Shopping Cart
- Remove All
 Your shopping cart is currently empty
Your shopping cart is currently empty

Legumain Protein, Mouse, Recombinant (His) is expressed in HEK293 mammalian cells with His tag. The predicted molecular weight is 49.8 kDa and the accession number is A2RTI3.

| Pack Size | Price | Availability | Quantity |
|---|---|---|---|
| 50 μg | $386 | In Stock | |
| 100 μg | $660 | 7-10 days | |
| 200 μg | $1,120 | 7-10 days | |
| 500 μg | $2,270 | 7-10 days |
| Biological Activity | Measured by its ability to cleave the fluorogenic peptide substrate, N-carbobenzyloxy-Ala-Ala-Asn-7-amido-4-methyl coumarin(Z-AAN-AMC). The specific activity is > 350 pmoles/min/μg. (Activation description: The enzyme achieves its activity under acidic pH) |
| Description | Legumain Protein, Mouse, Recombinant (His) is expressed in HEK293 mammalian cells with His tag. The predicted molecular weight is 49.8 kDa and the accession number is A2RTI3. |
| Species | Mouse |
| Expression System | HEK293 Cells |
| Tag | C-His |
| Accession Number | A2RTI3 |
| Synonyms | Prsc1,legumain,AU022324,AI746452,AEP |
| Construction | A DNA sequence encoding the extracellular domain (Val 18-Tyr 435) of mouse LGMN (NP_035305.1) precursor was expressed with a C-terminal polyhistidine tag. Predicted N terminal: Thr 22 |
| Protein Purity | ≥ 75 % as determined by SDS-PAGE. ≥ 95 % as determined by SEC-HPLC. 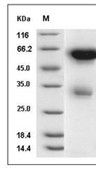 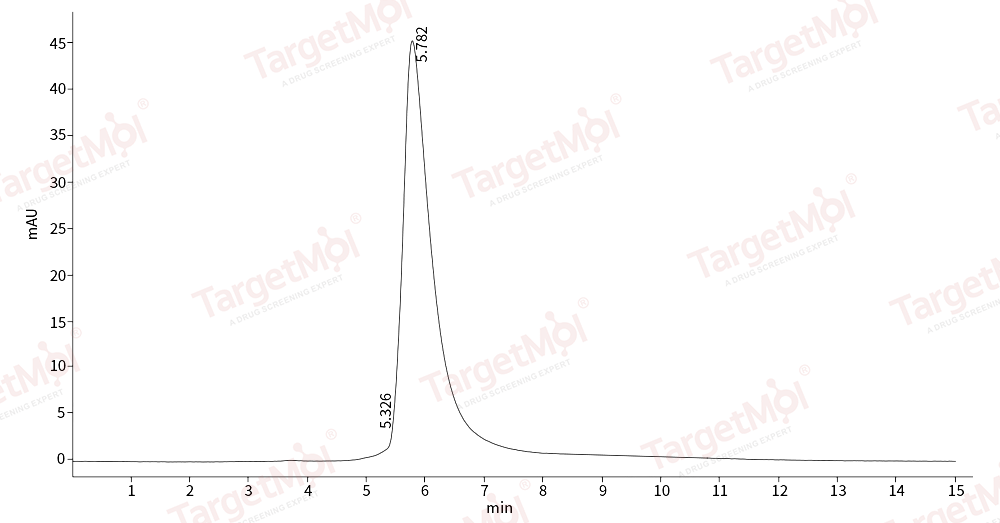 |
| Molecular Weight | 49.8 kDa (predicted); 55 kDa (reducing condition, due to glycosylation) |
| Endotoxin | < 1.0 EU/μg of the protein as determined by the LAL method. |
| Formulation | Supplied as sterile 25 mM Tris, 0.15M NaCl, 20% Glycerol, pH 7.5. |
| Reconstitution | A Certificate of Analysis (CoA) containing reconstitution instructions is included with the products. Please refer to the CoA for detailed information. |
| Stability & Storage | It is recommended to store the product under sterile conditions at -20°C to -80°C. Samples are stable for up to 12 months. Please avoid multiple freeze-thaw cycles and store products in aliquots. |
| Shipping | Shipping with blue ice. |
| Research Background | The Mammalian Legumain, also known as LGMN, also called asparaginyl endopeptidase (AEP), is a cysteine protease belonging to peptidase family C13 with strict specificity for hydrolysis of asparaginyl bonds. Known previously only from plants and invertebrates, Legumain is discovered as a lysosomal endopeptidase in mammals. Mammalian Legumain is a cysteine endopeptidase, inhibited by iodoacetamide and maleimides, but unaffected by compound E64. The Mammalian Legumain is involved in the processing of bacterial peptides and endogenous proteins for MHC class II presentation in the lysosomal/endosomal systems. Legumain has been observed to be highly expressed in several types of solid tumors. It was demonstrated in membrane-associated vesicles concentrated at the invadopodia of tumor cells and on cell surfaces where it colocalized with integrins. Legumain was demonstrated to activate progelatinase A. Cells overexpressing Legumain possessed increased migratory and invasive activity in vitro and adopted an invasive and metastatic phenotype in vivo, inferring significance of Legumain in tumor invasion and metastasis. Also, Legumain is expressed in both murine and human atherosclerotic lesions. The macrophage-specific expression of Legumain in vivo and the ability of Legumain to induce chemotaxis of monocytes and endothelial cells in vitro suggest that Legumain may play a functional role in atherogenesis. |

Copyright © 2015-2025 TargetMol Chemicals Inc. All Rights Reserved.