Shopping Cart
- Remove All
 Your shopping cart is currently empty
Your shopping cart is currently empty

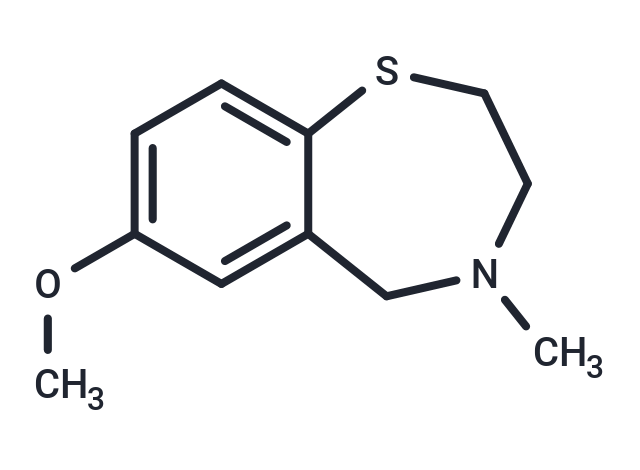
S107 is a RyR-selective 1, 4-benzothiazepine derivative that stabilizes RyR2 channels by enhancing the binding affinity of calstabin2 to mutant and/or PKA-phosphorylated channels.
| Pack Size | Price | Availability | Quantity |
|---|---|---|---|
| 2 mg | $32 | In Stock | |
| 5 mg | $58 | In Stock | |
| 10 mg | $88 | In Stock | |
| 25 mg | $160 | In Stock | |
| 50 mg | $268 | In Stock | |
| 100 mg | $382 | In Stock | |
| 200 mg | $543 | In Stock | |
| 1 mL x 10 mM (in DMSO) | $64 | In Stock |
| Description | S107 is a RyR-selective 1, 4-benzothiazepine derivative that stabilizes RyR2 channels by enhancing the binding affinity of calstabin2 to mutant and/or PKA-phosphorylated channels. |
| In vitro | S107, a small compound, enhances calstabin2 binding to RyR2 at low nanomolar concentrations and does not interact with over 400 receptors, enzymes, and ion channels at up to 10 μM. It shows no effect on cardiac ion channels, including voltage-gated Na+, K+, and Ca2+ channels, or on normal Ca2+ signaling in cells[1]. S107 is a potential candidate for treating catecholaminergic polymorphic ventricular tachycardia (CPVT), exerting antiarrhythmic effects on CPVT-hiPSC-CMs. Pre-incubation with 10 μM S107 significantly reduces the incidence of CPVT-hiPSC-CMs presenting DADs to 25% by stabilizing the closed state of ryanodine receptor 2[2]. S107 may improve skeletal muscle function by stabilizing the RyR1-FKBP12 complex, increasing FKBP12 binding to RyR1 in SR vesicles in the presence of reduced glutathione and the NO-donor NOC12 but not in the presence of oxidized glutathione. It reverses the harmful effects of redox active species on SR Ca2+ release in skeletal muscle by binding to RyR1 low affinity sites[3]. |
| In vivo | S107 effectively inhibits seizures and arrhythmias in mutant mice without blocking the channel or changing normal calcium (Ca2+) signaling; it specifically prevents leakage in the channel[1]. |
| Molecular Weight | 209.31 |
| Formula | C11H15NOS |
| Cas No. | 927871-76-9 |
| Smiles | COc1ccc2SCCN(C)Cc2c1 |
| Relative Density. | no data available |
| Storage | Powder: -20°C for 3 years | In solvent: -80°C for 1 year | Shipping with blue ice/Shipping at ambient temperature. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Solubility Information | DMSO: 55 mg/mL (262.77 mM), Sonication is recommended. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Solution Preparation Table | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
DMSO
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||

Copyright © 2015-2025 TargetMol Chemicals Inc. All Rights Reserved.