Shopping Cart
- Remove All
 Your shopping cart is currently empty
Your shopping cart is currently empty
Human RSV (B1) glycoprotein G/RSV-G Protein (His) is expressed in HEK293 mammalian cells with His tag. The predicted molecular weight is 27 kDa and the accession number is O36633-1.

| Pack Size | Price | Availability | Quantity |
|---|---|---|---|
| 100 μg | $648 | In Stock | |
| 200 μg | $1,110 | 7-10 days | |
| 500 μg | $2,240 | 7-10 days |
| Biological Activity | Activity testing is in progress. It is theoretically active, but we cannot guarantee it. If you require protein activity, we recommend choosing the eukaryotic expression version first. |
| Description | Human RSV (B1) glycoprotein G/RSV-G Protein (His) is expressed in HEK293 mammalian cells with His tag. The predicted molecular weight is 27 kDa and the accession number is O36633-1. |
| Species | RSV |
| Expression System | HEK293 Cells |
| Tag | C-His |
| Accession Number | O36633-1 |
| Synonyms | G Protein, RSV |
| Construction | A DNA sequence encoding the extracellular domain of human RSV strain B1 glycoprotein G (O36633-1) (His 67-Ala 299) was fused with a polyhistidine tag at the C-terminus and a signal peptide at the N-terminus. Predicted N terminal: His 67 |
| Protein Purity | > 95 % as determined by SDS-PAGE 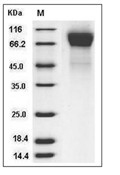 |
| Molecular Weight | 27 kDa (predicted); 80-90 kDa (reducing condition, due to glycosylation) |
| Endotoxin | < 1.0 EU/μg of the protein as determined by the LAL method. |
| Formulation | Lyophilized from a solution filtered through a 0.22 μm filter, containing 10 mM NaAc, 500 mM NaCl, pH 5. 5. Typically, a mixture containing 5% to 8% trehalose, mannitol, and 0.01% Tween 80 is incorporated as a protective agent before lyophilization. |
| Reconstitution | A Certificate of Analysis (CoA) containing reconstitution instructions is included with the products. Please refer to the CoA for detailed information. |
| Stability & Storage | It is recommended to store recombinant proteins at -20°C to -80°C for future use. Lyophilized powders can be stably stored for over 12 months, while liquid products can be stored for 6-12 months at -80°C. For reconstituted protein solutions, the solution can be stored at -20°C to -80°C for at least 3 months. Please avoid multiple freeze-thaw cycles and store products in aliquots. |
| Shipping | In general, Lyophilized powders are shipping with blue ice. |
| Research Background | Human respiratory syncytial virus (HRSV) is the most common etiological agent of acute lower respiratory tract disease in infants and can cause repeated infections throughout life. It is classified within the genus pneumovirus of the family paramyxoviridae. Like other members of the family, HRSV has two major surface glycoproteins (G and F) that play important roles in the initial stages of the infectious cycle. HRSV G protein is a type II glycoprotein of 289-299 amino acids (depending on the virus strain) with a signal/anchor hydrophobic domain and is extensively modified by the addition of both N-and O-linked oligosaccharides to achieve the mature form of 8-9 kDa. The C-terminal ectodomain of the G protein has a central region and four cysteines which are conserved in all HRSV isolates and have been proposed as the putative receptor binding site. The G protein mediates attachment of the virus to the host cell membrane by interacting with heparan sulfate, initiating the infection. As similar to mucins in amino acid compositions, the RSV G protein can interact with host CX3CR1, the receptor for the CX3C chemokine fractalkine, and thus modulates the immune response and facilitate infection. Secreted glycoprotein G helps RSV escape antibody-dependent restriction of replication by acting as an antigen decoy and by modulating the activity of leukocytes bearing Fcgamma receptors. Unlike the other paramyxovirus attachment proteins, HRSV-G lacks both neuraminidase and hemagglutinating activities. |

Copyright © 2015-2025 TargetMol Chemicals Inc. All Rights Reserved.