 Your shopping cart is currently empty
Your shopping cart is currently empty

TCIP 1 is a small molecule in the category of transcriptional/epigenetic covalent inhibitor probes (TCIPs) that forms covalent bonds with molecules targeting BCL6 and BRD4. This compound facilitates cell death gene expression by directing endogenous cancer drivers or transcription factors to the promoters of these genes. Additionally, TCIP 1 exhibits a gain-of-function mechanism, displaying both cell and tissue specificity, and it establishes a ternary complex with BCL6 and BRD4. It counteracts BCL6's inhibitory effect on apoptosis gene expression, leading to the activation of apoptosis. Furthermore, TCIP 1 markedly suppresses MYC oncogene expression and curtails the proliferation of diffuse large B-cell lymphoma (DLBCL) [1].
| Pack Size | Price | USA Warehouse | Global Warehouse | Quantity |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 25 mg | $6,055 | 3-6 months | 3-6 months | |
| 50 mg | $7,955 | 3-6 months | 3-6 months | |
| 100 mg | $10,755 | 3-6 months | 3-6 months |
| Description | TCIP 1 is a small molecule in the category of transcriptional/epigenetic covalent inhibitor probes (TCIPs) that forms covalent bonds with molecules targeting BCL6 and BRD4. This compound facilitates cell death gene expression by directing endogenous cancer drivers or transcription factors to the promoters of these genes. Additionally, TCIP 1 exhibits a gain-of-function mechanism, displaying both cell and tissue specificity, and it establishes a ternary complex with BCL6 and BRD4. It counteracts BCL6's inhibitory effect on apoptosis gene expression, leading to the activation of apoptosis. Furthermore, TCIP 1 markedly suppresses MYC oncogene expression and curtails the proliferation of diffuse large B-cell lymphoma (DLBCL) [1]. |
| In vitro | TCIP 1 enhanced the binding of BRD4 to BCL6 loci on the genome by 50%, while only reducing its binding at enhancers by 10%. This led to transcriptional elongation at pro-apoptotic target genes, significantly inhibiting diffuse large B-cell lymphoma cell lines, including chemotherapy-resistant TP53 mutant cell lines, with an EC50 of 1-10 nM [1]. The apoptosis induced by TCIP 1 could be blocked by either JQ1 (a BRD4 inhibitor) or BI3812 (a BCL6 inhibitor). TCIP 1 induced G1/S and G2/M cell cycle arrest in KARPAS422 cells. Further, TCIP 1 (10 or 100 nM; 20 h) significantly activated anti-apoptotic genes, while a 10 nM concentration for 8 h suppressed the expression of MYC and its target genes. |
| In vivo | TCIP1, administered intraperitoneally at a dosage of 10 mg/kg daily for five consecutive days, was well tolerated in wild-type C57BL/6 mice with a half-life (t 1/2) of 9.7 hours, a maximum concentration (C max) of 0.41 μM, and an area under the curve (AUC 0-last) of 1.92 μM/h [1]. |
| Molecular Weight | 1026.04 |
| Formula | C50H58Cl2N12O6S |
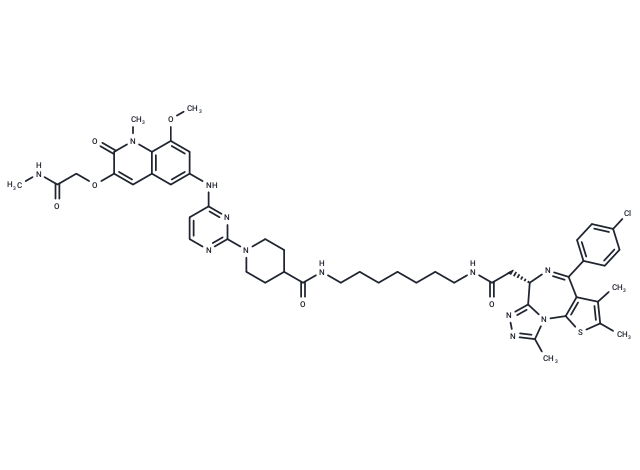
| Smiles | CNC(COC1=CC2=C(C(OC)=CC(NC3=NC(N4CCC(C(NCCCCCCCNC(C[C@@H]5N=C(C6=CC=C(Cl)C=C6)C7=C(SC(C)=C7C)N8C(C)=NN=C58)=O)=O)CC4)=NC=C3)=C2)N(C)C1=O)=O |
| Storage | Powder: -20°C for 3 years | In solvent: -80°C for 1 year | Shipping with blue ice/Shipping at ambient temperature. |
Dissolve 2 mg of the compound in 100 μL DMSO![]() to obtain a stock solution at a concentration of 20 mg/mL . If the required concentration exceeds the compound's known solubility, please contact us for technical support before proceeding.
to obtain a stock solution at a concentration of 20 mg/mL . If the required concentration exceeds the compound's known solubility, please contact us for technical support before proceeding.
1) Add 100 μL of the DMSO![]() stock solution to 400 μL PEG300
stock solution to 400 μL PEG300![]() and mix thoroughly until the solution becomes clear.
and mix thoroughly until the solution becomes clear.
2) Add 50 μL Tween 80 and mix well until fully clarified.
3) Add 450 μL Saline,PBS or ddH2O![]() and mix thoroughly until a homogeneous solution is obtained.
and mix thoroughly until a homogeneous solution is obtained.
| Size | Quantity | Unit Price | Amount | Operation |
|---|

Copyright © 2015-2026 TargetMol Chemicals Inc. All Rights Reserved.