Shopping Cart
- Remove All
 Your shopping cart is currently empty
Your shopping cart is currently empty
DLL4 Protein, Human, Recombinant (hFc) is expressed in HEK293 mammalian cells with hFc tag. The predicted molecular weight is 81 kDa and the accession number is Q9NR61.

| Pack Size | Price | Availability | Quantity |
|---|---|---|---|
| 5 μg | $47 | 7-10 days | |
| 10 μg | $74 | 7-10 days | |
| 20 μg | $118 | 7-10 days | |
| 50 μg | $228 | In Stock | |
| 100 μg | $405 | 7-10 days | |
| 200 μg | $716 | 7-10 days | |
| 500 μg | $1,520 | 7-10 days |
| Biological Activity | 1. Measured by its binding ability in a functional ELISA. Immobilized Mouse NOTCH1-His at 2 μg/ml (100 μl/well) can bind human DLL4-hFc , the EC50 of human DLL4-hFc is 15-90 ng/mL._x000D_
2. Measured by the ability of the immobilized protein to enhance BMP2-induced alkaline phosphatase activity in C3H10T1/2 mouse embryonic fibroblast cells. The ED50 for this effect is typically 1-8 µg/mL in the presence of 500 ng/mL recombinant human BMP2. 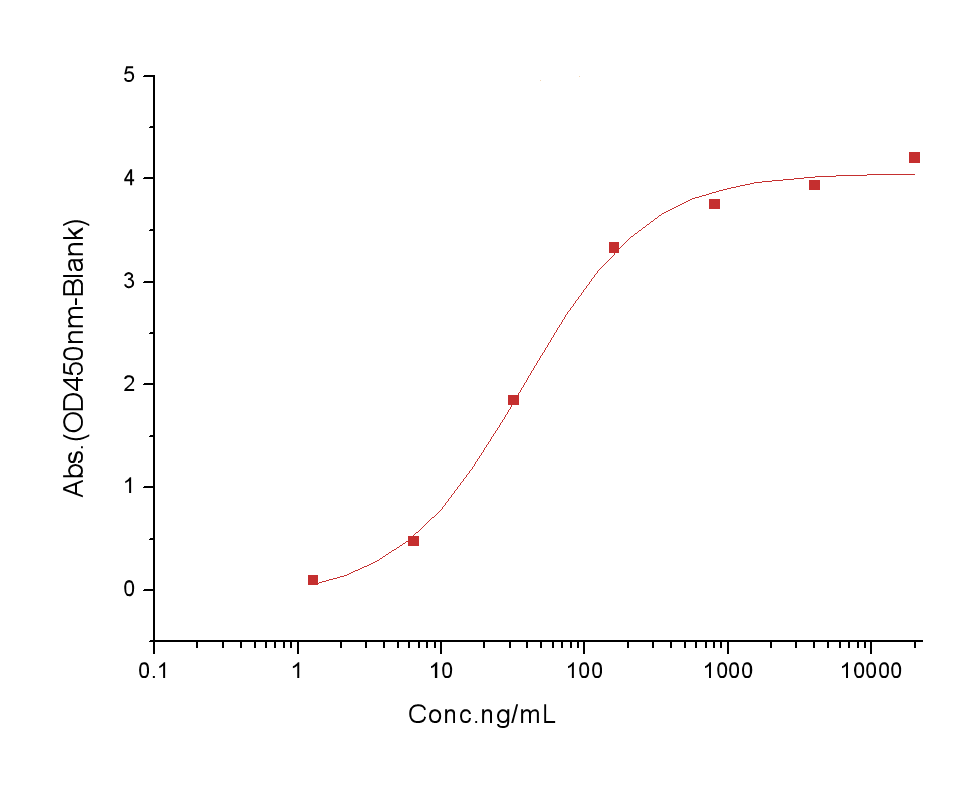 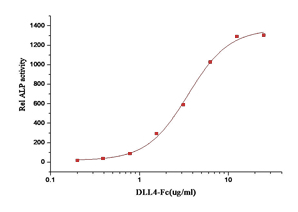 |
| Description | DLL4 Protein, Human, Recombinant (hFc) is expressed in HEK293 mammalian cells with hFc tag. The predicted molecular weight is 81 kDa and the accession number is Q9NR61. |
| Species | Human |
| Expression System | HEK293 Cells |
| Tag | C-hFc |
| Accession Number | Q9NR61 |
| Synonyms | δ-like 4 (Drosophila),δ-like 4,hδ2,hdelta2,delta-like 4 (Drosophila),Delta-like 4 |
| Construction | A DNA sequence encoding the extracellular domain (Met1-Pro524) of human DLL4 (NP_061947.1) was expressed with the Fc region of human IgG1 at the C-terminus. Predicted N terminal: Ser 27 |
| Protein Purity | ≥ 95 % as determined by SDS-PAGE. ≥ 85 % as determined by SEC-HPLC. 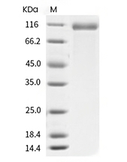 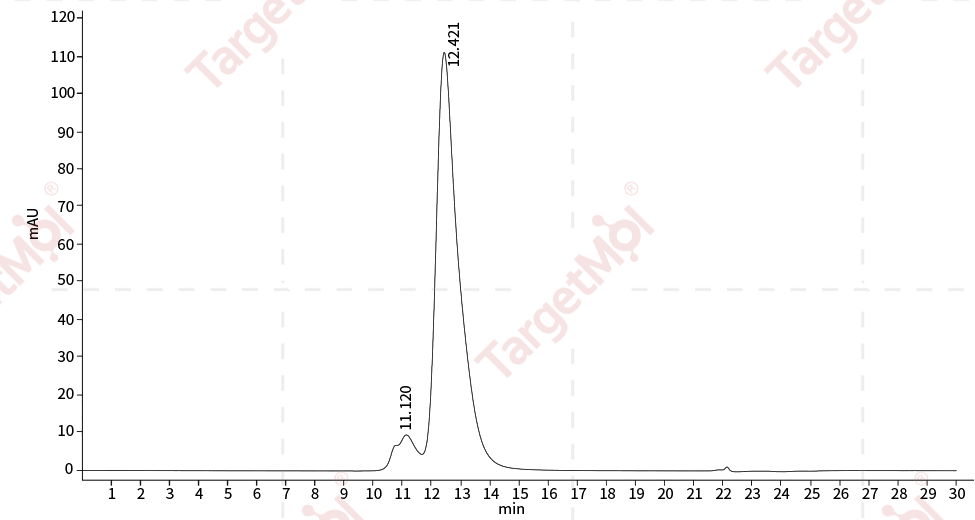 |
| Molecular Weight | 81 kDa (predicted); 100-110 kDa (reducing condition, due to glycosylation) |
| Endotoxin | < 1.0 EU/μg of the protein as determined by the LAL method. |
| Formulation | Lyophilized from a solution filtered through a 0.22 μm filter, containing PBS, pH 7.4. Typically, a mixture containing 5% to 8% trehalose, mannitol, and 0.01% Tween 80 is incorporated as a protective agent before lyophilization. |
| Reconstitution | A Certificate of Analysis (CoA) containing reconstitution instructions is included with the products. Please refer to the CoA for detailed information. |
| Stability & Storage | It is recommended to store recombinant proteins at -20°C to -80°C for future use. Lyophilized powders can be stably stored for over 12 months, while liquid products can be stored for 6-12 months at -80°C. For reconstituted protein solutions, the solution can be stored at -20°C to -80°C for at least 3 months. Please avoid multiple freeze-thaw cycles and store products in aliquots. |
| Shipping | In general, Lyophilized powders are shipping with blue ice. |
| Research Background | Delta-like protein 4 (DLL4, Delta4), a type I membrane-bound Notch ligand, is one of five known Notch ligands in mammals and interacts predominantly with Notch 1, which has a key role in vascular development. Recent studies yield substantial insights into the role of DLL4 in angiogenesis. DLL4 is induced by vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) and acts downstream of VEGF as a 'brake' on VEGF-induced vessel growth, forming an autoregulatory negative feedback loop inactivating VEGF. DLL4 is downstream of VEGF signaling and its activation triggers a negative feedback that restrains the effects of VEGF. Attenuation of DLL4/Notch signaling results in chaotic vascular network with excessive branching and sprouting. DLL4 is widely distributed in tissues other than vessels including many malignancies. Furthermore, the molecule is internalized on binding its receptor and often transported to the nucleus. In pathological conditions, such as cancer, DLL4 is up-regulated strongly in the tumour vasculature. Blockade of DLL4-mediated Notch signaling strikingly increases nonproductive angiogenesis, but significantly inhibits tumor growth in preclinical mouse models. In preclinical studies, blocking of DLL4/Notch signaling is associated with a paradoxical increase in tumor vessel density, yet causes marked growth inhibition due to functionally defective vasculature. Thus, DLL4 blockade holds promise as an additional strategy for angiogenesis-based cancer therapy. |

Copyright © 2015-2025 TargetMol Chemicals Inc. All Rights Reserved.