Shopping Cart
- Remove All
 Your shopping cart is currently empty
Your shopping cart is currently empty

Rhodamine 6G (Basic Red 1) is a rhodamine analog useful in Pgp efflux assays. It can be widely used in characterizing the kinetics of MRP1- mediated efflux as a laser dye and potential mitochondrial probe.
| Pack Size | Price | Availability | Quantity |
|---|---|---|---|
| 100 mg | $30 | In Stock | |
| 500 mg | $61 | In Stock | |
| 1 g | $78 | In Stock | |
| 5 g | $118 | In Stock | |
| 10 g | $173 | In Stock | |
| 1 mL x 10 mM (in DMSO) | $53 | In Stock |
| Description | Rhodamine 6G (Basic Red 1) is a rhodamine analog useful in Pgp efflux assays. It can be widely used in characterizing the kinetics of MRP1- mediated efflux as a laser dye and potential mitochondrial probe. |
| In vitro | Rhodamine 6G, also known as Rhodamine 590, is widely used as a lasing medium and as a fluorescence tracer. Rhodamine 6G is a fluorescent dye capable of penetrating a living cell. Upon entering the cell, Rhodamine 6G binds to the inner membranes of mitochondria. Based on these observations, it has been proposed that Rhodamine dyes may be used for producing fluorescent images of mitochondria with low background noise and high resolution. Extremely low concentrations of Rhodamine 6G appear to selectively destroy malignant cells in culture, sparing the normal cell populations[2]. |
| In vivo | Compared to their untreated counterparts, Melanoma-transplanted mice receiving Rhodamine 6G demonstrate prolonged survival, inhibited tumor growth, improved clinical parameters and metastases count. It is possible to monitor changes in the interactions between leukocytes and the endothelium by determining the numbers of rolling and adhering leukocytes as well as the total flux of these cells[3]. The Rhodamine-6G enters the circulatory system and labels leukocytes. Twice-a-week 10-6M Rhodamine 6G regimen yield the most prominent results[2]. |
| Alias | Basic Red 1 |
| Molecular Weight | 479.01 |
| Formula | C28H31ClN2O3 |
| Cas No. | 989-38-8 |
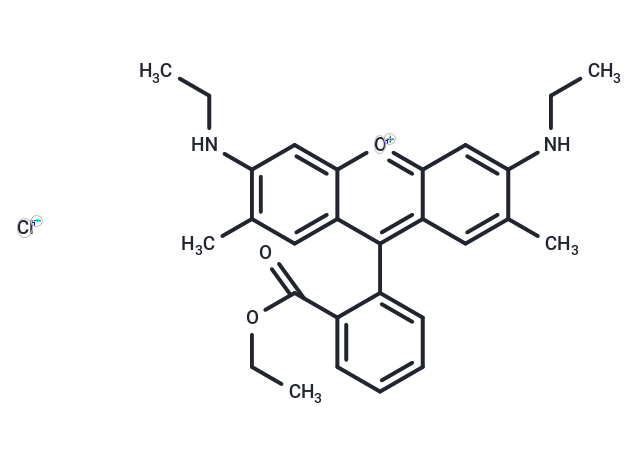
| Smiles | [Cl-].CCNc1cc2[o+]c3cc(NCC)c(C)cc3c(-c3ccccc3C(=O)OCC)c2cc1C |
| Relative Density. | 1.15g/cm3 |
| Storage | keep away from direct sunlight | Powder: -20°C for 3 years | In solvent: -80°C for 1 year | Shipping with blue ice. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Solubility Information | H2O: 83.3 mg/mL (173.97 mM), Sonication is recommended. DMSO: 7.5 mg/mL (15.66 mM), Sonication is recommended. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Solution Preparation Table | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
DMSO/H2O
H2O
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||

Copyright © 2015-2025 TargetMol Chemicals Inc. All Rights Reserved.