Shopping Cart
Remove All Your shopping cart is currently empty
Your shopping cart is currently empty
Anti-Insulin Receptor Polyclonal Antibody is a Rabbit antibody targeting Insulin Receptor. Anti-Insulin Receptor Polyclonal Antibody can be used in FCM,IF,IHC-Fr,IHC-P,WB.
| Pack Size | Price | USA Warehouse | Global Warehouse | Quantity |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 50 μL | $221 | 7-10 days | 7-10 days | |
| 100 μL | $373 | 7-10 days | 7-10 days | |
| 200 μL | $528 | 7-10 days | 7-10 days |
| Description | Anti-Insulin Receptor Polyclonal Antibody is a Rabbit antibody targeting Insulin Receptor. Anti-Insulin Receptor Polyclonal Antibody can be used in FCM,IF,IHC-Fr,IHC-P,WB. |
| Synonyms | Insulin Receptor, HHF5, CD220 |
| Ig Type | IgG |
| Reactivity | Human,Mouse,Rat (predicted:Chicken,Dog,Cow,Horse,Rabbit,Sheep) |
| Verified Activity | 1. Tissue/cell: rat liver tissue; 4% Paraformaldehyde-fixed and paraffin-embedded; Antigen retrieval: citrate buffer (0.01M, pH6.0), Boiling bathing for 15 min; Block endogenous peroxidase by 3% Hydrogen peroxide for 30 min; Blocking buffer (normal goat serum) at 37°C for 20 min; Incubation: Anti-Insulin Receptor/CD220 Polyclonal Antibody, Unconjugated (TMAB-00974) 1:200, overnight at 4°C, followed by conjugation to the secondary antibody and DAb staining. 2. Blank control: Raji (blue). Primary Antibody: Rabbit Anti-Insulin Receptor alpha antibody (TMAB-00974), Dilution: 1 μg in 100 μL 1X PBS containing 0.5% BSA; Isotype Control Antibody: Rabbit Igg (orange),used under the same conditions); Secondary Antibody: Goat anti-rabbit IgG-Pe (white blue), Dilution: 1:200 in 1 X PBS containing 0.5% BSA. Protocol The cells were fixed with 2% paraformaldehyde (10 min), then permeabilized with 90% ice-cold methanol for 30 min on ice. Primary antibody (TMAB-00974, 1 μg/1x10^6 cells) were incubated for 30 min on the ice, followed by 1 X PBS containing 0.5% BSA + 10% goat serum (15 min) to block non-specific protein-protein interactions. Then the Goat Anti-rabbit IgG/PE antibody was added into the blocking buffer mentioned above to react with the primary antibody at 1/200 dilution for 30 min on ice. 3. Sample: Lane 1: HepG2 (Human) Cell Lysate at 30 μg Lane 2: 293T (Human) Cell Lysate at 30 μg Lane 3: LOVO (Human) Cell Lysate at 30 μg Lane 4: Molt-4 (Human) Cell Lysate at 30 μg Lane 5: SW480 (Human) Cell Lysate at 30 μg Lane 6: K562 (Human) Cell Lysate at 30 μg Primary: Anti-Insulin Receptor (TMAB-00974) at 1/1000 dilution Secondary: IRDye800CW Goat Anti-Rabbit IgG at 1/20000 dilution Predicted band size: 120 kDa Observed band size: 120 kDa 4. Sample: Lane 1: MCF-7 (Human) Cell Lysate at 30 μg Lane 2: A549 (Human) Cell Lysate at 30 μg Lane 3: 293T (Human) Cell Lysate at 30 μg Lane 4: Hela (Human) Cell Lysate at 30 μg Lane 5: Liver (Rat) Lysate at 40 μg Lane 6: LympHnode (Mouse) Lysate at 40 μg Lane 7: MOLT-4 (Human) Cell Lysate at 30 μg Lane 8: NIH/3T3 (Mouse) Cell Lysate at 30 μg Primary: Anti-Insulin Receptor (TMAB-00974) at 1/1000 dilution Secondary: IRDye800CW Goat Anti-Rabbit IgG at 1/20000 dilution Predicted band size: 120 kDa Observed band size: 120 kDa 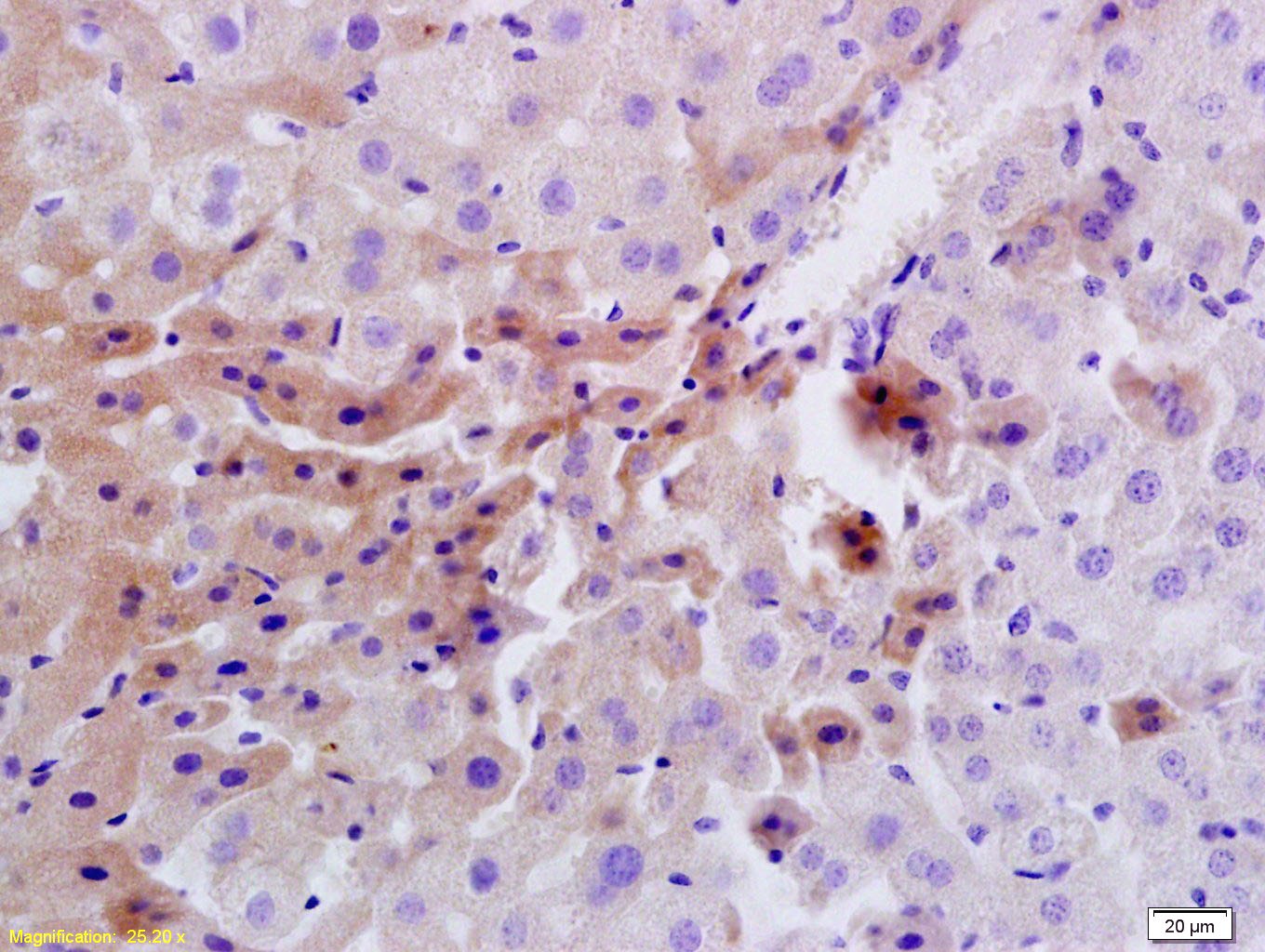 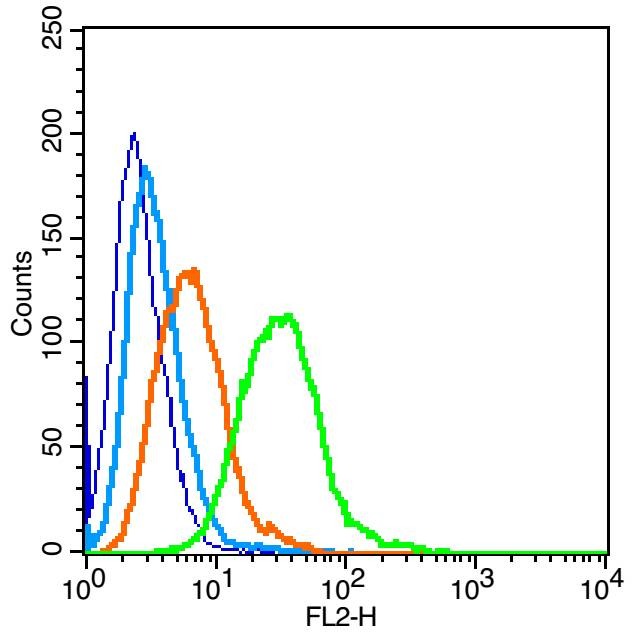 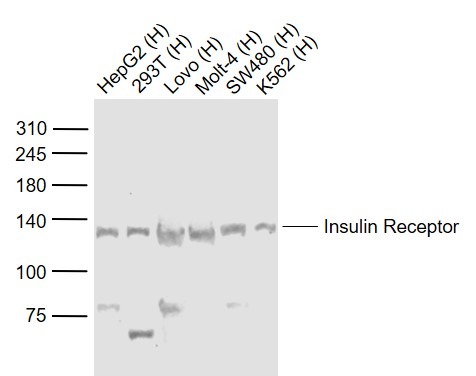 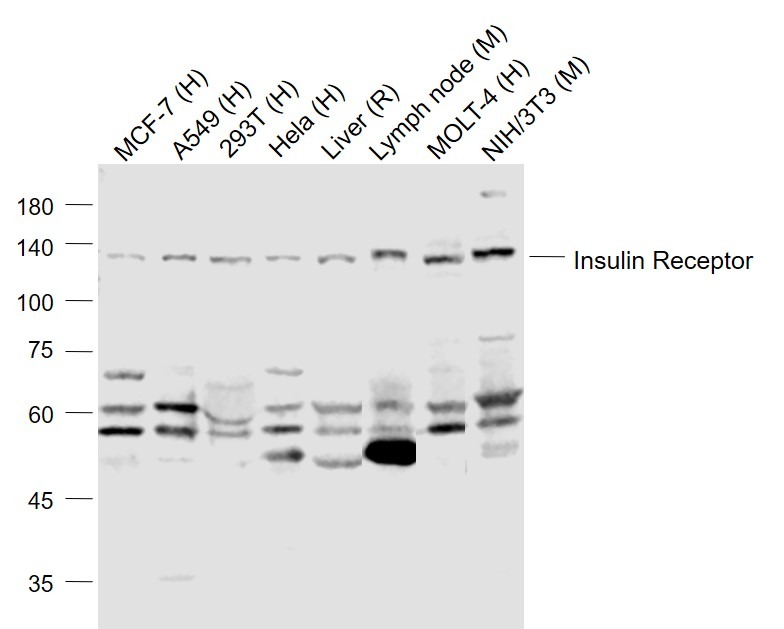 |
| Application | |
| Recommended Dose | WB: 1:500-2000; IHC-P: 1:100-500; IHC-Fr: 1:100-500; IF: 1:100-500; FCM: 1ug/Test |
| Antibody Type | Polyclonal |
| Host Species | Rabbit |
| Subcellular Localization | Membrane; Single-pass type I membrane protein. |
| Tissue Specificity | Isoform Long and isoform Short are predominantly expressed in tissue targets of insulin metabolic effects: liver, adipose tissue and skeletal muscle but are also expressed in the peripheral nerve, kidney, pulmonary alveoli, pancreatic acini, placenta vasc |
| Construction | Polyclonal Antibody |
| Purification | Protein A purified |
| Appearance | Liquid |
| Formulation | 0.01M TBS (pH7.4) with 1% BSA, 0.02% Proclin300 and 50% Glycerol. |
| Concentration | 1 mg/mL |
| Research Background | The human insulin receptor is a heterotetrameric membrane glycoprotein consisting of disulfide linked subunits in a beta-alpha-alpha-beta configuration. The beta subunit (95 kDa) possesses a single transmembrane domain, whereas the alpha subunit (135 kDa) is completely extracellular. The insulin receptor exhibits receptor tyrosine kinase (RTK) activity. RTKs are single pass transmembrane receptors that possess intrinsic cytoplasmic enzymatic activity, catalyzing the transfer of the gamma phosphate of ATP to tyrosine residues in protein substrates. RTKs are essential components of signal transduction pathways that affect cell proliferation, differentiation, migration and metabolism. Included in this large protein family are the insulin receptor and the receptors for growth factors such as epidermal growth factor, fibroblast growth factor and vascular endothelial growth factor. Receptor activation occurs through ligand binding, which facilitates receptor dimerization and autophosphorylation of specific tyrosine residues in the cytoplasmic portion. The interaction of insulin with the alpha subunit of the insulin receptor activates the protein tyrosine kinase of the beta subunit, which then undergoes an autophosphorylation that increases its tyrosine kinase activity. Three adapter proteins, IRS1, IRS2 and Shc, become phosphorylated on tyrosine residues following insulin receptor activation. These three phosphorylated proteins then interact with SH2 domain containing signaling proteins. |
| Immunogen | KLH conjugated synthetic peptide: human Insulin Receptor |
| Antigen Species | Human |
| Gene Name | INSR |
| Gene ID | |
| Protein Name | Insulin receptor |
| Uniprot ID | |
| Biology Area | Insulin and insulin-like,Diabetes associated,Diabetes,Heart disease,Metabolism,Insulin / Insulin-like,Receptor Tyrosine Kinases |
| Function | Receptor tyrosine kinase which mediates the pleiotropic actions of insulin. Binding of insulin leads to phosphorylation of several intracellular substrates, including, insulin receptor substrates (IRS1, 2, 3, 4), SHC, GAB1, CBL and other signaling intermediates. Each of these phosphorylated proteins serve as docking proteins for other signaling proteins that contain Src-homology-2 domains (SH2 domain) that specifically recognize different phosphotyrosines residues, including the p85 regulatory subunit of PI3K and SHP2. Phosphorylation of IRSs proteins lead to the activation of two main signaling pathways: the PI3K-AKT/PKB pathway, which is responsible for most of the metabolic actions of insulin, and the Ras-MAPK pathway, which regulates expression of some genes and cooperates with the PI3K pathway to control cell growth and differentiation. Binding of the SH2 domains of PI3K to phosphotyrosines on IRS1 leads to the activation of PI3K and the generation of phosphatidylinositol-(3, 4, 5)-triphosphate (PIP3), a lipid second messenger, which activates several PIP3-dependent serine/threonine kinases, such as PDPK1 and subsequently AKT/PKB. The net effect of this pathway is to produce a translocation of the glucose transporter SLC2A4/GLUT4 from cytoplasmic vesicles to the cell membrane to facilitate glucose transport. Moreover, upon insulin stimulation, activated AKT/PKB is responsible for: anti-apoptotic effect of insulin by inducing phosphorylation of BAD; regulates the expression of gluconeogenic and lipogenic enzymes by controlling the activity of the winged helix or forkhead (FOX) class of transcription factors. Another pathway regulated by PI3K-AKT/PKB activation is mTORC1 signaling pathway which regulates cell growth and metabolism and integrates signals from insulin. AKT mediates insulin-stimulated protein synthesis by phosphorylating TSC2 thereby activating mTORC1 pathway. The Ras/RAF/MAP2K/MAPK pathway is mainly involved in mediating cell growth, survival and cellular differentiation of insulin. Phosphorylated IRS1 recruits GRB2/SOS complex, which triggers the activation of the Ras/RAF/MAP2K/MAPK pathway. In addition to binding insulin, the insulin receptor can bind insulin-like growth factors (IGFI and IGFII). Isoform Short has a higher affinity for IGFII binding. When present in a hybrid receptor with IGF1R, binds IGF1. PubMed:12138094 shows that hybrid receptors composed of IGF1R and INSR isoform Long are activated with a high affinity by IGF1, with low affinity by IGF2 and not significantly activated by insulin, and that hybrid receptors composed of IGF1R and INSR isoform Short are activated by IGF1, IGF2 and insulin. In contrast, PubMed:16831875 shows that hybrid receptors composed of IGF1R and INSR isoform Long and hybrid receptors composed of IGF1R and INSR isoform Short have similar binding characteristics, both bind IGF1 and have a low affinity for insulin. |
| Molecular Weight | Theoretical: 80/152 kDa. |
| Stability & Storage | Store at -20°C or -80°C for 12 months. Avoid repeated freeze-thaw cycles. |
| Transport | Shipping with blue ice. |
| Size | Quantity | Unit Price | Amount | Operation |
|---|

Copyright © 2015-2026 TargetMol Chemicals Inc. All Rights Reserved.