Powder: -20°C for 3 years | In solvent: -80°C for 1 year


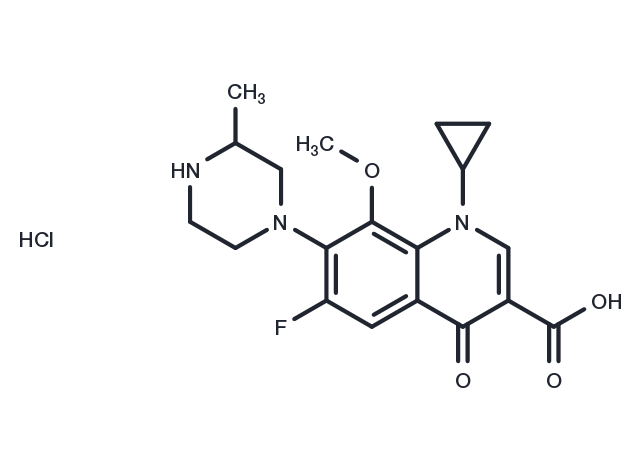
Gatifloxacin hydrochloride (AM-1155 hydrochloride) is an antibiotic of the fourth-generation fluoroquinolone family, which can inhibit the bacterial enzyme DNA rotase and topoisomerase IV.
| Pack Size | Availability | Price/USD | Quantity |
|---|---|---|---|
| 500 mg | In stock | $ 41.00 | |
| 1 mL * 10 mM (in DMSO) | In stock | $ 50.00 |



| Description | Gatifloxacin hydrochloride (AM-1155 hydrochloride) is an antibiotic of the fourth-generation fluoroquinolone family, which can inhibit the bacterial enzyme DNA rotase and topoisomerase IV. |
| Targets&IC50 | Topo II:36.7 μM |
| In vivo | All eyes showed evidence of infection by 48 hours postinoculation with 36 of 41 eyes (87.8%) exhibiting moderate-to-severe keratitis. All eyes exhibited corneal healing by day 15, with no significant differences among groups. Three of 4 groups receiving gatifloxacin tended to have smaller fluorescein retention area scores than did the ciprofloxacin group. No eyes tested positive for Pseudomonas at the end of the study. No corneal precipitates were found following as many as 48 doses/day of gatifloxacin[1]. |
| Animal Research | Heptanol-induced corneal ulcers in New Zealand White rabbits (n = 41; 8 females/group) were inoculated with 10(6) CFU of Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Gatifloxacin 0.3% dosing varied among 4 groups with frequencies of 16-48 doses/day (days 1-2), 3-16 doses/day (days 3-7), and maintenance dosing of 3-4 doses/day (days 8-22). Ciprofloxacin 0.3% was administered as labeled for corneal ulcers, with 44 doses on day 1, 16 doses on day 2, and 4 doses/day on days 3-21[1] |
| Synonyms | AM-1155 (hydrochloride), BMS-206584 (hydrochloride), PD135432 (hydrochloride) |
| Molecular Weight | 411.86 |
| Formula | C19H23ClFN3O4 |
| CAS No. | 121577-32-0 |
Powder: -20°C for 3 years | In solvent: -80°C for 1 year
H2O: 10 mg/mL (24.28 mM), Sonication is recommended.
DMSO: 5 mg/mL (12.14 mM), Sonication is recommended.
You can also refer to dose conversion for different animals. More
bottom
Please see Inhibitor Handling Instructions for more frequently ask questions. Topics include: how to prepare stock solutions, how to store products, and cautions on cell-based assays & animal experiments, etc.
Gatifloxacin hydrochloride 121577-32-0 DNA Damage/DNA Repair Microbiology/Virology Antibiotic Antibacterial Topoisomerase AM1155 BMS-206584 E. coli,?Pseudomonas aeruginosa,?Micrococcus luteus Gatifloxacin PD-135432 BMS 206584 conjunctivitis N. brasiliensis actinomycetoma AM-1155 (hydrochloride) Inhibitor S. aureus Bacterial BMS-206584 (hydrochloride) inhibit hypoglycemia AM 1155 Gatifloxacin Hydrochloride diabetic PD135432 (hydrochloride) PD135432 hyperglycemia PD 135432 BMS206584 AM-1155 inhibitor
