Powder: -20°C for 3 years | In solvent: -80°C for 1 year


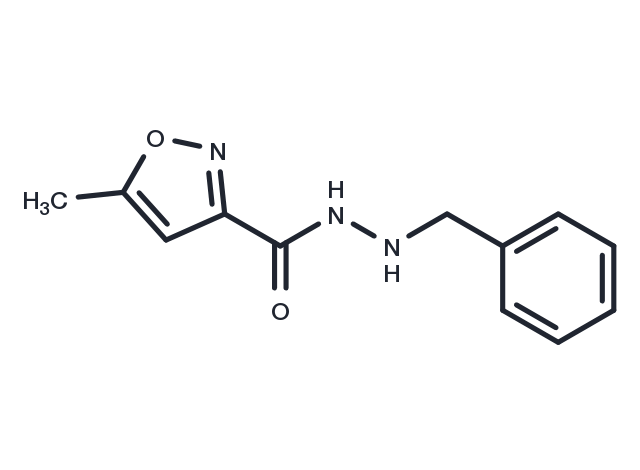
Isocarboxazid has the formula 1-benzyl-2-(5-methyl-3-isoxazolylcarbonyl)hydrazine-isocarboxazid. It is a monoamine oxidase inhibitor.[2] It is used in the treatment of major depression, dysthymic disorder, atypical disorder, panic disorder and the phobic disorders.
| Pack Size | Availability | Price/USD | Quantity |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 mg | In stock | $ 31.00 | |
| 2 mg | In stock | $ 44.00 | |
| 5 mg | In stock | $ 72.00 | |
| 10 mg | In stock | $ 97.00 | |
| 25 mg | In stock | $ 176.00 | |
| 50 mg | In stock | $ 262.00 | |
| 100 mg | In stock | $ 389.00 | |
| 500 mg | In stock | $ 883.00 | |
| 1 mL * 10 mM (in DMSO) | In stock | $ 79.00 |



| Description | Isocarboxazid has the formula 1-benzyl-2-(5-methyl-3-isoxazolylcarbonyl)hydrazine-isocarboxazid. It is a monoamine oxidase inhibitor.[2] It is used in the treatment of major depression, dysthymic disorder, atypical disorder, panic disorder and the phobic disorders. |
| Targets&IC50 | Monoamine oxidase (rat brain):4.8 μM |
| In vitro | In vivo studies demonstrated isocarboxazid-driven inhibition of MAO in the brain, heart, and liver. The reduced MAO activity, caused by isocarboxazid, results in an increased concentration of serotonin, epinephrine, norepinephrine, and dopamine in storage sites throughout the central nervous system (CNS) and sympathetic nervous system. The increase of one or more monoamines is the basis for the antidepressant activity of MAO inhibitors like isocarboxazid.[1] |
| In vivo | In vitro studies demonstrated isocarboxazid-driven inhibition of MAO in the brain, heart, and liver. The reduced MAO activity, caused by isocarboxazid, results in an increased concentration of serotonin, epinephrine, norepinephrine, and dopamine in storage sites throughout the central nervous system (CNS) and sympathetic nervous system. The increase of one or more monoamines is the basis for the antidepressant activity of MAO inhibitors like isocarboxazid.[1] |
| Molecular Weight | 231.25 |
| Formula | C12H13N3O2 |
| CAS No. | 59-63-2 |
Powder: -20°C for 3 years | In solvent: -80°C for 1 year
DMSO: 198.9 mM
You can also refer to dose conversion for different animals. More
bottom
Please see Inhibitor Handling Instructions for more frequently ask questions. Topics include: how to prepare stock solutions, how to store products, and cautions on cell-based assays & animal experiments, etc.
Isocarboxazid 59-63-2 Neuroscience Monoamine Oxidase inhibit MAO Inhibitor inhibitor
