Powder: -20°C for 3 years | In solvent: -80°C for 1 year


SRT 1720 is a selective activator of human SIRT1 (EC1.5: 0.16 μM) and is <230-fold less potent for SIRT2 and SIRT3.
| Pack Size | Availability | Price/USD | Quantity |
|---|---|---|---|
| 2 mg | In stock | $ 33.00 | |
| 5 mg | In stock | $ 53.00 | |
| 10 mg | In stock | $ 72.00 | |
| 25 mg | In stock | $ 155.00 | |
| 50 mg | In stock | $ 272.00 | |
| 100 mg | In stock | $ 455.00 | |
| 1 mL * 10 mM (in DMSO) | In stock | $ 92.00 |


| Description | SRT 1720 is a selective activator of human SIRT1 (EC1.5: 0.16 μM) and is >230-fold less potent for SIRT2 and SIRT3. |
| Targets&IC50 | SIRT1:0.16 μM (EC1.5, cell free), SIRT2:37 μM (EC1.5, cell free) |
| In vitro | The maximum activation ratio of SRT1720 versus the closest sirtuin homologs, SIRT2 (EC1.5 = 37 μM) and SIRT3 (EC1.5 > 300 μM) is up to 781%. SRT1720 binds to the SIRT1 enzyme-peptide substrate complex at an allosteric site amino-terminal to the catalytic domain and lower the Michaelis constant for acetylated substrates. Higher concentrations of SRT1720 (15 μM) induces a modest (10-20%) decrease in normal cell viability. SRT1720 also significantly inhibits VEGF-dependent MM cell migration [1]. |
| In vivo | SRT 1720 (10, 30, 100 mg/kg, p.o.) significantly reduces the hyperinsulinemia after 4 weeks, partially normalizing elevated insulin levels similar to rosiglitazone treatment. SRT 1720 treatment significantly reduces fasting blood glucose to near normal levels in Lepob/ob mice[1]. SRT 1720 has the ability to protect against the negative effects of diet-induced obesity in mice and has a connection to metabolic adaptation in fatty acid and oxidative metabolism through downstream targets of SIRT1 such as PGC1α and FOXO1[2]. SRT 1720 (50-100 mg/kg, p.o.), during emphysema development, attenuates elastase-induced airspace enlargement and lung function impairment as well as reduces arterial oxygen saturation in WT mice [3]. |
| Animal Research | Nine-week-old C57BL/6 male mice are fed a high-fat diet (60% calories from fat) until their mean body weight reaches approximately 40 g. The mice are then divided into test groups (6-10 per group). SRT1460 (100 mg/kg), SRT1720 (100 mg/kg), SRT501 (500 mg/kg) and rosiglitazone (5 mg/kg) are administered once daily via oral gavage. The vehicle used is 2% HPMC + 0.2% DOSS. Individual mouse body weights are measured twice weekly. At 2, 4, 6, 8 and 10 weeks of dosing a fed blood glucose measurement are taken and after 5 weeks of treatment, an IPGTT is conducted on all mice from each of the groups. After 10 weeks of treatment, an ITT is conducted. Statistical analysis is completed using the JMP program. Data are analyzed by a one way ANOVA with a comparison to control using a Dunnett's Test. A p-value < 0.05 indicates a significant difference between groups. |
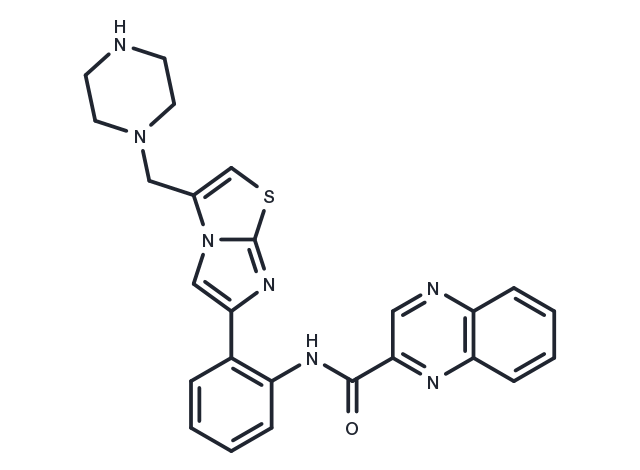
| Molecular Weight | 469.56 |
| Formula | C25H23N7OS |
| CAS No. | 925434-55-5 |
Powder: -20°C for 3 years | In solvent: -80°C for 1 year
You can also refer to dose conversion for different animals. More
bottom
Please see Inhibitor Handling Instructions for more frequently ask questions. Topics include: how to prepare stock solutions, how to store products, and cautions on cell-based assays & animal experiments, etc.
SRT 1720 925434-55-5 Autophagy Chromatin/Epigenetic DNA Damage/DNA Repair Sirtuin inhibit Inhibitor SRT1720 SRT-1720 inhibitor
