Shopping Cart
Remove All Your shopping cart is currently empty
Your shopping cart is currently empty
HEPES Sodium salt is a nonvolatile zwitterionic chemical buffering agent. HEPES Sodium salt is broadly applied in cell culture. HEPES Sodium salt is effective at pH 6.8 to 8.2. HEPES Sodium salt also induces of lysosome biogenesis.
| Pack Size | Price | USA Warehouse | Global Warehouse | Quantity |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 g | $29 | - | In Stock |
| Description | HEPES Sodium salt is a nonvolatile zwitterionic chemical buffering agent. HEPES Sodium salt is broadly applied in cell culture. HEPES Sodium salt is effective at pH 6.8 to 8.2. HEPES Sodium salt also induces of lysosome biogenesis. |
| In vitro | HEPES Sodium salt maintains superhydrophilicity of titanium for at least 3 months, leading to a continuous retention of bioactivity and osteoconductivity[1]. In cultured RAW264.7 cells, HEPES Sodium salt drives lysosome biogenesis, affects MiT/TFE cytoplasmic-nuclear distribution, disrupts global cellular transcriptional profiles, leading to the activation of a MiT/TFE-dependent lysosomal-autophagic gene network[3]. |
| Molecular Weight | 260.29 |
| Formula | C8H17N2NaO4S |
| Cas No. | 75277-39-3 |
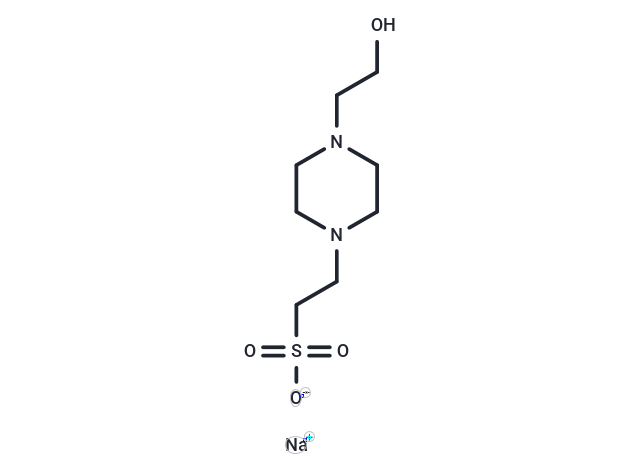
| Smiles | C1CN(CCN1CCO)CCS(=O)(=O)[O-].[Na+] |
| Relative Density. | 1.504 g/cm3 at 20℃ |
| Color | White |
| Appearance | Solid |
| Storage | Powder: -20°C for 3 years | In solvent: -80°C for 1 year | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Solubility Information | H2O: Soluble DMSO: 50 mg/mL (192.09 mM), Sonication is recommended. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Solution Preparation Table | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
DMSO
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Size | Quantity | Unit Price | Amount | Operation |
|---|

Copyright © 2015-2025 TargetMol Chemicals Inc. All Rights Reserved.