Shopping Cart
Remove All Your shopping cart is currently empty
Your shopping cart is currently empty
MazF Protein, E. coli, Recombinant (His) is expressed in yeast with C-6xHis tag. The predicted molecular weight is 13.6 kDa and the accession number is P0AE70.

| Pack Size | Price | USA Warehouse | Global Warehouse | Quantity |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 5 μg | $143 | - | In Stock | |
| 10 μg | $238 | - | In Stock | |
| 20 μg | $397 | - | In Stock | |
| 50 μg | $597 | 20 days | 20 days | |
| 100 μg | $845 | 20 days | 20 days | |
| 200 μg | $1,230 | 20 days | 20 days | |
| 500 μg | $1,980 | 20 days | 20 days | |
| 1 mg | $2,970 | 20 days | 20 days |
| Biological Activity | Activity has not been tested. It is theoretically active, but we cannot guarantee it. If you require protein activity, we recommend choosing the eukaryotic expression version first. |
| Description | MazF Protein, E. coli, Recombinant (His) is expressed in yeast with C-6xHis tag. The predicted molecular weight is 13.6 kDa and the accession number is P0AE70. |
| Species | E. coli |
| Expression System | P. pastoris (Yeast) |
| Tag | C-6xHis |
| Accession Number | P0AE70 |
| Synonyms | Toxin MazF,mRNA interferase MazF,mazF,Endoribonuclease toxin MazF,chpAK,chpA |
| Amino Acid | MVSRYVPDMGDLIWVDFDPTKGSEQAGHRPAVVLSPFMYNNKTGMCLCVPCTTQSKGYPFEVVLSGQERDGVALADQVKSIAWRARGATKKGTVAPEELQLIKAKINVLIG |
| Construction | 1-111 aa |
| Protein Purity | > 90% as determined by SDS-PAGE. 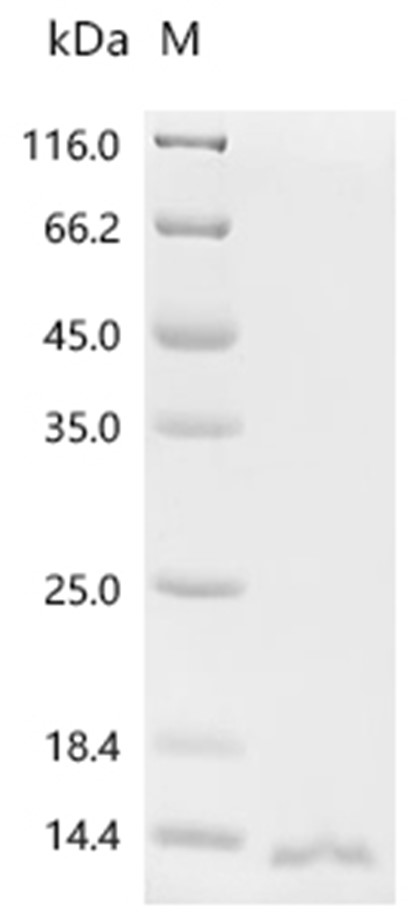 |
| Molecular Weight | 13.6 kDa (predicted) |
| Endotoxin | < 1.0 EU/μg of the protein as determined by the LAL method. |
| Formulation | If the delivery form is liquid, the default storage buffer is Tris/PBS-based buffer, 5%-50% glycerol.If the delivery form is lyophilized powder, the buffer before lyophilization is Tris/PBS-based buffer, 6% Trehalose, pH 8.0. |
| Reconstitution | Reconstitute the lyophilized protein in sterile deionized water. The product concentration should not be less than 100 μg/mL. Before opening, centrifuge the tube to collect powder at the bottom. After adding the reconstitution buffer, avoid vortexing or pipetting for mixing. |
| Stability & Storage | Lyophilized powders can be stably stored for over 12 months, while liquid products can be stored for 6-12 months at -80°C. For reconstituted protein solutions, the solution can be stored at -20°C to -80°C for at least 3 months. Please avoid multiple freeze-thaw cycles and store products in aliquots. |
| Shipping | In general, lyophilized powders are shipped with blue ice, while solutions are shipped with dry ice. |
| Research Background | Toxic component of a type II toxin-antitoxin (TA) system. A sequence-specific endoribonuclease it inhibits protein synthesis by cleaving mRNA and inducing bacterial stasis. It is stable, single-strand specific with mRNA cleavage independent of the ribosome, although translation enhances cleavage for some mRNAs. Cleavage occurs at the 5'-end of ACA sequences, yielding a 2',3'-cyclic phosphate and a free 5'-OH, although cleavage can also occur on the 3'-end of the first A. Digests 16S rRNA in vivo 43 nts upstream of the C-terminus; this removes the anti-Shine-Dalgarno sequence forming a mixed population of wild-type and 'stress ribosomes'. Stress ribosomes do not translate leader-containing mRNA but are proficient in translation of leaderless mRNA, which alters the protein expression profile of the cell; MazF produces some leaderless mRNA. The toxic endoribonuclease activity is inhibited by its labile cognate antitoxin MazE. Toxicity results when the levels of MazE decrease in the cell, leading to mRNA degradation. This effect can be rescued by expression of MazE, but after 6 hours in rich medium overexpression of MazF leads to programmed cell death. MazF-mediated cell death occurs following a number of stress conditions in a relA-dependent fashion and only when cells are in log phase; sigma factor S (rpoS) protects stationary phase cells from MazF-killing. Cell growth and viability are not affected when MazF and MazE are coexpressed. Both MazE and MazE-MazF bind to the promoter region of the mazE-mazF operon to inhibit their own transcription. MazE has higher affinity for promoter DNA in the presence of MazF. Cross-talk can occur between different TA systems, ectopic expression of this toxin induces transcription of the relBEF TA system operon with specific cleavage of the mRNA produced.; Might also serve to protect cells against bacteriophage; in the presence of MazE-MazF fewer P1 phages are produced than in a disrupted strain. For strain K38 most wild-type cells are killed but not by phage lysis; it was suggested that MazE-MazF causes P1 phage exclusion from the bacterial population. This phenomenon is strain dependent.; The physiological role of this TA system is debated. Programmed cell death (PCD) occurs when cells are at high density and depends on the presence of MazE-MazF and a quorum sensing pentapeptide, the extracellular death factor (EDF) with sequence Asn-Asn-Trp-Asn-Asn (NNWNN), probably produced from the zwf gene product glucose-6-phosphate 1-dehydrogenase. Cell death governed by the MazE-MazF and DinJ-YafQ TA systems seems to play a role in biofilm formation, while MazE-MazF is also implicated in cell death in liquid media. Implicated in hydroxy radical-mediated cell death induced by hydroxyurea treatment. In conjunction with EDF prevents apoptotic-like death (ALD) in the presence of DNA damaging agents, probably by reducing recA mRNA levels in a non-endonuclease-mediated manner. Other studies (in strains BW25113 and MC4100, the latter makes EDF) demonstrate MazF does not cause PCD but instead bacteriostasis and possibly a dormant state as well as persister cell generation. |
| Size | Quantity | Unit Price | Amount | Operation |
|---|

Copyright © 2015-2026 TargetMol Chemicals Inc. All Rights Reserved.