Powder: -20°C for 3 years | In solvent: -80°C for 1 year


Guanidine hydrochloride (Aminoformamidine Hydrochloride) is a strong organic base existing primarily as guanidium ions at physiological pH. It is found in the urine as a normal product of protein metabolism. It is also used in laboratory research as a protein denaturant.
| Pack Size | Availability | Price/USD | Quantity |
|---|---|---|---|
| 10 g | In stock | $ 47.00 | |
| 1 mL * 10 mM (in DMSO) | In stock | $ 26.00 |



| Description | Guanidine hydrochloride (Aminoformamidine Hydrochloride) is a strong organic base existing primarily as guanidium ions at physiological pH. It is found in the urine as a normal product of protein metabolism. It is also used in laboratory research as a protein denaturant. |
| In vitro | Guanidine HCl is the most popular protein denaturant. Analysis of unfolding transitions by Guanidine HCl provides several important parameters regarding the mechanism of conformational stability of proteins. [1] Guanidine HCl at low concentrations refolds acid-unfolds apomyoglobin and cytochrome c, stabilizing the molten globule state. Guanidine HCl (> 1 M) causes co-operative unfolding of the molten globule state. [2] Guanidine HCl is 2.8 times more effective than urea in unfolding ribonuclease but only 1.7 times more effective for lysozyme. △GWaterapp. values of Guanidine HCl are 9.7 Cal/mole for ribonuclease at pH 6.6, 6.1 for lysozyme at pH 2.9, 8.3 for α-chymotrypsin at pH 4.3, and 11.7 for β-lactoglobulin at pH 3.2. [3] Guanidine HCl at millimolar concentrations, is able to causes efficient loss of the normally stable [PSI+] element from yeast cells. 5 mM Guanidine HCl in growth media cures [PSI+] and other prions of yeast. [4] 5 mM Guanidine HCl significantly reduces Hsp104-mediated basal and acquired thermotolerance by 30-fold and 50 fold, respectively. Guanidine HCl also reduces the ability of Hsp104 to restore activity of thermally denatured luciferase. [5] |
| Synonyms | Guanidine HCl, Aminoformamidine HCl, Aminoformamidine Hydrochloride, Guanidinium chloride |
| Molecular Weight | 95.53 |
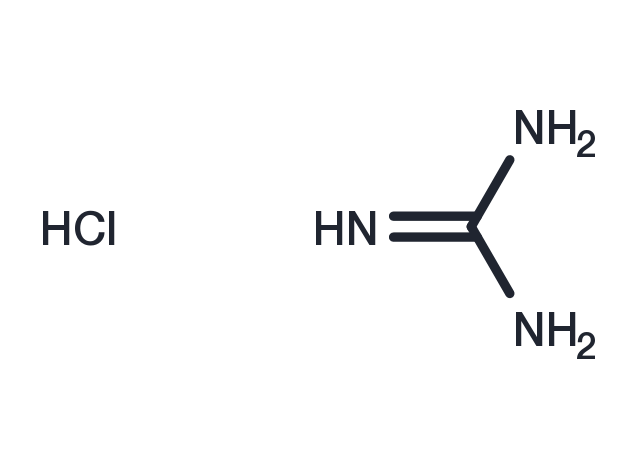
| Formula | CH6ClN3 |
| CAS No. | 50-01-1 |
Powder: -20°C for 3 years | In solvent: -80°C for 1 year
DMSO: 198.9 mM
H2O: 198.9 mM
You can also refer to dose conversion for different animals. More
bottom
Please see Inhibitor Handling Instructions for more frequently ask questions. Topics include: how to prepare stock solutions, how to store products, and cautions on cell-based assays & animal experiments, etc.
Guanidine hydrochloride 50-01-1 Autophagy Cell Cycle/Checkpoint DNA Damage/DNA Repair Immunology/Inflammation Metabolism Others Arginase DNA/RNA Synthesis Endogenous Metabolite unfolded Guanidinium Chloride Hsp104 chaotrope Guanidine HCl denaturant Aminoformamidine HCl Guanidinium Guanidine Aminoformamidine Inhibitor Guanidine Hydrochloride Aminoformamidine Hydrochloride Guanidinium chloride inhibit proteins inhibitor
