Shopping Cart
- Remove All
 Your shopping cart is currently empty
Your shopping cart is currently empty

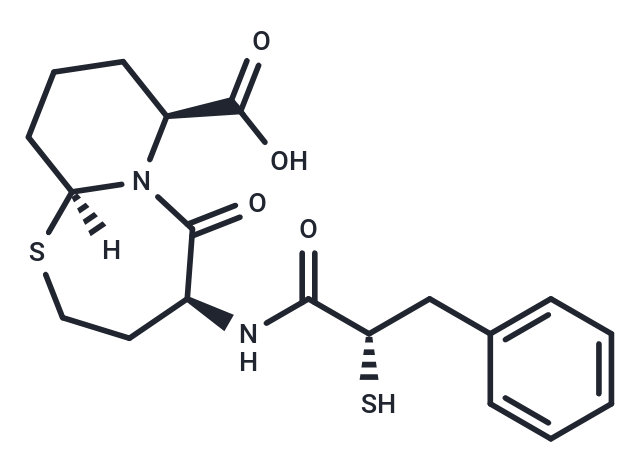
Omapatrilat is a metalloprotease ACE and NEP dual inhibitor (Ki: 0.64 and 0.45 nM, respectively).
| Pack Size | Price | Availability | Quantity |
|---|---|---|---|
| 2 mg | $61 | 5 days | |
| 100 mg | $996 | 6-8 weeks |
| Description | Omapatrilat is a metalloprotease ACE and NEP dual inhibitor (Ki: 0.64 and 0.45 nM, respectively). |
| Targets&IC50 | ACE:0.64 nM(ki), NEP:(ki)0.45 nM |
| In vitro | In vitro autoradiography using the specific NEP inhibitor radioligand 125I-RB104 and the specific ACE inhibitor radioligand 125I-MK351A display omapatril at (10 mg/kg) induces rapid and effective inhibition of renal NEP and ACE, respectively, for 24 h. Omapatrilat displays high potency for NEP, NEP2 and ACE, moderate strong activity against APP, but low activity against ECE1 (Ki=0.45, 25, 0.64, 250 nM) [1][4]. |
| In vivo | Omapatrilat is widely used in experimental protocols related to hypertension and heart failure. Omapatrilat reduces mean arterial pressure (MAP) approximately 40 mmHg below baseline from 10 to 24 h. Omapatrilat shows excellent blood pressure lowering in a variety of animal models characterized by various levels of plasma renin activity and significantly potentiates urinary sodium, ANP, and cGMP excretion in a cynomolgus monkey assay. Omapatrilat (p.o.; 100 μM/kg; once daily) causes a 38 mmHg decrease in systolic blood pressure at day three as compared to the vehicle [2]. Omapatrilat(Chronic oral administration) decreases aortic leakiness and atheroma formation with enhanced endothelial independent vasorelaxation to ANP[3]. Omapatrilat leads to significant inhibition of plasma ACE and increased plasma renin activity in rats[4]. |
| Alias | BMS-186716 |
| Molecular Weight | 408.53 |
| Formula | C19H24N2O4S2 |
| Cas No. | 167305-00-2 |
| Relative Density. | 1.31g/cm3 |
| Storage | Powder: -20°C for 3 years | In solvent: -80°C for 1 year | Shipping with blue ice. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Solubility Information | DMSO: 31 mg/mL (75.88 mM), Sonication is recommended. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Solution Preparation Table | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
DMSO
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||

Copyright © 2015-2025 TargetMol Chemicals Inc. All Rights Reserved.