 Your shopping cart is currently empty
Your shopping cart is currently empty

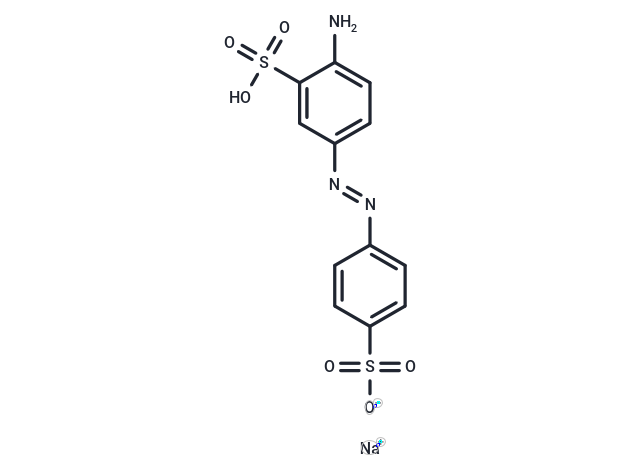
Acid Yellow 9 monosodium salt (Hydrogen 4-aminoazobenzene-3,4'-disulphonate (sodium salt)) is an azo dye, degraded by Pseudomonas fluorescens as a sole source of nitrogen, carbon, and energy for the bacterium.
| Pack Size | Price | USA Warehouse | Global Warehouse | Quantity |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 50 mg | $29 | In Stock | In Stock | |
| 1 mL x 10 mM (in DMSO) | $39 | In Stock | In Stock |
| Description | Acid Yellow 9 monosodium salt (Hydrogen 4-aminoazobenzene-3,4'-disulphonate (sodium salt)) is an azo dye, degraded by Pseudomonas fluorescens as a sole source of nitrogen, carbon, and energy for the bacterium. |
| In vitro | I. For bacterial degradation studies 1. Cultivate bacteria: Cultivate Pseudomonas fluorescens in a suitable nutrient medium. 2. Add dye: Add Acid Yellow 9 monosodium salt (usually at a concentration of 50-200 mg/L) to the medium to provide the dye as the only source of carbon and nitrogen. 3. Cultivate: Cultivate at a suitable growth temperature (usually 30-37°C) and monitor bacterial growth and dye degradation. 4. Monitor degradation: Use an ultraviolet-visible spectrophotometer (UV-Vis) or liquid chromatography (HPLC) to detect the reduction in dye concentration or degradation products. II. For bioremediation studies 1. Contaminated water sample: Prepare wastewater or water sample containing Acid Yellow 9 with a known dye concentration. 2. Inoculate bacteria: Inoculate Pseudomonas fluorescens or other suitable microorganisms into the wastewater. 3. Monitor degradation: Regularly monitor the degradation of Acid Yellow 9 and track changes in dye concentration using a spectrophotometer or chromatography. 4. Evaluation of remediation effect: Evaluate the effect of microbial treatment by analyzing the degradation of dyes and comparing with control samples. III. For environmental toxicity testing: 1. Toxicity test: Expose different concentrations of Acid Yellow 9 monosodium salt to Pseudomonas fluorescens or other environmental microorganisms to monitor bacterial growth and metabolic activity. 2. Biodegradation evaluation: Evaluate the degradation ability and growth of microorganisms in the presence of the dye by tracking changes in dye concentration. IV. For dye and pigment research 1. Dye exposure study: Expose different concentrations of Acid Yellow 9 monosodium salt to microbial culture medium to study the degradation pathway of microorganisms. 2. Enzyme activity analysis: Use enzyme activity assay to evaluate the enzyme system of bacteria that decompose dyes and further explore its degradation mechanism. The above information is based on published literature. Experimental procedures should be appropriately modified to meet specific research demands. |
| Synonyms | Hydrogen 4-aminoazobenzene-3,4'-disulphonate (sodium salt) |
| Molecular Weight | 379.34 |
| Formula | C12H10N3NaO6S2 |
| Cas No. | 74543-21-8 |
| Smiles | [Na+].Nc1ccc(cc1S(=O)(=O)O)\N=N\c2ccc(cc2)S(=O)(=O)[O-] |
| Relative Density. | no data available |
| Storage | keep away from direct sunlight | Powder: -20°C for 3 years | In solvent: -80°C for 1 year | Shipping with blue ice/Shipping at ambient temperature. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Solubility Information | DMSO: 55 mg/mL (144.99 mM), Sonication is recommended. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Solution Preparation Table | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
DMSO
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Dissolve 2 mg of the compound in 100 μL DMSO![]() to obtain a stock solution at a concentration of 20 mg/mL . If the required concentration exceeds the compound's known solubility, please contact us for technical support before proceeding.
to obtain a stock solution at a concentration of 20 mg/mL . If the required concentration exceeds the compound's known solubility, please contact us for technical support before proceeding.
1) Add 100 μL of the DMSO![]() stock solution to 400 μL PEG300
stock solution to 400 μL PEG300![]() and mix thoroughly until the solution becomes clear.
and mix thoroughly until the solution becomes clear.
2) Add 50 μL Tween 80 and mix well until fully clarified.
3) Add 450 μL Saline,PBS or ddH2O![]() and mix thoroughly until a homogeneous solution is obtained.
and mix thoroughly until a homogeneous solution is obtained.
| Size | Quantity | Unit Price | Amount | Operation |
|---|

Copyright © 2015-2026 TargetMol Chemicals Inc. All Rights Reserved.