Powder: -20°C for 3 years | In solvent: -80°C for 1 year


TCA1 (TCA 1) is a small molecule with activity against drug-resistant and persistent tuberculosis.
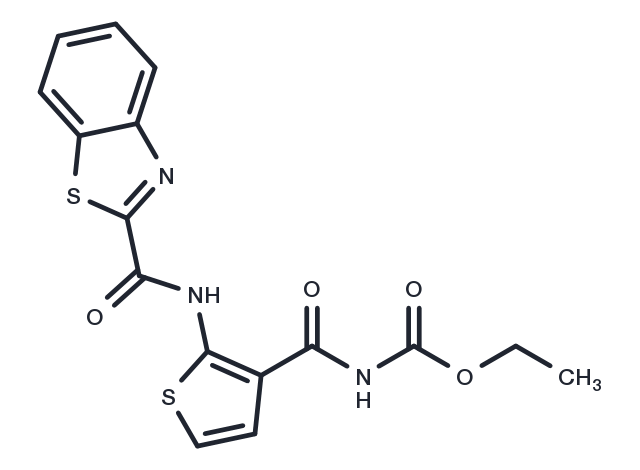
| Pack Size | Availability | Price/USD | Quantity |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 mg | In stock | $ 44.00 | |
| 2 mg | In stock | $ 63.00 | |
| 5 mg | In stock | $ 97.00 | |
| 10 mg | In stock | $ 155.00 | |
| 25 mg | In stock | $ 287.00 | |
| 50 mg | In stock | $ 438.00 | |
| 100 mg | In stock | $ 649.00 | |
| 1 mL * 10 mM (in DMSO) | In stock | $ 116.00 |


| Description | TCA1 (TCA 1) is a small molecule with activity against drug-resistant and persistent tuberculosis. |
| In vitro | The activities of TCA1 against M. smegmatis, M. bovis bacillus Calmette–Guérin, and Mtb are 20- to 150-fold higher in biofilm medium (MIC50 = 0.03, 0.04, and 0.01 μg/mL, respectively) than 7H9 medium (MIC50 = 4.5, 3, and 0.19 μg/mL, respectively). TCA1 is bactericidal with an MIC99 value of 2.1 μg/mL in solid medium. |
| In vivo | After i.v. administration, TCA1 exhibited a low clearance and steady-state volume of distribution, with an elimination half-life of 0.73 h. After oral administration of 20 and 50 mg/kg in solution formulation, TCA1 showed a high Cmax (2,122 and 5,653 nM, respectively), moderate exposure with oral bioavailability ranging from 19% to 46%, and a half-life of 1.8 h. BALB/c mice were infected with a low dose of Mtb H37Rv (~200 bacilli); 2 wk after infection, mice were treated with TCA1 (40 mg/kg) for 4 wk (dosed 1 time/d for 5 d/wk). After 4 wk of treatment with TCA1, the cfu dropped 0.5 log in lung and 1.5 logs in spleen. |
| Cell Research | For kinetic killing assays, exponentially growing cultures of mycobacteria were diluted in fresh media to an OD600 of 0.1–0.2. Various drugs were added to the culture at the indicated concentrations. The number of cfus at the start of the experiment was estimated by plating appropriate dilutions of the culture onto 7H10 agar plates. The effect of drug was monitored by plating for cfus at the indicated time points. All experiments were carried out in triplicate. MICs were determined by a turbidity assay. Threefold serial dilutions in DMSO were prepared for each compound. Mtb cultures (OD = 0.04) were incubated with compounds at 37 °C for 5 d, and OD600 was determined with an Envision plate reader. All experiments were carried out in duplicate. For assays under starvation conditions, a log-phase growing Mtb culture was centrifuged, and the cell pellet was washed two times with PBS, resuspended in PBS with Tyloxapol (0.05%; OD = 0.3), and incubated with DMSO, TCA1 (7.5 μg/mL), and RIF (2 μg/mL). All experiments were carried out in triplicate. For intracellular macrophage assays, J744.1 murine macrophage cells were infected with Mtb at a multiplicity of infection (MOI) of 1:3 and incubated for 2 h at 37 °C. After washing the cell monolayer three times, 20 μM amikacin was added, and the culture was incubated for an additional 2 h to kill the remaining extracellular bacteria. Infected cells were then incubated in the presence of serial dilutions of compounds for 5 d. Cells were washed three times and lysed in each well; the lysate was transferred to a 96-well plate for serial dilution and then plated on 7H11 agar medium for cfu assays. |
| Animal Research | Six- to eight-week-old female BALB/c mice were infected by aerosol with a low dose (~50 bacilli) of Mtb H37Rv. Infection dose was verified by plating the inoculum and the whole-lung homogenates onto 7H10 plates at 24 h postinfection. Treatment of BALB/c mice began at either 2 or 4 wk postinfection, with RIF (10 mg/kg) and INH (25 mg/kg) administered ad libitum in drinking water (changed one time every 2 d). TCA1 was administered by oral gavage one time daily for 5 d/wk at a dosage of either 40 or 100 mg/kg for the indicated durations. At predetermined time points or humane endpoints, animals were heavily sedated and euthanized, and tissues were collected for culture and pathology. Treatment efficacy was assessed on the basis of cfu in the lungs and spleen of treated mice compared with untreated controls and bacterial burden in these organs before treatment start. Organs were homogenized in PBS containing Tween-80 [0.05% (vol/vol)], and various dilutions were placed on 7H10 plates. Plates were incubated at 37 °C for 3 wk, and cfus on the various plates were recorded. |
| Synonyms | TCA-1, TCA 1 |
| Molecular Weight | 375.42 |
| Formula | C16H13N3O4S2 |
| CAS No. | 864941-32-2 |
Powder: -20°C for 3 years | In solvent: -80°C for 1 year
DMSO: 60 mg/mL (159.82 mM)
You can also refer to dose conversion for different animals. More
bottom
Please see Inhibitor Handling Instructions for more frequently ask questions. Topics include: how to prepare stock solutions, how to store products, and cautions on cell-based assays & animal experiments, etc.
TCA1 864941-32-2 Microbiology/Virology Antibacterial Antibiotic Inhibitor DprE1 Bacterial inhibit TCA-1 MoeW Mycobacterium tuberculosis TCA 1 oral inhibitor
