Shopping Cart
- Remove All
 Your shopping cart is currently empty
Your shopping cart is currently empty

DFHBI, a small molecule resembling the chromophore of green fluorescent protein (GFP), is essentially nonfluorescent when unbound. The Spinach-DFHBI complex, however, exhibits bright fluorescence both in vitro and in living cells.
| Pack Size | Price | Availability | Quantity |
|---|---|---|---|
| 2 mg | $38 | In Stock | |
| 5 mg | $61 | In Stock | |
| 10 mg | $101 | In Stock | |
| 25 mg | $215 | In Stock | |
| 50 mg | $360 | In Stock | |
| 100 mg | $535 | In Stock | |
| 1 mL x 10 mM (in DMSO) | $65 | In Stock |
| Description | DFHBI, a small molecule resembling the chromophore of green fluorescent protein (GFP), is essentially nonfluorescent when unbound. The Spinach-DFHBI complex, however, exhibits bright fluorescence both in vitro and in living cells. |
| In vitro | Spinach and Spinach2 bind to DFHBI have fluorescence excitation maxima of 447 nm and peak fluorescence emission of 501 nm[1] and they are RNA aptamers that can be used for the genetic encoding of fluorescent RNA. Spinach is a 98-nt-long RNA aptamer that binds to and switches on the fluorescence of DFHBI. Both Spinach and DFHBI are essentially nonfluorescent when unbound, whereas the Spinach-DFHBI complex is brightly fluorescent both in vitro and in living cells. Spinach2 binds and activates the fluorescence of DFHBI, allowing the dynamic localizations of Spinach2-tagged RNAs to be imaged in live cells. The spectral properties of Spinach2 are limited by DFHBI, which produces fluorescence that is bluish-green and is not optimized for filters commonly used in fluorescence microscopes. DFHBI should be shielded from light. All stock solutions of DFHBI should be maintained in dark tubes or wrapped in foil. Plates containing cultures incubated with DFHBI should be kept in the dark by using a foil overwrap[2]. |
| Molecular Weight | 252.22 |
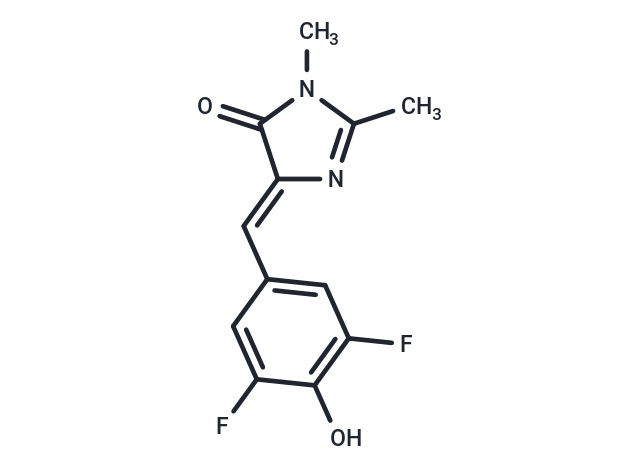
| Formula | C12H10F2N2O2 |
| Cas No. | 1241390-29-3 |
| Smiles | CN1C(C)=N\C(=C/c2cc(F)c(O)c(F)c2)C1=O |
| Relative Density. | no data available |
| Storage | keep away from direct sunlight | Powder: -20°C for 3 years | In solvent: -80°C for 1 year | Shipping with blue ice. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Solubility Information | DMSO: 83.33 mg/mL (330.39 mM), Sonication is recommended. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Solution Preparation Table | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
DMSO
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||

Copyright © 2015-2025 TargetMol Chemicals Inc. All Rights Reserved.