 Your shopping cart is currently empty
Your shopping cart is currently empty

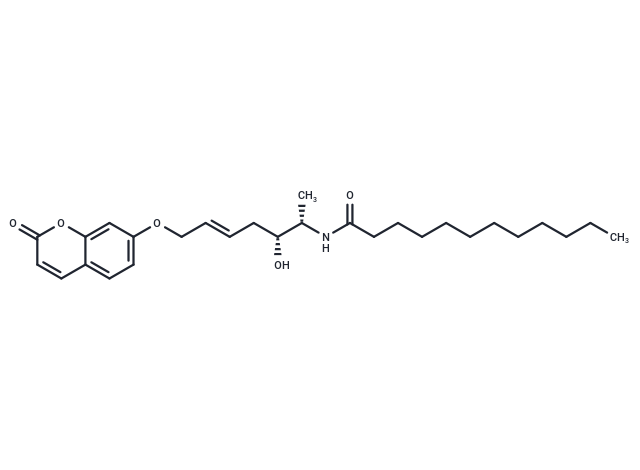
RBM1-151 is a 1-deoxy derivative and vinyl analog of RBM14-C12, serving as a fluorescent substrate for amidases (Ex/Em = 355/460 nm). It is hydrolyzed by acidic ceramidase (AC) (appKm = 7.0 μM; appVmax = 99.3 nM/min), N-acylethanolamine hydrolyzing acid amidase (appKm = 0.73 μM; appVmax = 0.24 nM/min), and fatty acid amide hydrolase (FAAH) (appKm = 3.6 μM; appVmax = 7.6 nM/min), but is not hydrolyzed by other ceramidases. RBM1-151 is useful for studying the basic biology of lipid amidase functions and for potential diagnostic/prognostic assessments in disorders involving AC, NAAA, or FAAH dysregulation, such as Farber disease and cancer.
| Pack Size | Price | USA Warehouse | Global Warehouse | Quantity |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 10 mg | Inquiry | 10-14 weeks | 10-14 weeks | |
| 50 mg | Inquiry | 10-14 weeks | 10-14 weeks |
| Description | RBM1-151 is a 1-deoxy derivative and vinyl analog of RBM14-C12, serving as a fluorescent substrate for amidases (Ex/Em = 355/460 nm). It is hydrolyzed by acidic ceramidase (AC) (appKm = 7.0 μM; appVmax = 99.3 nM/min), N-acylethanolamine hydrolyzing acid amidase (appKm = 0.73 μM; appVmax = 0.24 nM/min), and fatty acid amide hydrolase (FAAH) (appKm = 3.6 μM; appVmax = 7.6 nM/min), but is not hydrolyzed by other ceramidases. RBM1-151 is useful for studying the basic biology of lipid amidase functions and for potential diagnostic/prognostic assessments in disorders involving AC, NAAA, or FAAH dysregulation, such as Farber disease and cancer. |
| In vitro | RBM1-151 (20 μM, 1 hour) is hydrolyzed to form RBM1-151-NH2 solely by acidic ceramidase in a cell-free system (using A375/AC cell lysate). In acidic buffer, RBM1-151 (0-20 μM, 30 minutes) is hydrolyzed by A375/AC cell lysate (20 μg), with kinetic parameters calculated via Michaelis-Menten analysis showing an app Km of 7.0 μM and an app Vmax of 99.3 nM/min. In HEK293/NAAA cell lysate (10 μg, overexpressing NAAA), RBM1-151 (5 μM, 3 hours) exhibits higher hydrolysis compared to HEK293/mock lysate, as indicated by fluorescence product. In Farber disease (FD) cells (lacking AC), RBM1-151 (20 μM, 3 hours) yields minimal fluorescence, whereas fluorescence is significantly higher in FD/AC cells (overexpressing AC) in whole cells. In A375/AC cells (overexpressing AC), RBM1-151 (20 μM, 3 hours) shows greater hydrolysis than in A375/WT cells. Guidelines: 1. Cell Preparation: 1.1 For suspension cells (e.g., AML cell lines: MM-6, HL-60), culture cells in RPMI-1640 medium with 20% FBS; adjust density to 2 × 10^4 cells per well before plating. 1.2 For adherent cells (e.g., melanoma cell lines: A375/AC, C8161; HEK293), use Dulbecco modified Eagle medium (high glucose) with 10% FBS and 1% penicillin/streptomycin; seed 2 × 10^4 cells per well in a 96-well plate and incubate overnight for adherence. Note: For antibiotic-selective cell lines (e.g., A375/AC using blasticidin and hygromycin), remove antibiotics before experimentation to prevent interference. 2. RBM1-151 Incubation and Signal Detection: 2.1 Add 50 μL of 20 μM RBM1-151 working solution (prepared in medium with 20% FBS, final concentration 20 μM) to each well. 2.2 Incubate at 37°C with 5% CO2 for 1 hour. 2.3 Add 25 μL of 100% methanol to each well to stop the reaction. 2.4 Immediately add 100 μL of NaIO4 solution (2.5 mg/mL, prepared in 100 mM glycine-NaOH buffer, pH 10.6). 2.5 Incubate in the dark at 37°C with 5% CO2 for 30 minutes. 2.6 Measure fluorescence signals using a microplate reader, subtracting background signals from wells containing only medium and RBM1-151 without cells. The above information is based on published literature. Experimental procedures should be appropriately modified to meet specific research demands. |
| Molecular Weight | 471.63 |
| Formula | C28H41NO5 |
| Cas No. | 3077081-47-8 |
| Smiles | O(C/C=C/C[C@H]([C@@H](NC(CCCCCCCCCCC)=O)C)O)C=1C=C2C(=CC1)C=CC(=O)O2 |
| Storage | keep away from direct sunlight | Powder: -20°C for 3 years | In solvent: -80°C for 1 year | Shipping with blue ice/Shipping at ambient temperature. |
Dissolve 2 mg of the compound in 100 μL DMSO![]() to obtain a stock solution at a concentration of 20 mg/mL . If the required concentration exceeds the compound's known solubility, please contact us for technical support before proceeding.
to obtain a stock solution at a concentration of 20 mg/mL . If the required concentration exceeds the compound's known solubility, please contact us for technical support before proceeding.
1) Add 100 μL of the DMSO![]() stock solution to 400 μL PEG300
stock solution to 400 μL PEG300![]() and mix thoroughly until the solution becomes clear.
and mix thoroughly until the solution becomes clear.
2) Add 50 μL Tween 80 and mix well until fully clarified.
3) Add 450 μL Saline,PBS or ddH2O![]() and mix thoroughly until a homogeneous solution is obtained.
and mix thoroughly until a homogeneous solution is obtained.
| Size | Quantity | Unit Price | Amount | Operation |
|---|

Copyright © 2015-2026 TargetMol Chemicals Inc. All Rights Reserved.