Shopping Cart
Remove All Your shopping cart is currently empty
Your shopping cart is currently empty
Anti-CDK2 Polyclonal Antibody 2 is a Rabbit antibody targeting CDK2. Anti-CDK2 Polyclonal Antibody 2 can be used in FCM,WB.
| Pack Size | Price | USA Warehouse | Global Warehouse | Quantity |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 50 μL | $220 | 7-10 days | 7-10 days | |
| 100 μL | $372 | 7-10 days | 7-10 days | |
| 200 μL | $527 | 7-10 days | 7-10 days |
| Description | Anti-CDK2 Polyclonal Antibody 2 is a Rabbit antibody targeting CDK2. Anti-CDK2 Polyclonal Antibody 2 can be used in FCM,WB. |
| Synonyms | p33(CDK2), cyclin-dependent kinase 2, CDKN2 |
| Ig Type | IgG |
| Reactivity | Human,Mouse (predicted:Rat,Pig,Cow,Horse,Rabbit) |
| Verified Activity | 1. Blank control (Black line): U87Mg (Black). Primary Antibody (green line): Rabbit Anti-CDK2 antibody (TMAB-00404) Dilution: 3 μg/10^6 cells; Isotype Control Antibody (orange line): Rabbit IgG. Secondary Antibody (white blue line): Goat anti-rabbit IgG-AF647 Dilution: 1 μg/test. Protocol The cells were fixed with 4% PFA (10 min at room temperature) and then permeabilized with 90% ice-cold methanol for 20 min at room temperature. The cells were then incubated in 5% BSA to block non-specific protein-protein interactions for 30 min at room temperature. Cells stained with Primary Antibody for 30 min at room temperature. The secondary antibody used for 40 min at room temperature. 2. Sample: Lane 1: LympHnode (Mouse) Lysate at 40 μg Lane 2: Esophagus (Mouse) Lysate at 40 μg Lane 3: K562 (Human) Cell Lysate at 30 μg Lane 4: Molt-4 (Human) Cell Lysate at 30 μg Lane 5: Siha (Human) Cell Lysate at 30 μg Primary: Anti-CDK2 (TMAB-00404) at 1/1000 dilution Secondary: IRDye800CW Goat Anti-Rabbit IgG at 1/20000 dilution Predicted band size: 30 kDa Observed band size: 30 kDa 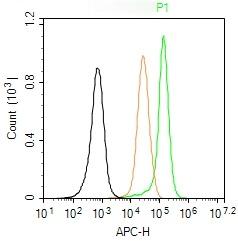 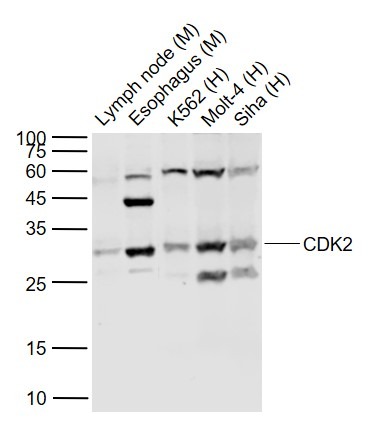 |
| Application | |
| Recommended Dose | WB: 1:500-2000; FCM: 3μg/Test |
| Antibody Type | Polyclonal |
| Host Species | Rabbit |
| Subcellular Localization | Cytoplasm, cytoskeleton, centrosome. Nucleus, Cajal body. Cytoplasm. Endosome. Note=Localized at the centrosomes in late G2 phase after separation of the centrosomes but before the start of prophase. Nuclear-cytoplasmic trafficking is mediated during the inhibition by 1,25-(OH)(2)D(3). |
| Construction | Polyclonal Antibody |
| Purification | Protein A purified |
| Appearance | Liquid |
| Formulation | 0.01M TBS (pH7.4) with 1% BSA, 0.02% Proclin300 and 50% Glycerol. |
| Concentration | 1 mg/mL |
| Research Background | The protein encoded by this gene is a member of the Ser/Thr protein kinase family. This protein kinase is highly similar to the gene products of S. cerevisiae cdc28, and S. pombe cdc2. It is a catalytic subunit of the cyclin-dependent protein kinase complex, whose activity is restricted to the G1-S phase, and essential for cell cycle G1/S phase transition. This protein associates with and regulated by the regulatory subunits of the complex including cyclin A or E, CDK inhibitor p21Cip1 (CDKN1A) and p27Kip1 (CDKN1B). Its activity is also regulated by its protein phosphorylation. Two alternatively spliced variants and multiple transcription initiation sites of this gene have been reported. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2008]. |
| Immunogen | KLH conjugated synthetic peptide: human CDK2 |
| Antigen Species | Human |
| Gene Name | CDK2 |
| Gene ID | |
| Protein Name | Cyclin-dependent kinase 2 |
| Uniprot ID | |
| Biology Area | Cdks,Cdks,Cdks |
| Function | Serine/threonine-protein kinase involved in the control of the cell cycle; essential for meiosis, but dispensable for mitosis. Phosphorylates CTNNB1, USP37, p53/TP53, NPM1, CDK7, RB1, BRCA2, MYC, NPAT, EZH2. Interacts with cyclins A, B1, B3, D, or E. Triggers duplication of centrosomes and DNA. Acts at the G1-S transition to promote the E2F transcriptional program and the initiation of DNA synthesis, and modulates G2 progression; controls the timing of entry into mitosis/meiosis by controlling the subsequent activation of cyclin B/CDK1 by phosphorylation, and coordinates the activation of cyclin B/CDK1 at the centrosome and in the nucleus. Crucial role in orchestrating a fine balance between cellular proliferation, cell death, and DNA repair in human embryonic stem cells (hESCs). Activity of CDK2 is maximal during S phase and G2; activated by interaction with cyclin E during the early stages of DNA synthesis to permit G1-S transition, and subsequently activated by cyclin A2 (cyclin A1 in germ cells) during the late stages of DNA replication to drive the transition from S phase to mitosis, the G2 phase. EZH2 phosphorylation promotes H3K27me3 maintenance and epigenetic gene silencing. Phosphorylates CABLES1 (By similarity). Cyclin E/CDK2 prevents oxidative stress-mediated Ras-induced senescence by phosphorylating MYC. Involved in G1-S phase DNA damage checkpoint that prevents cells with damaged DNA from initiating mitosis; regulates homologous recombination-dependent repair by phosphorylating BRCA2, this phosphorylation is low in S phase when recombination is active, but increases as cells progress towards mitosis. In response to DNA damage, double-strand break repair by homologous recombination a reduction of CDK2-mediated BRCA2 phosphorylation. Phosphorylation of RB1 disturbs its interaction with E2F1. NPM1 phosphorylation by cyclin E/CDK2 promotes its dissociates from unduplicated centrosomes, thus initiating centrosome duplication. Cyclin E/CDK2-mediated phosphorylation of NPAT at G1-S transition and until prophase stimulates the NPAT-mediated activation of histone gene transcription during S phase. Required for vitamin D-mediated growth inhibition by being itself inactivated. Involved in the nitric oxide- (NO) mediated signaling in a nitrosylation/activation-dependent manner. USP37 is activated by phosphorylation and thus triggers G1-S transition. CTNNB1 phosphorylation regulates insulin internalization. |
| Molecular Weight | Theoretical: 33 kDa. |
| Stability & Storage | Store at -20°C or -80°C for 12 months. Avoid repeated freeze-thaw cycles. |
| Transport | Shipping with blue ice. |
| Size | Quantity | Unit Price | Amount | Operation |
|---|

Copyright © 2015-2026 TargetMol Chemicals Inc. All Rights Reserved.