 Your shopping cart is currently empty
Your shopping cart is currently empty

Naph-EA-mal (Thiol-green 1) is a highly efficient and rapid-response thiol fluorescence probe specifically designed for protein labeling and bioimaging applications. This compound provides ultrafast turn-on fluorescence upon interacting with thiols, allowing for thiol detection in live cells, protein thiol labeling, quantification of total thiol concentrations in cell lysates, and determination of reversible protein thiol oxidation in fixed cells. It has an excitation wavelength of 488 nM and an emission wavelength of 540 nM.

| Description | Naph-EA-mal (Thiol-green 1) is a highly efficient and rapid-response thiol fluorescence probe specifically designed for protein labeling and bioimaging applications. This compound provides ultrafast turn-on fluorescence upon interacting with thiols, allowing for thiol detection in live cells, protein thiol labeling, quantification of total thiol concentrations in cell lysates, and determination of reversible protein thiol oxidation in fixed cells. It has an excitation wavelength of 488 nM and an emission wavelength of 540 nM. |
| In vitro | In a study on imaging thiols within living cells, Hep G2 cells were exposed to Naph-EA-mal (Thiol-green 1) at a concentration of 1 μM for 5 minutes, resulting in strong green fluorescence. However, preincubation of cells with NEM (a thiol-blocking agent; 100 μM) led to notably weaker fluorescence, indicating the compound's sensitivity to intracellular thiol levels[1]. In separate experiments aimed at monitoring thiol-disulfide balance in fixed cells, Hep G2 cells displayed intense fluorescence upon treatment with Naph-EA-mal (10 μM), attributable to the high incidence of reduced thiols. This fluorescence significantly diminished following diamide exposure, which promotes oxidation. Subsequently, cells oxidized with diamide (200 μM for 30 minutes) were fixed with 70% ethanol, treated with NEM (100 μM) to block remaining free thiols, and then exposed to TCEP (5 mM) before being reintroduced to Naph-EA-mal (10 μM). This protocol reinstated the green fluorescent signal, underscoring the methodology's utility in assessing thiol-disulfide dynamics within cells[1]. |
| Synonyms | Thiol-green 1, Naph-EA-mal |
| Molecular Weight | 391.427 |
| Formula | C22H21N3O4 |
| Cas No. | 210292-65-2 |
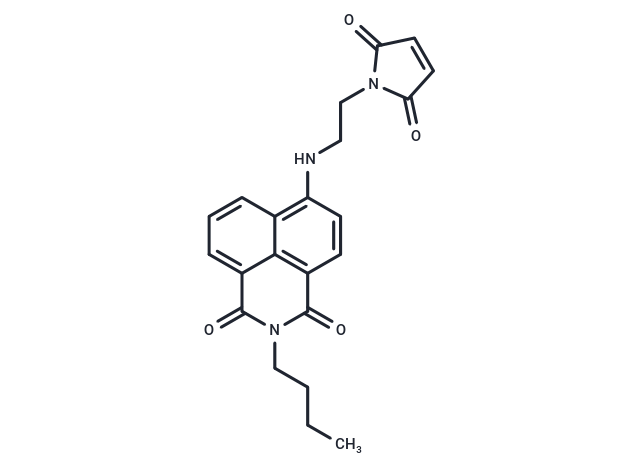
| Smiles | CCCCN1C(=O)c2cccc3c(NCCN4C(=O)C=CC4=O)ccc(C1=O)c23 |
| Storage | keep away from direct sunlight | Powder: -20°C for 3 years | In solvent: -80°C for 1 year | Shipping with blue ice/Shipping at ambient temperature. |
Dissolve 2 mg of the compound in 100 μL DMSO![]() to obtain a stock solution at a concentration of 20 mg/mL . If the required concentration exceeds the compound's known solubility, please contact us for technical support before proceeding.
to obtain a stock solution at a concentration of 20 mg/mL . If the required concentration exceeds the compound's known solubility, please contact us for technical support before proceeding.
1) Add 100 μL of the DMSO![]() stock solution to 400 μL PEG300
stock solution to 400 μL PEG300![]() and mix thoroughly until the solution becomes clear.
and mix thoroughly until the solution becomes clear.
2) Add 50 μL Tween 80 and mix well until fully clarified.
3) Add 450 μL Saline,PBS or ddH2O![]() and mix thoroughly until a homogeneous solution is obtained.
and mix thoroughly until a homogeneous solution is obtained.
| Size | Quantity | Unit Price | Amount | Operation |
|---|

Copyright © 2015-2026 TargetMol Chemicals Inc. All Rights Reserved.