 Your shopping cart is currently empty
Your shopping cart is currently empty

BMS 195614 (BMS614) is a selective RARα antagonist. BMS 195614 can bind to the RARα subunit.
| Pack Size | Price | USA Warehouse | Global Warehouse | Quantity |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 mg | $181 | - | In Stock | |
| 5 mg | $418 | - | In Stock | |
| 10 mg | $619 | - | In Stock | |
| 25 mg | $988 | - | In Stock | |
| 50 mg | $1,330 | - | In Stock | |
| 100 mg | $1,780 | - | In Stock | |
| 500 mg | $3,580 | - | In Stock |
| Description | BMS 195614 (BMS614) is a selective RARα antagonist. BMS 195614 can bind to the RARα subunit. |
| In vitro | BMS 195614 reversed the induction effect of selective RARα agonists, AM580, AM80 and BMS 194753 on differentiation of the acute promyelocytic leukemia cell lines, NB4 and HL60 [1]. Treatment with retinoic acid (RA) (1 uM) for 72 hrs significantly reduced T47D breast cancer cells migration. But RA in combination with BMS 195614 did not affect the cell movement [2]. In cells of a bovine stromal-vascular fraction from intramuscular fat, BMS 195614 significantly diminished the anti-adipogenic effect of ATRA [3]. |
| In vivo | BMS 195614 displayed poor in vivo activity in mice when administered orally. Treatment with BMS 195614 at oral doses for 1 month showed no inhibition to spermatogenesis [4]. Oral administration of BMS 195614 did not suppress spermatogenesis in mice [5]. |
| Synonyms | BMS614, 182135-66-6 |
| Molecular Weight | 448.51 |
| Formula | C29H24N2O3 |
| Cas No. | 253310-42-8 |
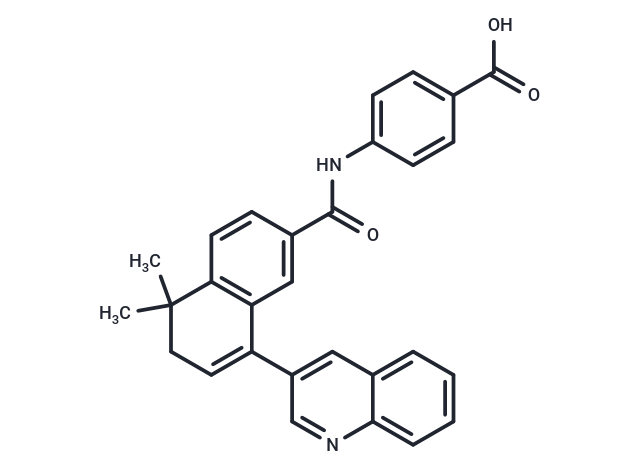
| Smiles | CC1(CC=C(C2=C1C=CC(=C2)C(=O)NC3=CC=C(C=C3)C(=O)O)C4=CC5=CC=CC=C5N=C4)C |
| Relative Density. | 1.31g/cm3 |
| Storage | Powder: -20°C for 3 years | In solvent: -80°C for 1 year | Shipping with blue ice/Shipping at ambient temperature. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Solubility Information | DMSO: 10.1 mg/mL (22.52 mM), Sonication is recommended. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
Solution Preparation Table | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
DMSO
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Dissolve 2 mg of the compound in 100 μL DMSO![]() to obtain a stock solution at a concentration of 20 mg/mL . If the required concentration exceeds the compound's known solubility, please contact us for technical support before proceeding.
to obtain a stock solution at a concentration of 20 mg/mL . If the required concentration exceeds the compound's known solubility, please contact us for technical support before proceeding.
1) Add 100 μL of the DMSO![]() stock solution to 400 μL PEG300
stock solution to 400 μL PEG300![]() and mix thoroughly until the solution becomes clear.
and mix thoroughly until the solution becomes clear.
2) Add 50 μL Tween 80 and mix well until fully clarified.
3) Add 450 μL Saline,PBS or ddH2O![]() and mix thoroughly until a homogeneous solution is obtained.
and mix thoroughly until a homogeneous solution is obtained.
| Size | Quantity | Unit Price | Amount | Operation |
|---|

Copyright © 2015-2026 TargetMol Chemicals Inc. All Rights Reserved.