 Your shopping cart is currently empty
Your shopping cart is currently empty

PEG400 (Polyethylene glycol 400) is a polymer formed from repeating units of ethylene glycol that is water soluble, low immunogenicity, and biocompatible. PEG400 is a neutral polymer with a molecular weight of 400.
| Pack Size | Price | USA Warehouse | Global Warehouse | Quantity |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 100 mL | $46 | In Stock | In Stock |
| Description | PEG400 (Polyethylene glycol 400) is a polymer formed from repeating units of ethylene glycol that is water soluble, low immunogenicity, and biocompatible. PEG400 is a neutral polymer with a molecular weight of 400. |
| Targets&IC50 | HeLa cells:32.5 mg/mL, L929 cells:24.7 mg/mL |
| In vitro | METHODS: Human colorectal adenocarcinoma cells Caco-2 were treated with PEG400 (30 w/v% in 100 μL) for 30 min, and cell growth inhibition was detected by MTT. RESULTS: PEG400 treatment reduced cell viability, which was 42%±2% compared with the control. [1] |
| In vivo | METHODS: To study in vivo activity, Simvastatin (60 mg/kg, aqueous 2% DMSO+30% PEG 400+5% Tween 80) was administered by gavage to C57BL/6J mice once daily for six weeks on a CF diet. RESULTS: Simvastatin treatment reduced serum cholesterol levels by 18%, and retinal cholesterol and lipoprotein cholesterol levels by 24% and 21%, respectively. [2] METHODS: To study the effect of Rapamycin on life expectancy, Rapamycin (8 mg/kg in DMSO+5% PEG-400+5% Tween-80) was administered intraperitoneally to 20-21 month old C57BL/6J mice once daily for three months. RESULTS: Three months of Rapamycin treatment was sufficient to increase the life expectancy of middle-aged mice by 60% and improve their healthy lifespan. [3] |
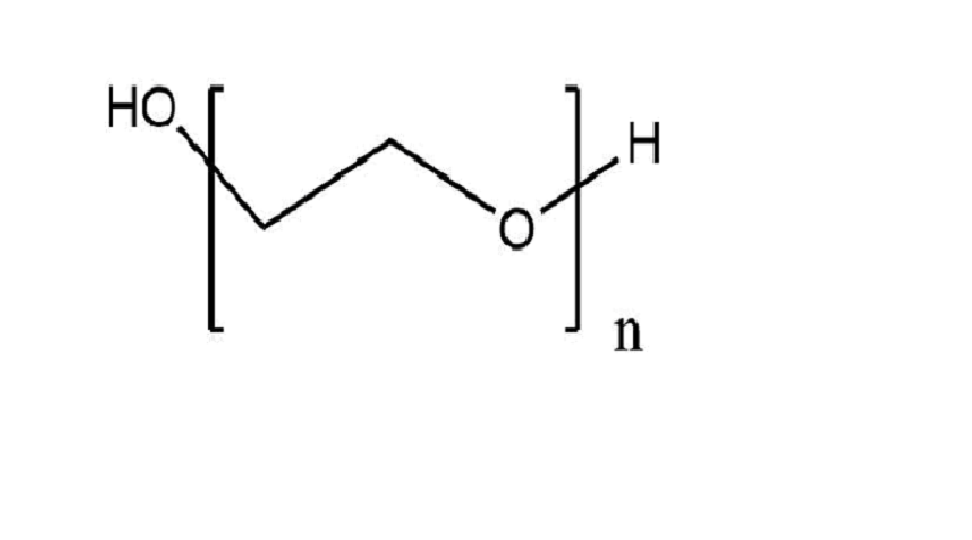
| Formula | HO(CH2CH2O)nH |
| Relative Density. | no data available |
| Storage | store at -80°C | Shipping with blue ice/Shipping at ambient temperature. |
| Solubility Information | DMSO: 100 mg/mL, Sonication is recommended. H2O: 100 mg/mL, Sonication is recommended. |
| In Vivo Formulation | 10% DMSO+40% PEG300+5% Tween-80+45% Saline: 3.3 mg/mL, Sonication is recommended. Please add the solvents sequentially, clarifying the solution as much as possible before adding the next one. Dissolve by heating and/or sonication if necessary. Working solution is recommended to be prepared and used immediately. The formulation provided above is for reference purposes only. In vivo formulations may vary and should be modified based on specific experimental conditions. |
Dissolve 2 mg of the compound in 100 μL DMSO![]() to obtain a stock solution at a concentration of 20 mg/mL . If the required concentration exceeds the compound's known solubility, please contact us for technical support before proceeding.
to obtain a stock solution at a concentration of 20 mg/mL . If the required concentration exceeds the compound's known solubility, please contact us for technical support before proceeding.
1) Add 100 μL of the DMSO![]() stock solution to 400 μL PEG300
stock solution to 400 μL PEG300![]() and mix thoroughly until the solution becomes clear.
and mix thoroughly until the solution becomes clear.
2) Add 50 μL Tween 80 and mix well until fully clarified.
3) Add 450 μL Saline,PBS or ddH2O![]() and mix thoroughly until a homogeneous solution is obtained.
and mix thoroughly until a homogeneous solution is obtained.
| Size | Quantity | Unit Price | Amount | Operation |
|---|

Copyright © 2015-2026 TargetMol Chemicals Inc. All Rights Reserved.