 Your shopping cart is currently empty
Your shopping cart is currently empty

CP-610431 is a reversible, ATP-uncompetitive inhibitor of acetyl-CoA carboxylase (ACC) that exhibits isozyme nonselectivity, inhibiting both ACC1 and ACC2 with IC50 values of approximately 50 nM. CP-610431 offers potential application in metabolic syndrome research.
| Pack Size | Price | USA Warehouse | Global Warehouse | Quantity |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 5 mg | $970 | Inquiry | Inquiry |
| Description | CP-610431 is a reversible, ATP-uncompetitive inhibitor of acetyl-CoA carboxylase (ACC) that exhibits isozyme nonselectivity, inhibiting both ACC1 and ACC2 with IC50 values of approximately 50 nM. CP-610431 offers potential application in metabolic syndrome research. |
| In vitro | CP-610431, the active R-enantiomer of CP-497485, demonstrates greater potency than its racemate, CP-497485, and significantly surpasses the S-enantiomer, CP-610432, in inhibiting rat ACC1 (IC 50=35.7 nM) and ACC2 (IC 50=55 nM), with the latter showing negligible inhibition up to 3 μM. It notably inhibits fatty acid and triglyceride synthesis, along with TG and apolipoprotein B secretion in HepG2 cells, achieving EC 50 values of 1.6, 1.8, 3.0, and 5.7 μM, respectively, without impacting cholesterol synthesis or apolipoprotein CIII secretion. Consistently, CP-610431 inhibits ACC activity in the liver and skeletal muscle of rats, mice, and cynomolgus macaques with comparable effectiveness. Furthermore, it efficiently inhibits fatty acid and TG synthesis in mouse primary hepatocytes, with IC 50 values of 0.11 and 1.2 μM respectively, and TG secretion with an IC 50 of 10 μM. A Cell Viability Assay on HepG2 cells, treated with concentrations of 0.1, 1, and 10 μM for 24 hours, revealed dose-dependent inhibition of fatty acid and TG synthesis, as well as TG and apoB secretion, confirming its impactful biochemical activities. |
| In vivo | CP-610431 effectively inhibits fatty acid synthesis in both CD1 and ob/ob mice within one hour of administration, demonstrating ED50 values of 22 and 4 mg/kg, respectively[1]. In CD1 mice, doses of 30 and 100 mg/kg reduced hepatic fatty acid synthesis by 64±12% and 77±4% in fasting conditions, while in non-fasting conditions, doses of 10, 30, and 100 mg/kg achieved inhibition rates of 18%, 51%, and 75%, respectively. These results were achieved through intraperitoneal administration, highlighting CP-610431's potent effect on fatty acid synthesis suppression across different physiological states. |
| Molecular Weight | 471.645 |
| Formula | C30H37N3O2 |
| Cas No. | 591778-83-5 |
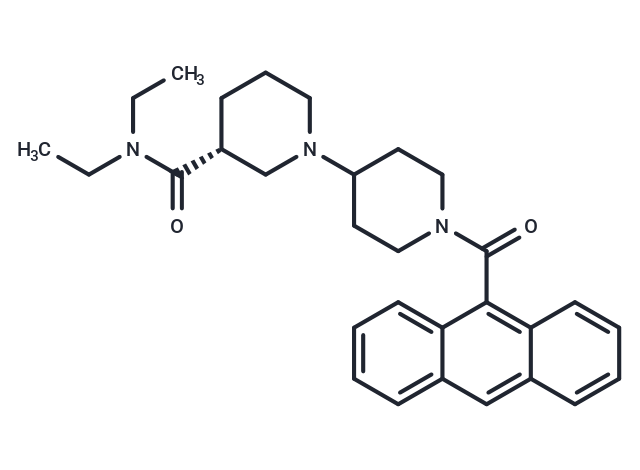
| Smiles | CCN(CC)C(=O)[C@@H]1CCCN(C1)C1CCN(CC1)C(=O)c1c2ccccc2cc2ccccc12 |
| Relative Density. | no data available |
| Storage | Powder: -20°C for 3 years | In solvent: -80°C for 1 year | Shipping with blue ice/Shipping at ambient temperature. |
Dissolve 2 mg of the compound in 100 μL DMSO![]() to obtain a stock solution at a concentration of 20 mg/mL . If the required concentration exceeds the compound's known solubility, please contact us for technical support before proceeding.
to obtain a stock solution at a concentration of 20 mg/mL . If the required concentration exceeds the compound's known solubility, please contact us for technical support before proceeding.
1) Add 100 μL of the DMSO![]() stock solution to 400 μL PEG300
stock solution to 400 μL PEG300![]() and mix thoroughly until the solution becomes clear.
and mix thoroughly until the solution becomes clear.
2) Add 50 μL Tween 80 and mix well until fully clarified.
3) Add 450 μL Saline,PBS or ddH2O![]() and mix thoroughly until a homogeneous solution is obtained.
and mix thoroughly until a homogeneous solution is obtained.
| Size | Quantity | Unit Price | Amount | Operation |
|---|

Copyright © 2015-2026 TargetMol Chemicals Inc. All Rights Reserved.