 Your shopping cart is currently empty
Your shopping cart is currently empty

NBD-Cl (NBD chloride) is a nonfluorescent compound that becomes highly fluorescent after reaction with amino or thiol groups.
| Pack Size | Price | USA Warehouse | Global Warehouse | Quantity |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 g | $35 | - | In Stock | |
| 1 mL x 10 mM (in DMSO) | $29 | In Stock | In Stock |

| Description | NBD-Cl (NBD chloride) is a nonfluorescent compound that becomes highly fluorescent after reaction with amino or thiol groups. |
| Cell Research | 1. Protein labeling Experimental steps: 1. Prepare NBD-Cl solution: Dissolve NBD-Cl in an appropriate organic solvent, such as dimethylsulfide (DMSO), and prepare a stock solution with a concentration of usually 1-10 mM. 2. Reaction with protein: Mix the NBD-Cl solution with a protein sample containing free thiol or amino groups. The reaction is usually carried out at room temperature or slightly alkaline to facilitate the reaction with the thiol group. 3. Incubation: The reaction incubation time is usually 30 minutes to 1 hour to ensure the reaction is complete. 4. Purification: After the reaction is completed, the unreacted NBD-Cl can be removed by dialysis or filtration to ensure that only the labeled protein is left. 5. Fluorescence measurement: Fluorescence emission is measured using a fluorescence spectrophotometer, usually with excitation wavelength of 460 nm and emission wavelength of approximately 530 nm to confirm the labeling efficiency. 2. Quantification of thiol groups Experimental steps: 1. Prepare NBD-Cl solution: Dissolve NBD-Cl in DMSO or other appropriate solvent to prepare a stock solution. 2. Sample Preparation: Add NBD-Cl to a biological sample or buffer containing free thiol. The concentration of NBD-Cl should be optimized to ensure complete reaction with the thiol group. 3. Incubation: The reaction incubation time is usually 10-30 minutes, allowing the thiol to react with NBD-Cl. 4. Fluorescence measurement: Use a fluorescence meter to measure the emission spectrum, the emission wavelength is usually 530 nm and the excitation wavelength is 460 nm. The fluorescence intensity is proportional to the number of thiol groups in the sample. III. Amino detection Experimental steps: 1. Prepare NBD-Cl solution: Dissolve NBD-Cl in DMSO or other appropriate solvent to prepare a stock solution. 2. Sample preparation: Add NBD-Cl solution to a sample containing free amino groups (such as small molecules or peptides). 3. Incubation: The reaction is usually carried out at room temperature and the incubation time is 15-30 minutes. 4. Fluorescence measurement: Use a fluorescence meter to measure the emission spectrum, which is usually 530 nm and excitation wavelength is 460 nm, to detect the labeling of amino groups. The above information is based on published literature. Experimental procedures should be appropriately modified to meet specific research demands. |
| Synonyms | NBD chloride |
| Molecular Weight | 199.55 |
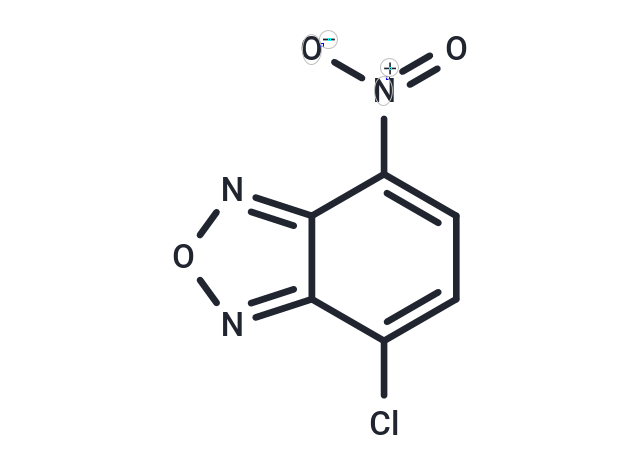
| Formula | C6H2ClN3O3 |
| Cas No. | 10199-89-0 |
| Smiles | [O-][N+](=O)c1ccc(Cl)c2nonc12 |
| Relative Density. | 2.0589 g/cm3 (Estimated) |
| Storage | keep away from direct sunlight,store under nitrogen | Powder: -20°C for 3 years | In solvent: -80°C for 1 year | Shipping with blue ice/Shipping at ambient temperature. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Solubility Information | DMSO: 100 mg/mL (501.13 mM), Sonication is recommended. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| In Vivo Formulation | 10% DMSO+90% Saline: 3.3 mg/mL (16.54 mM), Sonication is recommended. Please add the solvents sequentially, clarifying the solution as much as possible before adding the next one. Dissolve by heating and/or sonication if necessary. Working solution is recommended to be prepared and used immediately. The formulation provided above is for reference purposes only. In vivo formulations may vary and should be modified based on specific experimental conditions. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Solution Preparation Table | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
DMSO
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Dissolve 2 mg of the compound in 100 μL DMSO![]() to obtain a stock solution at a concentration of 20 mg/mL . If the required concentration exceeds the compound's known solubility, please contact us for technical support before proceeding.
to obtain a stock solution at a concentration of 20 mg/mL . If the required concentration exceeds the compound's known solubility, please contact us for technical support before proceeding.
1) Add 100 μL of the DMSO![]() stock solution to 400 μL PEG300
stock solution to 400 μL PEG300![]() and mix thoroughly until the solution becomes clear.
and mix thoroughly until the solution becomes clear.
2) Add 50 μL Tween 80 and mix well until fully clarified.
3) Add 450 μL Saline,PBS or ddH2O![]() and mix thoroughly until a homogeneous solution is obtained.
and mix thoroughly until a homogeneous solution is obtained.
| Size | Quantity | Unit Price | Amount | Operation |
|---|

Copyright © 2015-2026 TargetMol Chemicals Inc. All Rights Reserved.