Powder: -20°C for 3 years | In solvent: -80°C for 1 year


Rufloxacin is a drug that belongs to the class of fluoroquinolones, which act mainly as specific inhibitors of bacterial Topoisomerase II. These drugs involve in various diseases including cutaneous reactions, aging, etc.
| Pack Size | Availability | Price/USD | Quantity |
|---|---|---|---|
| 25 mg | 8-10 weeks | $ 1,820.00 | |
| 50 mg | 8-10 weeks | $ 2,380.00 | |
| 100 mg | 8-10 weeks | $ 3,100.00 |
| Description | Rufloxacin is a drug that belongs to the class of fluoroquinolones, which act mainly as specific inhibitors of bacterial Topoisomerase II. These drugs involve in various diseases including cutaneous reactions, aging, etc. |
| Synonyms | MF 934 |
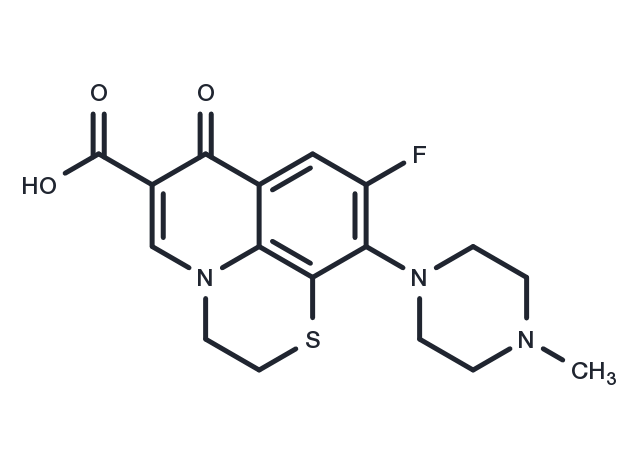
| Molecular Weight | 363.41 |
| Formula | C17H18FN3O3S |
| CAS No. | 101363-10-4 |
Powder: -20°C for 3 years | In solvent: -80°C for 1 year
DMSO: Soluble
You can also refer to dose conversion for different animals. More
bottom
Please see Inhibitor Handling Instructions for more frequently ask questions. Topics include: how to prepare stock solutions, how to store products, and cautions on cell-based assays & animal experiments, etc.
Rufloxacin 101363-10-4 MF-934 MF934 MF 934 inhibitor inhibit
