Shopping Cart
Remove All Your shopping cart is currently empty
Your shopping cart is currently empty
Anti-NFKB1 Polyclonal Antibody is a Rabbit antibody targeting NFKB1. Anti-NFKB1 Polyclonal Antibody can be used in IF,IHC-Fr,IHC-P,WB.
| Pack Size | Price | USA Warehouse | Global Warehouse | Quantity |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 50 μL | $221 | 7-10 days | 7-10 days | |
| 100 μL | $374 | 7-10 days | 7-10 days | |
| 200 μL | $527 | 7-10 days | 7-10 days |
| Description | Anti-NFKB1 Polyclonal Antibody is a Rabbit antibody targeting NFKB1. Anti-NFKB1 Polyclonal Antibody can be used in IF,IHC-Fr,IHC-P,WB. |
| Synonyms | Nuclear factor of kappa light polypeptide gene enhancer in B-cells 1, Nuclear factor NF-kappa-B p105 subunit, NFKB1, EBP-1, DNA-binding factor KBF1 |
| Ig Type | IgG |
| Reactivity | Human,Mouse,Rat (predicted:Chicken,Dog,Pig,Cow) |
| Verified Activity | 1. Sample: Lung (Mouse) lysate at 30 μg; Primary: Anti-NFkB p105/p50 (TMAB-01233) at 1:300 dilution; Secondary: HRP conjugated Goat-Anti-rabbit Igg (secondary antibody) at 1: 5000 dilution; Predicted band size: 48/105 kDa Observed band size: 110 kDa 2. Sample: Brain (Mouse) lysate at 30 μg; Primary: Anti-NFkB p105/p50 (TMAB-01233) at 1:300 dilution; Secondary: HRP conjugated Goat-Anti-rabbit Igg (secondary antibody) at 1: 5000 dilution; Predicted band size: 48/105 kDa Observed band size: 50 kD 3. Paraformaldehyde-fixed, paraffin embedded (Mouse brain); Antigen retrieval by boiling in sodium citrate buffer (pH6.0) for 15 min; Block endogenous peroxidase by 3% hydrogen peroxide for 20 min; Blocking buffer (normal goat serum) at 37°C for 30 min; Antibody incubation with (NFkB p50) Polyclonal Antibody, Unconjugated (TMAB-01233) at 1:500 overnight at 4°C, followed by a conjugated secondary for 20 min and DAB staining. 4. Paraformaldehyde-fixed, paraffin embedded (rat brain); Antigen retrieval by boiling in sodium citrate buffer (pH6.0) for 15 min; Block endogenous peroxidase by 3% hydrogen peroxide for 20 min; Blocking buffer (normal goat serum) at 37°C for 30 min; Antibody incubation with (NFkB p105) Polyclonal Antibody, Unconjugated (TMAB-01233) at 1:200 overnight at 4°C, followed by operating according to SP Kit (Rabbit) instructionsand DAB staining. 5. Paraformaldehyde-fixed, paraffin embedded (rat bladder); Antigen retrieval by boiling in sodium citrate buffer (pH6.0) for 15 min; Block endogenous peroxidase by 3% hydrogen peroxide for 20 min; Blocking buffer (normal goat serum) at 37°C for 30 min; Antibody incubation with (NFkB p105) Polyclonal Antibody, Unconjugated (TMAB-01233) at 1:200 overnight at 4°C, followed by operating according to SP Kit (Rabbit) instructionsand DAB staining. 6. Paraformaldehyde-fixed, paraffin embedded (rat uterus); Antigen retrieval by boiling in sodium citrate buffer (pH6.0) for 15 min; Block endogenous peroxidase by 3% hydrogen peroxide for 20 min; Blocking buffer (normal goat serum) at 37°C for 30 min; Antibody incubation with (NFkB p105) Polyclonal Antibody, Unconjugated (TMAB-01233) at 1:200 overnight at 4°C, followed by operating according to SP Kit (Rabbit) instructionsand DAB staining. 7. Sample: Lane 1: Human Raji cell lysates Lane 2: Human MCF-7 cell lysates Lane 3: Human Jurkat cell lysates Primary: Anti-NFKB1 (TMAB-01233) at 1/1000 dilution Secondary: IRDye800CW Goat Anti-Rabbit IgG at 1/20000 dilution Predicted band size: 48/105 kDa Observed band size: 135 kDa  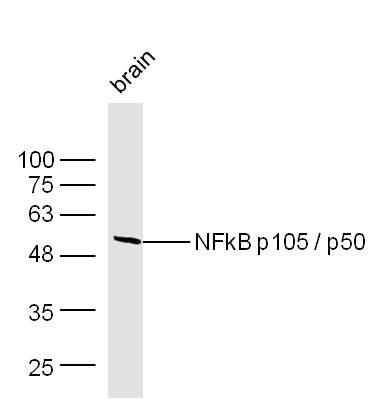 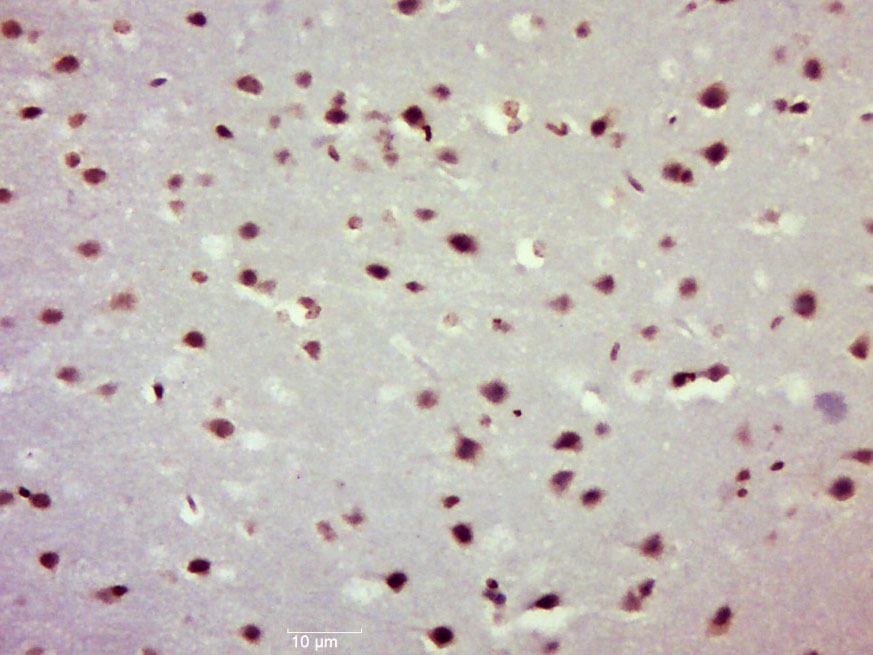 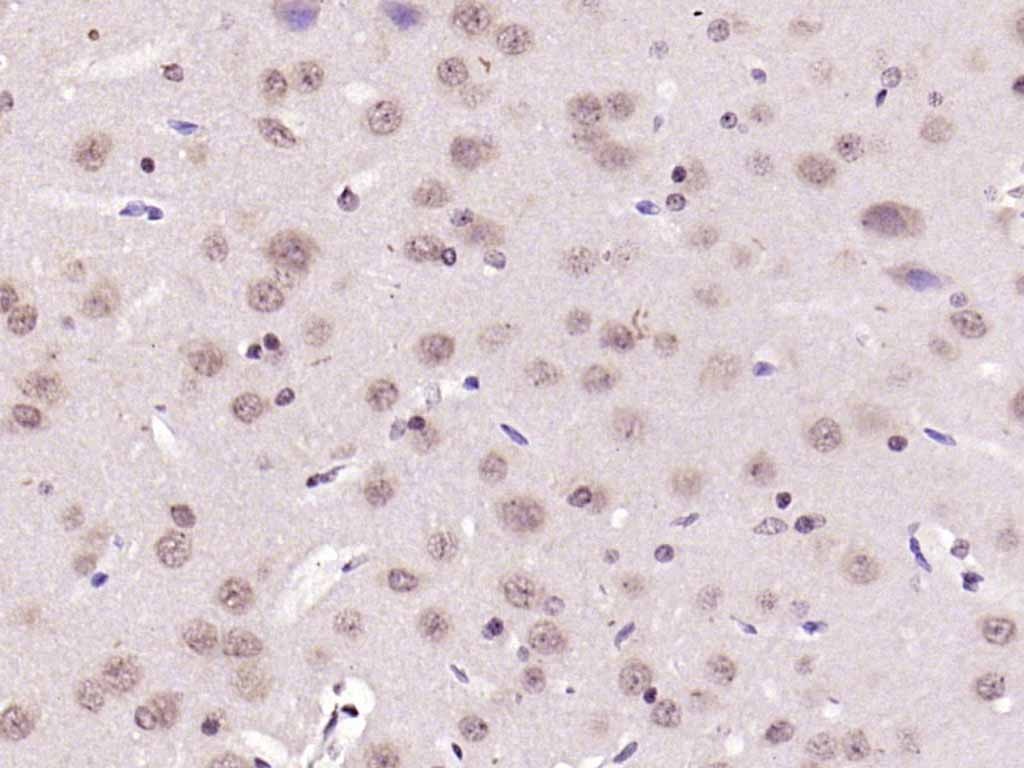 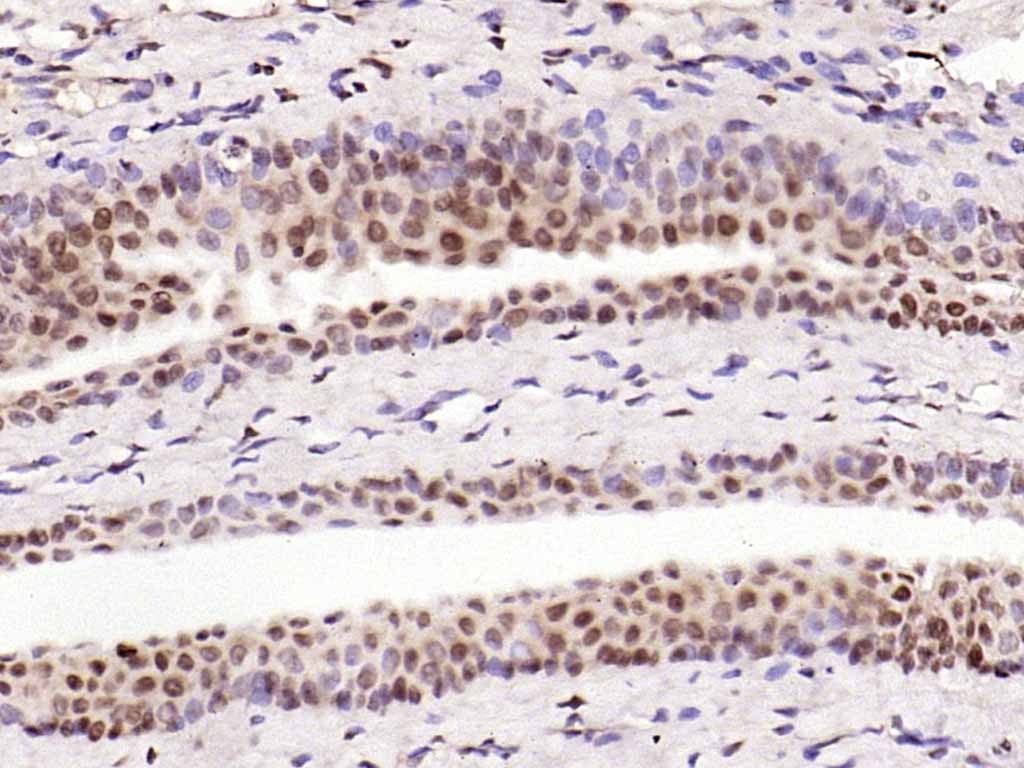 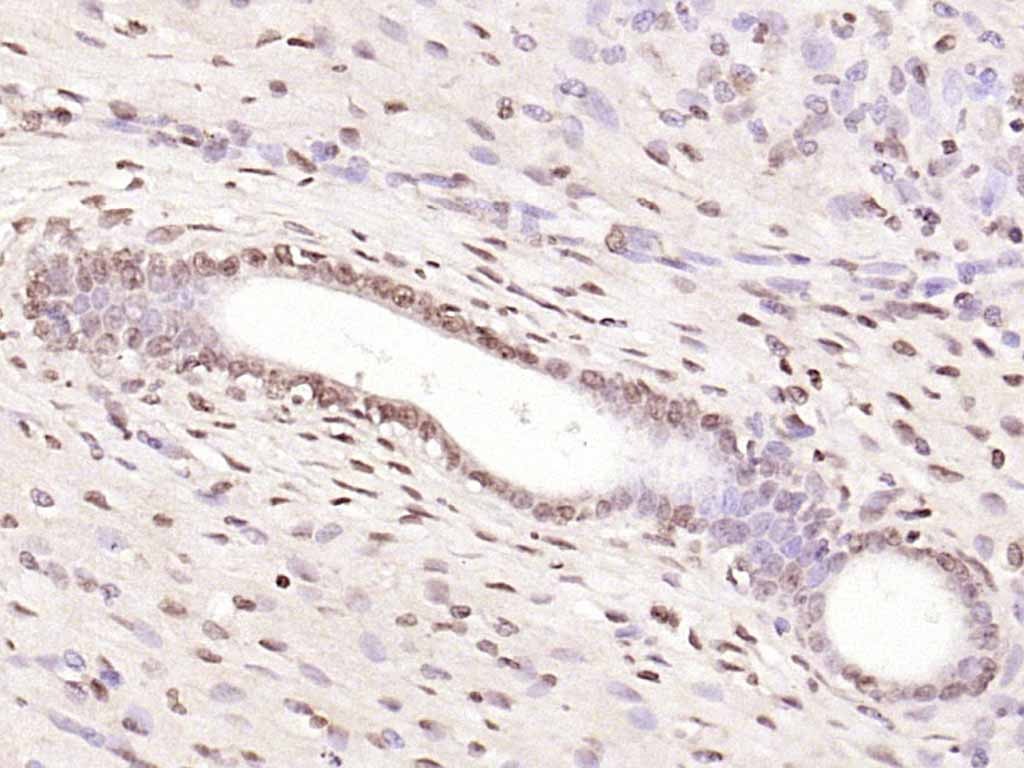 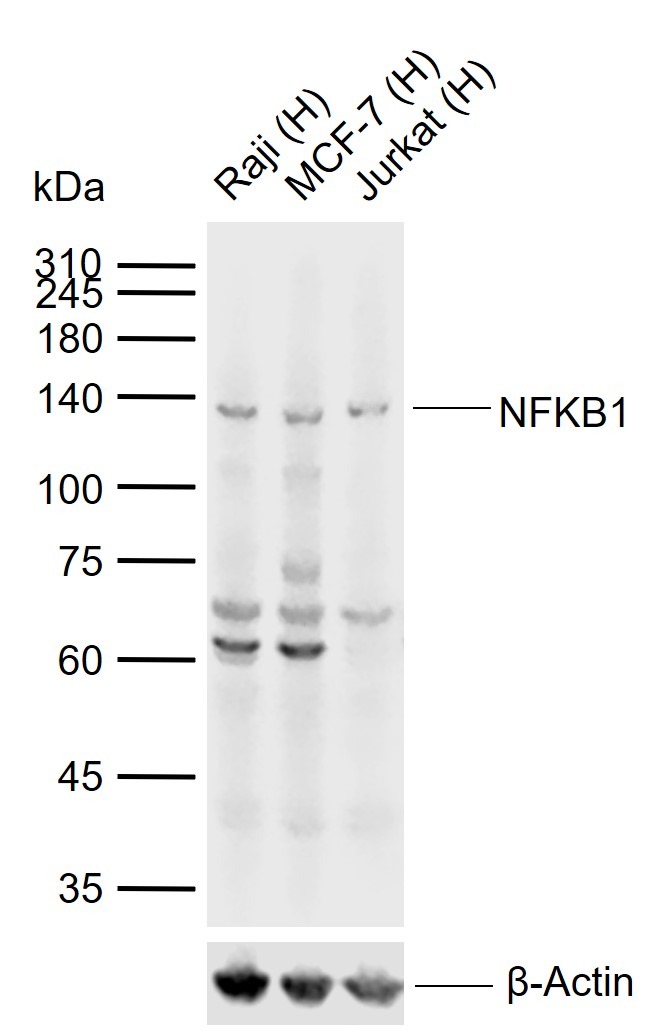 |
| Application | |
| Recommended Dose | WB: 1:500-2000; IHC-P: 1:100-500; IHC-Fr: 1:100-500; IF: 1:100-500 |
| Antibody Type | Polyclonal |
| Host Species | Rabbit |
| Subcellular Localization | Nucleus. Cytoplasm. Note=Nuclear, but also found in the cytoplasm in an inactive form complexed to an inhibitor (I-kappa-B). |
| Construction | Polyclonal Antibody |
| Purification | Protein A purified |
| Appearance | Liquid |
| Formulation | 0.01M TBS (pH7.4) with 1% BSA, 0.02% Proclin300 and 50% Glycerol. |
| Concentration | 1 mg/mL |
| Research Background | This gene encodes a 105 kD protein which can undergo cotranslational processing by the 26S proteasome to produce a 50 kD protein. The 105 kD protein is a Rel protein-specific transcription inhibitor and the 50 kD protein is a DNA binding subunit of the NF-kappa-B (NFKB) protein complex. NFKB is a transcription regulator that is activated by various intra- and extra-cellular stimuli such as cytokines, oxidant-free radicals, ultraviolet irradiation, and bacterial or viral products. Activated NFKB translocates into the nucleus and stimulates the expression of genes involved in a wide variety of biological functions. Inappropriate activation of NFKB has been associated with a number of inflammatory diseases while persistent inhibition of NFKB leads to inappropriate immune cell development or delayed cell growth. Two transcript variants encoding different isoforms have been found for this gene. [provided by RefSeq, Sep 2009]. |
| Immunogen | KLH conjugated synthetic peptide: human Nuclear factor NF-kappa-B p50 subunit |
| Antigen Species | Human |
| Gene Name | NFKB1 |
| Gene ID | |
| Protein Name | Nuclear factor NF-kappa-B p105 subunit |
| Uniprot ID | |
| Biology Area | p50,NFkB pathway,p50,NFkB pathway,Transcription Factors,Macrophage / Inflamm.,NFkB Pathway |
| Function | NF-kappa-B is a pleiotropic transcription factor present in almost all cell types and is the endpoint of a series of signal transduction events that are initiated by a vast array of stimuli related to many biological processes such as inflammation, immunity, differentiation, cell growth, tumorigenesis and apoptosis. NF-kappa-B is a homo- or heterodimeric complex formed by the Rel-like domain-containing proteins RELA/p65, RELB, NFKB1/p105, NFKB1/p50, REL and NFKB2/p52 and the heterodimeric p65-p50 complex appears to be most abundant one. The dimers bind at kappa-B sites in the DNA of their target genes and the individual dimers have distinct preferences for different kappa-B sites that they can bind with distinguishable affinity and specificity. Different dimer combinations act as transcriptional activators or repressors, respectively. NF-kappa-B is controlled by various mechanisms of post-translational modification and subcellular compartmentalization as well as by interactions with other cofactors or corepressors. NF-kappa-B complexes are held in the cytoplasm in an inactive state complexed with members of the NF-kappa-B inhibitor (I-kappa-B) family. In a conventional activation pathway, I-kappa-B is phosphorylated by I-kappa-B kinases (IKKs) in response to different activators, subsequently degraded thus liberating the active NF-kappa-B complex which translocates to the nucleus. NF-kappa-B heterodimeric p65-p50 and RelB-p50 complexes are transcriptional activators. The NF-kappa-B p50-p50 homodimer is a transcriptional repressor, but can act as a transcriptional activator when associated with BCL3. NFKB1 appears to have dual functions such as cytoplasmic retention of attached NF-kappa-B proteins by p105 and generation of p50 by a cotranslational processing. The proteasome-mediated process ensures the production of both p50 and p105 and preserves their independent function, although processing of NFKB1/p105 also appears to occur post-translationally. p50 binds to the kappa-B consensus sequence 5'-GGRNNYYCC-3', located in the enhancer region of genes involved in immune response and acute phase reactions. In a complex with MAP3K8, NFKB1/p105 represses MAP3K8-induced MAPK signaling; active MAP3K8 is released by proteasome-dependent degradation of NFKB1/p105. |
| Molecular Weight | Theoretical: 48/105 kDa. |
| Stability & Storage | Store at -20°C or -80°C for 12 months. Avoid repeated freeze-thaw cycles. |
| Transport | Shipping with blue ice. |
| Size | Quantity | Unit Price | Amount | Operation |
|---|

Copyright © 2015-2026 TargetMol Chemicals Inc. All Rights Reserved.