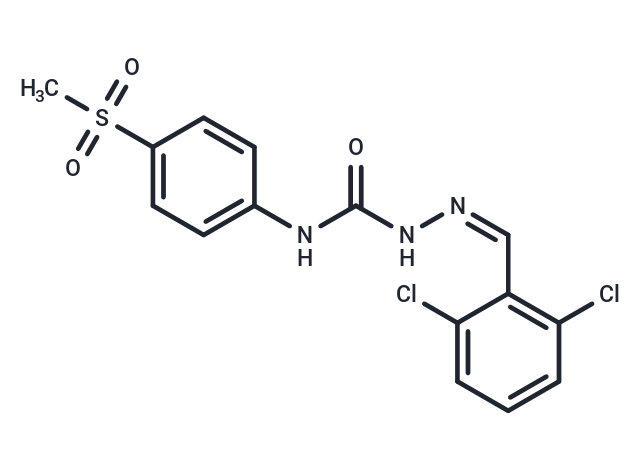
FAAH/MAGL-IN-2, a potent and reversible inhibitor of FAAH and MAGL, demonstrates oral activity and the ability to cross the blood-brain barrier. It exhibits IC50 values of 11 nM for FAAH and 36 nM for MAGL (Ki values of 28 nM and 60 nM, respectively). This compound shows promise for neuropathic pain research, without impairing locomotion [1].
| Pack Size | Price | USA Warehouse | Global Warehouse | Quantity |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 25 mg | $1,520 | 10-14 weeks | 10-14 weeks | |
| 50 mg | $1,980 | 10-14 weeks | 10-14 weeks | |
| 100 mg | $2,500 | 10-14 weeks | 10-14 weeks |
| Description | FAAH/MAGL-IN-2, a potent and reversible inhibitor of FAAH and MAGL, demonstrates oral activity and the ability to cross the blood-brain barrier. It exhibits IC50 values of 11 nM for FAAH and 36 nM for MAGL (Ki values of 28 nM and 60 nM, respectively). This compound shows promise for neuropathic pain research, without impairing locomotion [1]. |
| In vitro | FAAH/MAGL-IN-2 (compound 14) exhibited notable neuroprotective effects in a Cell Cytotoxicity Assay with SH-SY5Y cells at 1, 3, 10, 30, and 100 μM concentrations over 24 hours [1]. |
| In vivo | FAAH/MAGL-IN-2, administered at dosages of 10 mg/kg, demonstrates the potential for significant anti-nociceptive effects without impairing motor coordination and locomotor activity. At varying doses (5, 10, 20 mg/kg), it also shows promise in treating neuropathic pain without affecting locomotion. Tolerability and safety assessments reveal that FAAH/MAGL-IN-2, at an oral dose up to 2000 mg/kg in female rats, does not alter liver enzyme activity, signifying its safety at high doses. Additionally, at 20 mg/kg, this compound exhibits favorable oral absorption characteristics. Pharmacokinetic analysis in male Wistar rats, weighing 200–250 g, receiving a 20 mg/kg oral dose, discloses a peak plasma concentration (C max) of 22.04±2.5 μg/mL, occurring at 0.5 hours post-administration, with an area under the curve (AUC 0-t) of 535±1.5 μg min/mL and a half-life (t 1/2) of 20.58 hours, indicating substantial systemic exposure and prolonged circulation time. In neuropathic pain models, both the nerve injury model in rats (CCI model) and studies in 200–250 g male Wistar rats have shown that FAAH/MAGL-IN-2, at dosages of 5, 10, 20 mg/kg administered orally, significantly increases paw withdrawal thresholds and reduces tail flick latency, further supporting its analgesic potential and effective absorption post-oral administration. |
| Molecular Weight | 386.25 |
| Formula | C15H13Cl2N3O3S |
| Cas No. | 2765077-82-3 |
| Smiles | N(C(N/N=C\C1=C(Cl)C=CC=C1Cl)=O)C2=CC=C(S(C)(=O)=O)C=C2 |
| Storage | Powder: -20°C for 3 years | In solvent: -80°C for 1 year | Shipping with blue ice/Shipping at ambient temperature. |
Dissolve 2 mg of the compound in 100 μL DMSO![]() to obtain a stock solution at a concentration of 20 mg/mL . If the required concentration exceeds the compound's known solubility, please contact us for technical support before proceeding.
to obtain a stock solution at a concentration of 20 mg/mL . If the required concentration exceeds the compound's known solubility, please contact us for technical support before proceeding.
1) Add 100 μL of the DMSO![]() stock solution to 400 μL PEG300
stock solution to 400 μL PEG300![]() and mix thoroughly until the solution becomes clear.
and mix thoroughly until the solution becomes clear.
2) Add 50 μL Tween 80 and mix well until fully clarified.
3) Add 450 μL Saline,PBS or ddH2O![]() and mix thoroughly until a homogeneous solution is obtained.
and mix thoroughly until a homogeneous solution is obtained.
| Size | Quantity | Unit Price | Amount | Operation |
|---|

Copyright © 2015-2026 TargetMol Chemicals Inc. All Rights Reserved.