 Your shopping cart is currently empty
Your shopping cart is currently empty

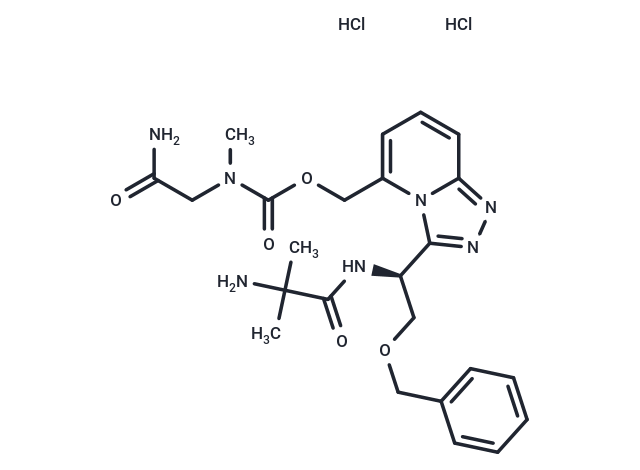
BMS-604992 (EX-1314) dihydrochloride is a selective, orally active small-molecule agonist of the growth hormone secretagogue receptor (GHSR). It exhibits high-affinity binding (k i = 2.3 nM) and potent functional activity (EC 50 = 0.4 nM). Additionally, BMS-604992 dihydrochloride stimulates food intake in rodents.
| Pack Size | Price | USA Warehouse | Global Warehouse | Quantity |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 5 mg | $970 | Inquiry | Inquiry |
| Description | BMS-604992 (EX-1314) dihydrochloride is a selective, orally active small-molecule agonist of the growth hormone secretagogue receptor (GHSR). It exhibits high-affinity binding (k i = 2.3 nM) and potent functional activity (EC 50 = 0.4 nM). Additionally, BMS-604992 dihydrochloride stimulates food intake in rodents. |
| Targets&IC50 | GHSR:0.4 nM (EC50), GHSR:Ki: 2.3 nM |
| In vitro | BMS-604992 demonstrates high-affinity binding (K i =2.3 nM) and potent functional activity (EC 50 =0.4 nM) at the ghrelin receptor[1]. |
| In vivo | BMS-604992 demonstrates diverse pharmacological activities across different dosages and administration methods in animal studies. At a dosage of 500 μg/kg administered intraperitoneally (i.p.) for 5 minutes, it significantly enhances gastric emptying in C57BL/6 mice compared to those receiving a vehicle[1]. When given orally (p.o.) at dosages ranging from 1 to 1000 mg/kg for 1 hour, BMS-604992 shows a linear relationship between dose and plasma concentration at the 1-hour mark, along with a dose-dependent increase in food consumption in C57BL/6 mice, identifying a minimum effective dose of approximately 10 mg/kg[1]. A specific 300 mg/kg oral dosage results in a notable difference in effect within just 5 minutes in SD rats[1]. Lastly, an i.p. administration of 500 μg/kg over 4 hours leads to a twofold increase in food intake in male GhrR KO and WT mice compared to vehicle-treated controls[1], highlighting its potential impact on feeding behavior and gastric processes. |
| Synonyms | EX-1314 dihydrochloride, BMS-604992 dihydrochloride |
| Molecular Weight | 570.47 |
| Formula | C24H33Cl2N7O5 |
| Cas No. | 1469750-46-6 |
| Smiles | Cl.Cl.CN(CC(N)=O)C(=O)OCc1cccc2nnc([C@@H](COCc3ccccc3)NC(=O)C(C)(C)N)n12 |
| Storage | Powder: -20°C for 3 years | In solvent: -80°C for 1 year | Shipping with blue ice/Shipping at ambient temperature. |
Dissolve 2 mg of the compound in 100 μL DMSO![]() to obtain a stock solution at a concentration of 20 mg/mL . If the required concentration exceeds the compound's known solubility, please contact us for technical support before proceeding.
to obtain a stock solution at a concentration of 20 mg/mL . If the required concentration exceeds the compound's known solubility, please contact us for technical support before proceeding.
1) Add 100 μL of the DMSO![]() stock solution to 400 μL PEG300
stock solution to 400 μL PEG300![]() and mix thoroughly until the solution becomes clear.
and mix thoroughly until the solution becomes clear.
2) Add 50 μL Tween 80 and mix well until fully clarified.
3) Add 450 μL Saline,PBS or ddH2O![]() and mix thoroughly until a homogeneous solution is obtained.
and mix thoroughly until a homogeneous solution is obtained.
| Size | Quantity | Unit Price | Amount | Operation |
|---|

Copyright © 2015-2026 TargetMol Chemicals Inc. All Rights Reserved.