Shopping Cart
Remove All Your shopping cart is currently empty
Your shopping cart is currently empty
DLL1 Protein, Mouse, Recombinant (His) is expressed in HEK293 mammalian cells with His tag. The predicted molecular weight is 55 kDa and the accession number is Q61483.

| Pack Size | Price | USA Warehouse | Global Warehouse | Quantity |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 5 μg | $48 | 7-10 days | 7-10 days | |
| 10 μg | $75 | 7-10 days | 7-10 days | |
| 20 μg | $118 | 7-10 days | 7-10 days | |
| 50 μg | $229 | 7-10 days | 7-10 days | |
| 100 μg | $386 | - | In Stock | |
| 200 μg | $682 | 7-10 days | 7-10 days | |
| 500 μg | $1,430 | 7-10 days | 7-10 days |
| Biological Activity | 1. Measured by its ability to bind human NOTCH1 in a functional ELISA.
2. Measured by the ability of the immobilized protein to enhance BMP2-induced alkaline phosphatase activity in C3H10T1/2 mouse embryonic fibroblast cells. The ED50 for this effect is typically 2-20 μg/mL. |
| Description | DLL1 Protein, Mouse, Recombinant (His) is expressed in HEK293 mammalian cells with His tag. The predicted molecular weight is 55 kDa and the accession number is Q61483. |
| Species | Mouse |
| Expression System | HEK293 Cells |
| Tag | C-His |
| Accession Number | Q61483 |
| Synonyms | δ-like 1 (Drosophila),δ1,Dll1,delta-like 1 (Drosophila),Delta1 |
| Construction | A DNA sequence encoding the extracellular domain of mouse DLL1 (NP_031891.2) (Met 1-Gln 516) was expressed, with a polyhistidine tag at the C-terminus. Predicted N terminal: Ser 22 |
| Protein Purity | > 95 % as determined by SDS-PAGE 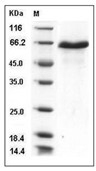 |
| Molecular Weight | 55 kDa (predicted); 65 kDa (reducing condition, due to glycosylation) |
| Endotoxin | < 1.0 EU/μg of the protein as determined by the LAL method. |
| Formulation | Lyophilized from a solution filtered through a 0.22 μm filter, containing PBS, pH 7.4, 20% glycerol. Typically, a mixture containing 5% to 8% trehalose, mannitol, and 0.01% Tween 80 is incorporated as a protective agent before lyophilization. |
| Reconstitution | Reconstituted with sterile deionized water to 0.25 mg/mL. Reconstitution conditions may vary depending on the lot. |
| Stability & Storage | It is recommended to store recombinant proteins at -20°C to -80°C for future use. Lyophilized powders can be stably stored for over 12 months, while liquid products can be stored for 6-12 months at -80°C. For reconstituted protein solutions, the solution can be stored at -20°C to -80°C for at least 3 months. Please avoid multiple freeze-thaw cycles and store products in aliquots. |
| Shipping | In general, Lyophilized powders are shipping with blue ice. |
| Research Background | Delta-like protein 1(DLL1), also known as Delta1, a single-pass type I membrane protein which contains one DSL domain and eight EGF-like domains, acts as a ligand for Notch receptors, and positively regulates T-cell development. DLL1 is proteolytically processed in a similar manner to the Notch receptor, and it has been speculated to participate in bidirectional signaling. The proteolytic processing of DLL1 helps achieve an asymmetry in Notch signaling in initially equivalent myogenic cells and helps sustain the balance between differentiation and self-renewal. Interactions between DLL1 and Notch in trans activate the Notch pathway, whereas DLL1 binding to Notch in cis inhibits Notch signaling. DLL1 undergoes proteolytic processing in its extracellular domain by ADAM10. It had been demonstrated that DLL1 represents a substrate for several other members of the ADAM family. In co-transfected cells, DLL1 is constitutively cleaved by ADAM12, and the N-terminal fragment of DLL1 is released to medium. ADAM12-mediated cleavage of DLL1 is cell density-dependent, takes place in cis orientation, and does not require the presence of the cytoplasmic domain of ADAM12. Full-length DLL1, but not its N- or C-terminal proteolytic fragment, co-immunoprecipitates with ADAM12. By using a Notch reporter construct, we show that DLL1 processing by ADAM12 increases Notch signaling in a cell-autonomous manner. Furthermore, ADAM9 and ADAM17 have the ability to process DLL1. In contrast, ADAM15 does not cleave DLL1, although the two proteins still co-immunoprecipitate with each other. During fetal development, DLL1 is an essential Notch ligand in the vascular endothelium of large arteries to activate Notch1 and maintain arterial identity. DLL1-Notch signaling was required for VEGF receptor expression in fetal arteries. |
| Size | Quantity | Unit Price | Amount | Operation |
|---|

Copyright © 2015-2026 TargetMol Chemicals Inc. All Rights Reserved.