 Your shopping cart is currently empty
Your shopping cart is currently empty

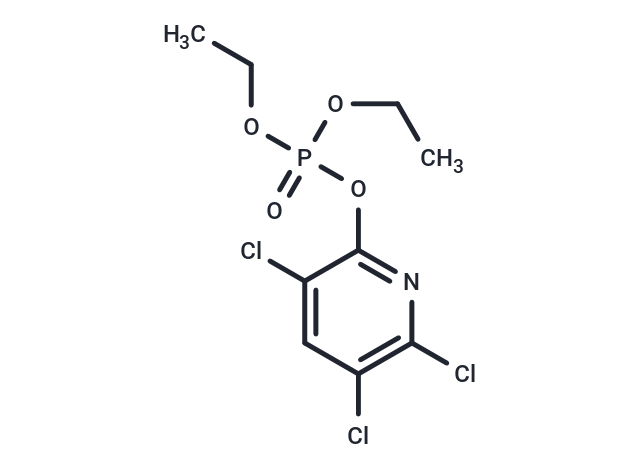
Chlorpyrifos-oxon, an active metabolite of Chlorpyrifos, is a potent phosphorylating agent that significantly inhibits AChE activity and induces cross-linking between tubulin subunits, thereby disrupting microtubule function [4].
| Pack Size | Price | USA Warehouse | Global Warehouse | Quantity |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 mg | $60 | 6-8 weeks | 6-8 weeks | |
| 5 mg | $130 | 6-8 weeks | 6-8 weeks | |
| 10 mg | $195 | 6-8 weeks | 6-8 weeks | |
| 25 mg | $330 | 6-8 weeks | 6-8 weeks | |
| 50 mg | $495 | 6-8 weeks | 6-8 weeks | |
| 100 mg | $740 | 6-8 weeks | 6-8 weeks |
| Description | Chlorpyrifos-oxon, an active metabolite of Chlorpyrifos, is a potent phosphorylating agent that significantly inhibits AChE activity and induces cross-linking between tubulin subunits, thereby disrupting microtubule function [4]. |
| In vitro | Treatment with 1.5 mM Chlorpyrifos-oxon (CPO) induces aggregation in tubulin proteins. Remarkably, at a concentration as low as 1.5 μM, Chlorpyrifos-oxon still facilitates the formation of cross-linked trimers. This compound enhances the cross-linking of tubulin monomers through isopeptide bonds, resulting in the formation of multimers[2]. In the context of cultured PC12 cells, exposure to Chlorpyrifos at a concentration 10 times lower than that required to inhibit acetylcholinesterase (AChE) activity (3.0 μM) adversely affects neurite outgrowth. Conversely, Chlorpyrifos-oxon exhibits its inhibitory effect on neurite extension at an even lower concentration of 1.0 nM[3]. |
| In vivo | Chlorpyrifos-oxon (CPO) undergoes rapid detoxification in human liver microsomes through CYP-dependent deethylation and dearylation, as well as glutathione-S-transferase activity. Additionally, it is efficiently degraded or scavenged by liver enzymes, including A-esterases like paraoxonase 1 (PON 1) and B-esterases such as carboxylesterase and butyrylcholinesterase (BChE). Moreover, when wild-type mice are treated with Chlorpyrifos-oxon (3 mg/kg, ip; once), it significantly affects microtubule integrity, reducing their size to approximately 60% compared to those in control mice, indicating altered amino acid covalency and compromised microtubule structure, which suggests a disruption of their function[1][4]. |
| Molecular Weight | 334.52 |
| Formula | C9H11Cl3NO4P |
| Cas No. | 5598-15-2 |
| Smiles | O=P(OC1=NC(Cl)=C(Cl)C=C1Cl)(OCC)OCC |
| Storage | Powder: -20°C for 3 years | In solvent: -80°C for 1 year | Shipping with blue ice/Shipping at ambient temperature. |
Dissolve 2 mg of the compound in 100 μL DMSO![]() to obtain a stock solution at a concentration of 20 mg/mL . If the required concentration exceeds the compound's known solubility, please contact us for technical support before proceeding.
to obtain a stock solution at a concentration of 20 mg/mL . If the required concentration exceeds the compound's known solubility, please contact us for technical support before proceeding.
1) Add 100 μL of the DMSO![]() stock solution to 400 μL PEG300
stock solution to 400 μL PEG300![]() and mix thoroughly until the solution becomes clear.
and mix thoroughly until the solution becomes clear.
2) Add 50 μL Tween 80 and mix well until fully clarified.
3) Add 450 μL Saline,PBS or ddH2O![]() and mix thoroughly until a homogeneous solution is obtained.
and mix thoroughly until a homogeneous solution is obtained.
| Size | Quantity | Unit Price | Amount | Operation |
|---|

Copyright © 2015-2026 TargetMol Chemicals Inc. All Rights Reserved.