Shopping Cart
Remove All Your shopping cart is currently empty
Your shopping cart is currently empty
Complement C2 Protein, Human, Recombinant (His) is expressed in HEK293 mammalian cells with His tag. The predicted molecular weight is 82.5 kDa and the accession number is P06681-1.

| Pack Size | Price | USA Warehouse | Global Warehouse | Quantity |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 5 μg | $73 | 7-10 days | 7-10 days | |
| 10 μg | $116 | 7-10 days | 7-10 days | |
| 20 μg | $191 | - | In Stock | |
| 50 μg | $385 | 7-10 days | 7-10 days | |
| 100 μg | $660 | 7-10 days | 7-10 days | |
| 200 μg | $1,130 | 7-10 days | 7-10 days | |
| 500 μg | $2,270 | 7-10 days | 7-10 days |
| Biological Activity | Measured by its ability to cleave a colorimetric peptide substrate, N-carbobenzyloxy-Gly-Arg-ThioBenzyl ester (Z-GR-SBzl), in the presence of 5,5’Dithiobis (2-nitrobenzoic acid) (DTNB). The specific activity is >100 pmoles/min/μg. |
| Description | Complement C2 Protein, Human, Recombinant (His) is expressed in HEK293 mammalian cells with His tag. The predicted molecular weight is 82.5 kDa and the accession number is P06681-1. |
| Species | Human |
| Expression System | HEK293 Cells |
| Tag | C-His |
| Accession Number | P06681-1 |
| Synonyms | complement component 2,CO2,ARMD14 |
| Construction | A DNA sequence encoding the human complement component 2 (C2) precursor (NP_000054.2) (Met 1-Leu 752) was expressed with a C-terminal polyhistidine tag. Predicted N terminal: Ala 21 |
| Protein Purity | > 97 % as determined by SDS-PAGE. 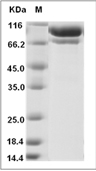 |
| Molecular Weight | 82.5 kDa (predicted) |
| Endotoxin | < 1.0 EU/μg of the protein as determined by the LAL method. |
| Formulation | Lyophilized from a solution filtered through a 0.22 μm filter, containing PBS, pH 7.4. Typically, a mixture containing 5% to 8% trehalose, mannitol, and 0.01% Tween 80 is incorporated as a protective agent before lyophilization. |
| Reconstitution | Reconstituted with sterile deionized water to 0.25 mg/mL. Reconstitution conditions may vary depending on the lot. |
| Stability & Storage | It is recommended to store recombinant proteins at -20°C to -80°C for future use. Lyophilized powders can be stably stored for over 12 months, while liquid products can be stored for 6-12 months at -80°C. For reconstituted protein solutions, the solution can be stored at -20°C to -80°C for at least 3 months. Please avoid multiple freeze-thaw cycles and store products in aliquots. |
| Shipping | In general, lyophilized powders are shipped with blue ice, while solutions are shipped with dry ice. |
| Research Background | Complement component C2 is part of the classical complement pathway which plays a major role in innate immunity against infection. C2 is a glycoprotein synthesized in liver hepatocytes and several other cell types in extrahepatic tissues. This pathway is triggered by a multimolecular complex C1, and subsequently the single-chain form of C2 is cleaved into two chains referred to C2a and C2b by activated C1. The second component of complement (C2) is a multi-domain serine protease that provides catalytic activity for the C3 and C5 convertases of the classical and lectin pathways of human complement. C4b and C2 was investigated by surface plasmon resonance. C2a containing a serine protease domain combines with complement component C4b to form the C3 convertase C4b2a which is responsible for C3 activation, and leads to the stimulation of adaptive immune responses via Lectin pathway. C2 bound to C4b is cleaved by classical (C1s) or lectin (MASP2) proteases to produce C4bC2a. C2 has the same serine protease domain as C4bC2a but in an inactive zymogen-like conformation, requiring cofactor-induced conformational change for activity. Deficiency of C2 (C2D) is the most common genetic deficiency of the complement system, and two types of C2D have been recognized in the context of specific MHC haplotypes. C2D in human is reported to increase susceptibility to infection, and is associated with certain autoimmune diseases, such as rheumatological disorders. |
| Size | Quantity | Unit Price | Amount | Operation |
|---|

Copyright © 2015-2026 TargetMol Chemicals Inc. All Rights Reserved.