 Your shopping cart is currently empty
Your shopping cart is currently empty

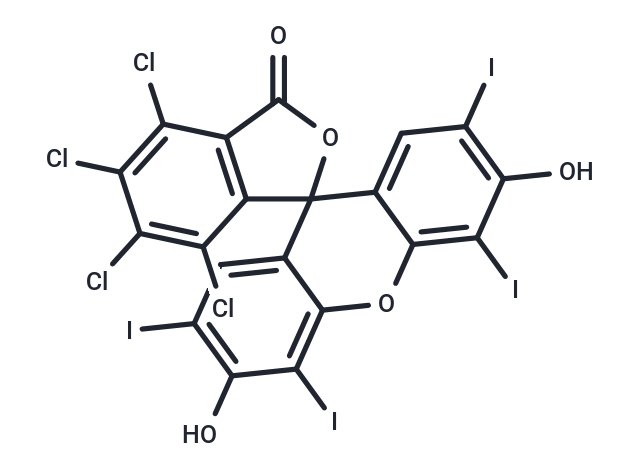
Rose bengal lactone (C.I. Solvent Red 141) is a rose bengal lactone stain commonly used to stain the nuclei of plant and animal cells.
| Pack Size | Price | USA Warehouse | Global Warehouse | Quantity |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 50 mg | $40 | Inquiry | Inquiry | |
| 100 mg | $64 | Inquiry | Inquiry | |
| 200 mg | $93 | Inquiry | Inquiry |
| Description | Rose bengal lactone (C.I. Solvent Red 141) is a rose bengal lactone stain commonly used to stain the nuclei of plant and animal cells. |
| Cell Research | Instructions I. Dye preparation: 1. Stock solution preparation: Dissolve it in an appropriate solvent (usually water, ethanol or buffer solution) to prepare a stock solution. 2. Working solution preparation: The commonly used working concentration range is 1–10 µM, and the specific concentration can be adjusted according to experimental needs. II. Operation steps 1. Cell preparation: 1) Inoculate the cells to be stained onto a microscope slide, culture dish or other suitable substrate. 2) Incubation: Add the prepared rose bengal lactone solution to the cells. The incubation time is usually 30 minutes to 1 hour at 37°C, but it can be optimized according to the cell type and staining intensity requirements. 3) Washing: After incubation, wash the cells with an appropriate buffer or PBS (phosphate buffered saline) to remove unbound dye. 2. Imaging and analysis: 1) After the cells are stained and washed, they can be observed under a fluorescence microscope. Rose bengal lactone usually emits strong fluorescence, which facilitates the visualization of the cell nucleus. 2) The excitation wavelength of rose bengal lactone is usually around 550 nm, and the emission wavelength is in the red to orange spectrum. 3. Data interpretation: 1) Fluorescence intensity is related to the amount of dye uptake and can be used to determine the number and state of cells. 2) It can also be used to evaluate cell morphological changes or observe specific cell structures and processes, depending on the context of the experiment. Notes: 1. Toxicity: Rose bengal lactone is a synthetic dye and should be used with caution. It is recommended to wear gloves and goggles during operation and work in a well-ventilated area. 2. Photosensitivity: Like many fluorescent dyes, rose bengal lactone is light-sensitive, so long-term exposure to strong light should be avoided during operation and storage to prevent photobleaching. 3. Concentration control: The concentration of the dye needs to be properly controlled. Excessive staining concentration may cause high background fluorescence or cytotoxicity. The above information is based on published literature. Experimental procedures should be appropriately modified to meet specific research demands. |
| Synonyms | Rose Bengal, C.I. Solvent Red 141 |
| Molecular Weight | 973.67 |
| Formula | C20H4Cl4I4O5 |
| Cas No. | 4159-77-7 |
| Smiles | O=C1OC2(C3=CC(I)=C(O)C(I)=C3OC4=C(I)C(O)=C(I)C=C42)C=5C(Cl)=C(Cl)C(Cl)=C(Cl)C15 |
| Storage | Powder: -20°C for 3 years | In solvent: -80°C for 1 year | Shipping with blue ice. |
Dissolve 2 mg of the compound in 100 μL DMSO![]() to obtain a stock solution at a concentration of 20 mg/mL . If the required concentration exceeds the compound's known solubility, please contact us for technical support before proceeding.
to obtain a stock solution at a concentration of 20 mg/mL . If the required concentration exceeds the compound's known solubility, please contact us for technical support before proceeding.
1) Add 100 μL of the DMSO![]() stock solution to 400 μL PEG300
stock solution to 400 μL PEG300![]() and mix thoroughly until the solution becomes clear.
and mix thoroughly until the solution becomes clear.
2) Add 50 μL Tween 80 and mix well until fully clarified.
3) Add 450 μL Saline,PBS or ddH2O![]() and mix thoroughly until a homogeneous solution is obtained.
and mix thoroughly until a homogeneous solution is obtained.
| Size | Quantity | Unit Price | Amount | Operation |
|---|

Copyright © 2015-2026 TargetMol Chemicals Inc. All Rights Reserved.