 Your shopping cart is currently empty
Your shopping cart is currently empty

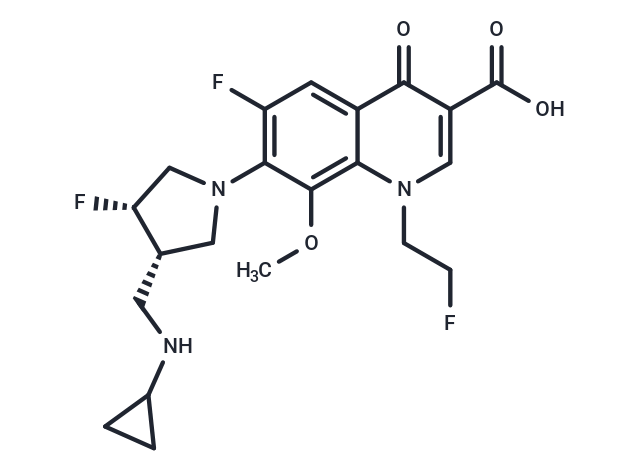
Lascufloxacin, a potent and orally active fluoroquinolone antibacterial agent, holds potential for the treatment of various infectious diseases, including lower respiratory tract infections. It effectively inhibits infections caused by a wide range of pathogens, encompassing those resistant to quinolones.
| Pack Size | Price | USA Warehouse | Global Warehouse | Quantity |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 25 mg | $1,670 | 6-8 weeks | 6-8 weeks | |
| 50 mg | $2,180 | 6-8 weeks | 6-8 weeks | |
| 100 mg | $2,800 | 6-8 weeks | 6-8 weeks |
| Description | Lascufloxacin, a potent and orally active fluoroquinolone antibacterial agent, holds potential for the treatment of various infectious diseases, including lower respiratory tract infections. It effectively inhibits infections caused by a wide range of pathogens, encompassing those resistant to quinolones. |
| In vitro | Lascufloxacin demonstrates pronounced efficacy against both Gram-positive and Gram-negative bacteria, including macrolide-resistant M. pneumoniae, with a minimum inhibitory concentration for 90% of organisms (MIC90) as low as 0.12 μg/mL. It exhibits a broad spectrum of activity, with MIC values ranging from 0.008 to 0.015 μg/mL for S. aureus strains and maintaining effectiveness against various S. aureus mutant strains at 2 μg/mL, albeit showing some level of incomplete cross-resistance. Its potency surpasses that of other quinolones against first- and second-step mutants of S. pneumoniae, with MIC values for double mutants between 0.25 and 0.5 μg/mL. In the realm of Gram-negative bacteria, Lascufloxacin is active against Moraxella catarrhalis and both ampicillin-susceptible and -resistant Haemophilus influenzae strains, maintaining an MIC90 of 0.06 μg/mL. Additionally, it exhibits notable MIC90 values against Enterobacter spp., Klebsiella pneumoniae, and Acinetobacter spp. at 0.25 μg/mL, 0.25 μg/mL, and 0.5 μg/mL respectively, and displays efficacy against E. coli and P. aeruginosa with MIC90s of 0.25 μg/mL and 4 μg/mL, respectively. The MIC50 and MIC90 values against M. pneumoniae are 0.12 μg/mL and 0.25 μg/mL, showcasing its significant antibacterial activity across a range of pathogens[1]. |
| In vivo | A pharmacodynamic study employing a mouse thigh infection model demonstrates that to achieve bacteriostasis, or a 1-log or 2-log reduction in S. pneumoniae colony-forming units (CFU), the necessary ratios of the free area under the concentration-time curve (fAUC) to the minimum inhibitory concentration (MIC) in plasma are 10, 16, and 28, respectively. Lascufloxacin effectively eliminates bacterial presence in this mouse model when the plasma concentration-time curve (AUC) is replicated with a daily dosage of 75 mg [q.d.]) [1]. |
| Synonyms | KRP-AM1977X |
| Molecular Weight | 439.43 |
| Formula | C21H24F3N3O4 |
| Cas No. | 848416-07-9 |
| Smiles | O(C)C1=C2C(C(=O)C(C(O)=O)=CN2CCF)=CC(F)=C1N3C[C@H](CNC4CC4)[C@H](F)C3 |
| Relative Density. | 1.44 g/cm3 (Predicted) |
| Storage | In solvent: -80°C for 1 year | Shipping with blue ice/Shipping at ambient temperature. |
Dissolve 2 mg of the compound in 100 μL DMSO![]() to obtain a stock solution at a concentration of 20 mg/mL . If the required concentration exceeds the compound's known solubility, please contact us for technical support before proceeding.
to obtain a stock solution at a concentration of 20 mg/mL . If the required concentration exceeds the compound's known solubility, please contact us for technical support before proceeding.
1) Add 100 μL of the DMSO![]() stock solution to 400 μL PEG300
stock solution to 400 μL PEG300![]() and mix thoroughly until the solution becomes clear.
and mix thoroughly until the solution becomes clear.
2) Add 50 μL Tween 80 and mix well until fully clarified.
3) Add 450 μL Saline,PBS or ddH2O![]() and mix thoroughly until a homogeneous solution is obtained.
and mix thoroughly until a homogeneous solution is obtained.
| Size | Quantity | Unit Price | Amount | Operation |
|---|

Copyright © 2015-2026 TargetMol Chemicals Inc. All Rights Reserved.